Abstract
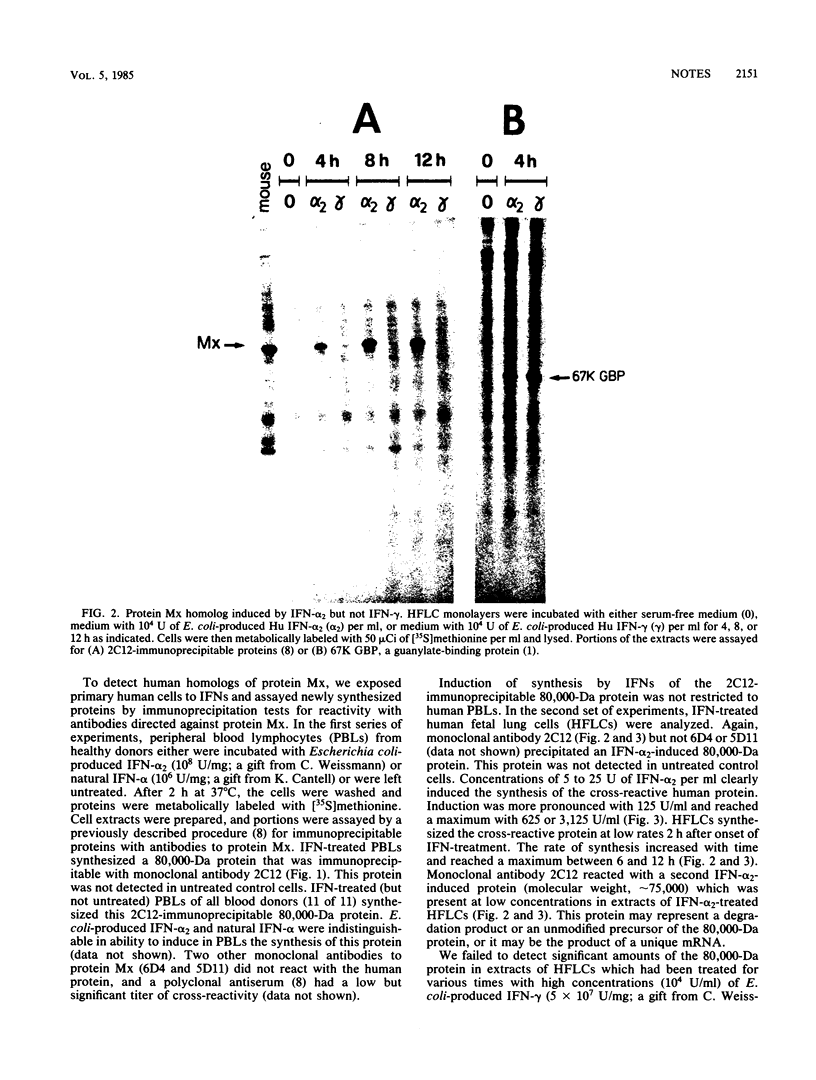
Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies with specificity for protein Mx (a karyophilic 75,000-dalton protein induced by interferon [IFN] in mouse cells carrying the influenza virus resistance allele Mx+) detected an IFN-induced 80,000-dalton protein in peripheral blood lymphocytes and in fibroblasts of healthy human donors. The human protein, like protein Mx, was induced by IFN-alpha but not by IFN-gamma. Unlike the mouse protein, it was predominantly localized in the cell cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng Y. S., Colonno R. J., Yin F. H. Interferon induction of fibroblast proteins with guanylate binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7746–7750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreiding P., Staeheli P., Haller O. Interferon-induced protein Mx accumulates in nuclei of mouse cells expressing resistance to influenza viruses. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):192–196. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90460-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Arnheiter H., Gresser I., Lindenmann J. Virus-specific interferon action. Protection of newborn Mx carriers against lethal infection with influenza virus. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):199–203. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O. Inborn resistance of ice to orthomyxoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;92:25–52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68069-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. A., Staeheli P., Haller O. Interferon induces a unique protein in mouse cells bearing a gene for resistance to influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1910–1914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Gupta S. L. Differential efficacies of human type I and type II interferons as antiviral and antiproliferative agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5928–5932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Dreiding P., Haller O., Lindenmann J. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies to the interferon-inducible protein Mx of influenza virus-resistant mice. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1821–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Horisberger M. A., Haller O. Mx-dependent resistance to influenza viruses is induced by mouse interferons alpha and beta but not gamma. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):456–461. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Prochazka M., Steigmeier P. A., Haller O. Genetic control of interferon action: mouse strain distribution and inheritance of an induced protein with guanylate-binding property. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B., Sedmak J. J., Sabran J. L., Grossberg S. E. A unique set of polypeptides is induced by gamma interferon in addition to those induced in common with alpha and beta interferons. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):437–439. doi: 10.1038/301437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V., Jeffreys A. J., Barrie P. A., Boseley P. G., Slocombe P. M., Easton A., Burke D. C. A comparison of vertebrate interferon gene families detected by hybridization with human interferon DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):457–475. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






