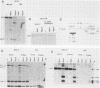
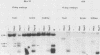
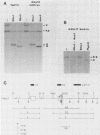
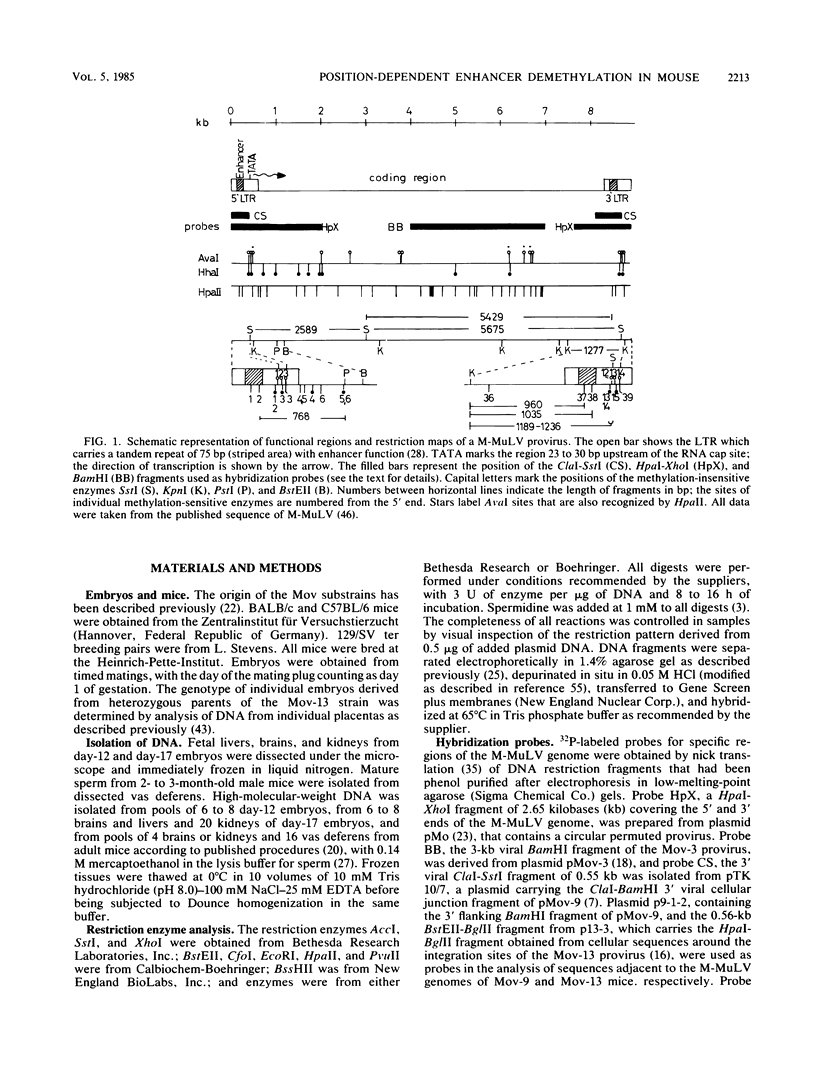
Abstract
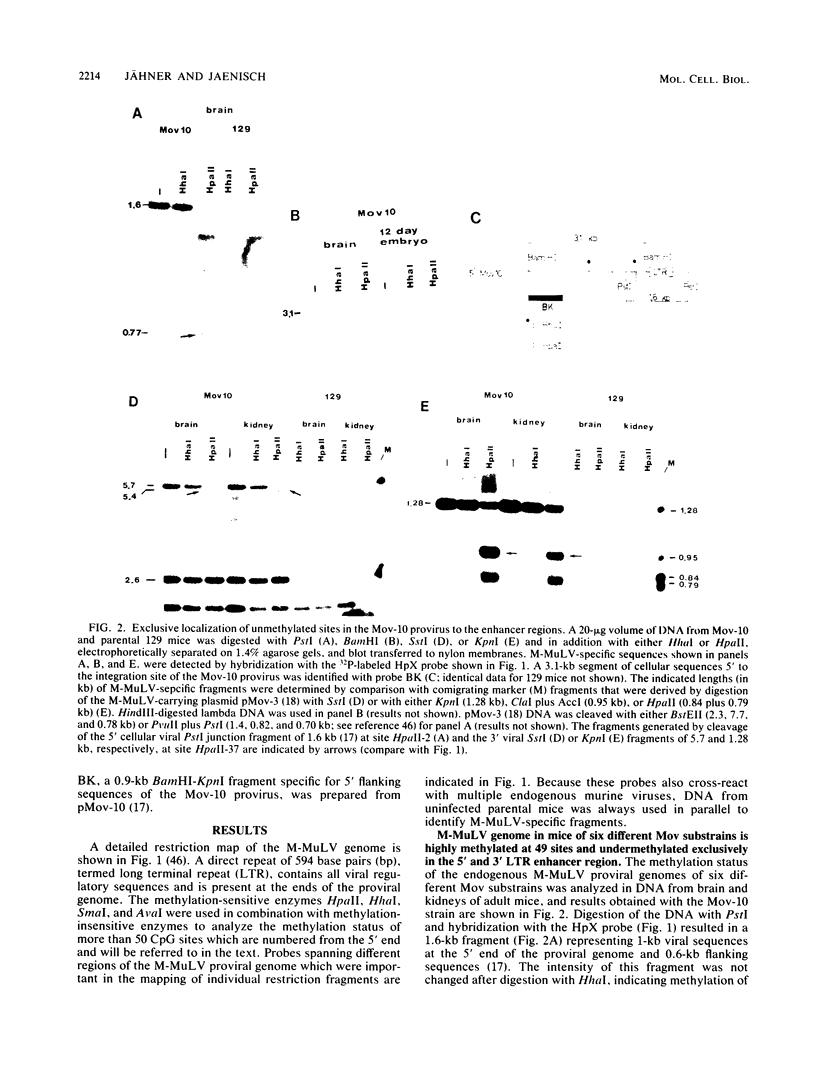
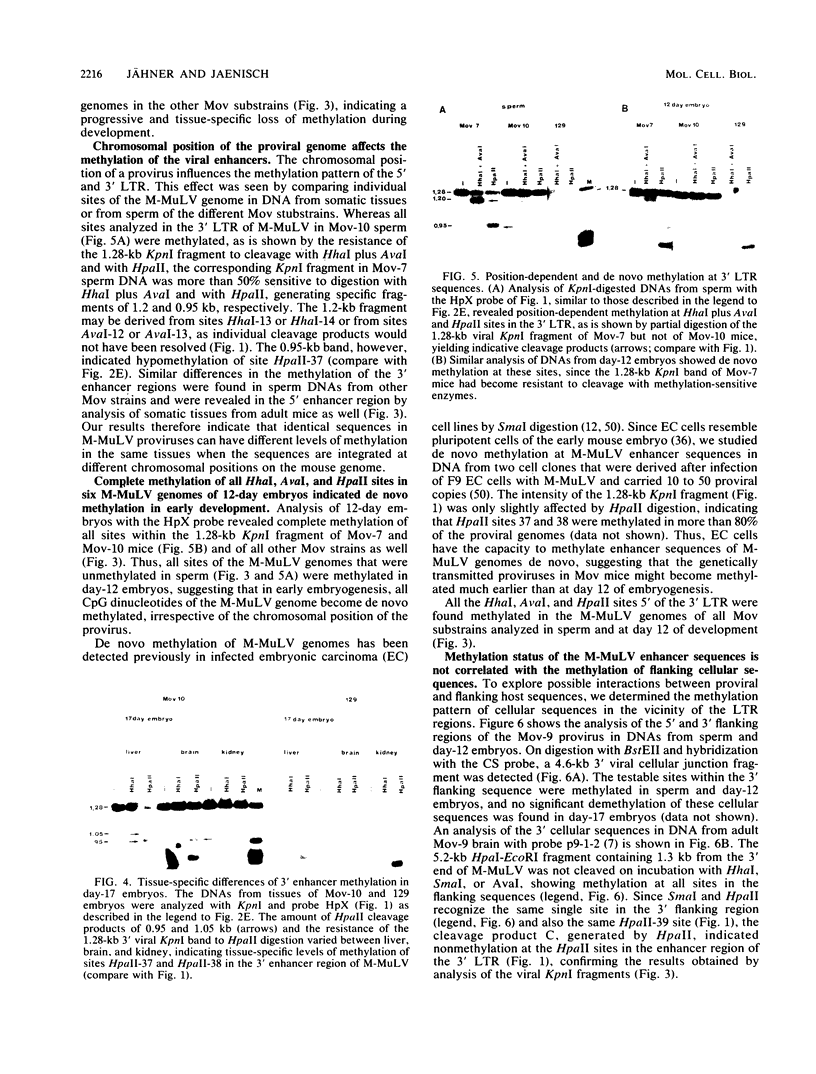
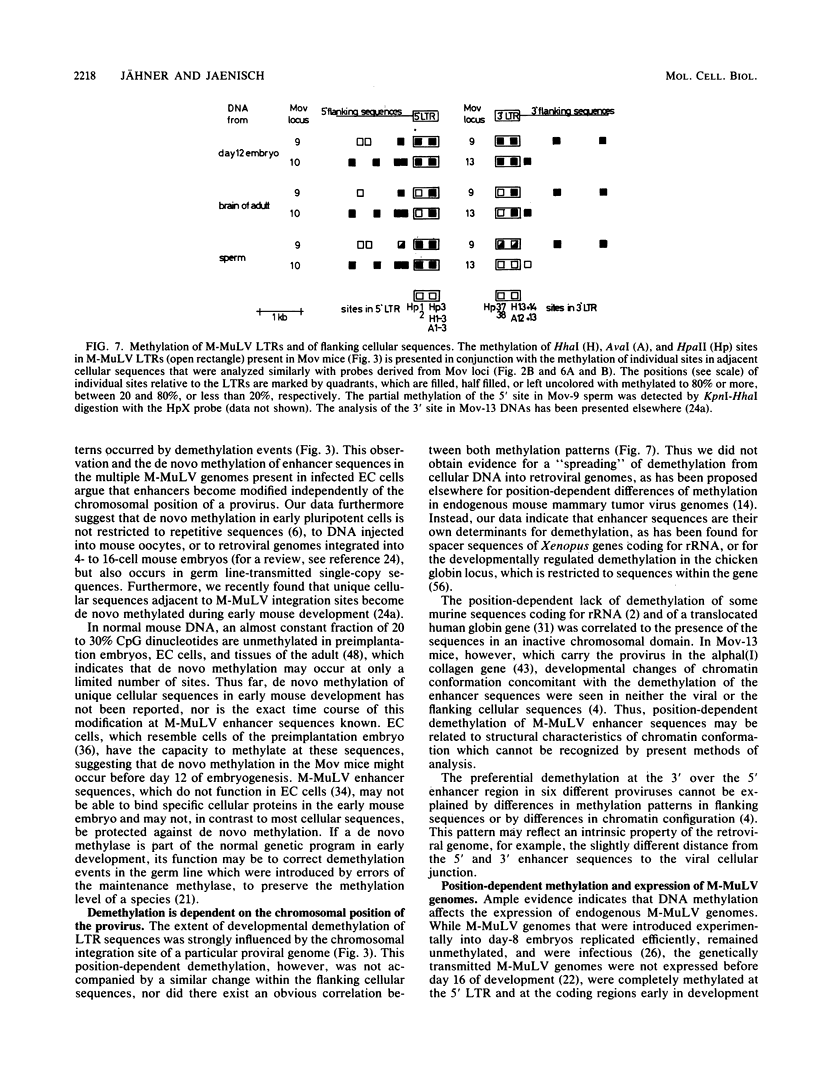
The methylation pattern of the germ line-transmitted Moloney leukemia proviral genome was analyzed in DNA of sperm, of day-12 and day-17 embryos, and of adult mice from six different Mov substrains. At day 12 of gestation, all 50 testable CpG sites in the individual viral genomes as well as sites in flanking host sequences were highly methylated. Some sites were unmethylated in sperm, indicating de novo methylation of unique DNA sequences during normal mouse development. At subsequent stages of development, specific CpG sites which were localized exclusively in the 5' and 3' enhancer regions of the long terminal repeat became progressively demethylated in all six proviruses. The extent of enhancer demethylation, however, was tissue specific and strongly affected by the chromosomal position of the respective proviral genome. This position-dependent demethylation of enhancer sequences was not accompanied by a similar change within the flanking host sequences, which remained virtually unchanged. Our results indicate that viral enhancer sequences, but not other sequences in the M-MuLV genome, may have an intrinsic ability to interact with cellular proteins, which can perturb the interaction of the methylase with DNA. Demethylation of enhancer sequences is not sufficient for gene expression but may be a necessary event which enables the enhancer to respond to developmental signals which ultimately lead to gene activation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. DNA methylation--how important in gene control? Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):503–504. doi: 10.1038/307503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P., Taggart M. H., Gehring C. A. Methylated and unmethylated ribosomal RNA genes in the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 15;152(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouché J. P. The effect of spermidine on endonuclease inhibition by agarose contaminants. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 15;115(1):42–45. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90519-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Retrovirus-induced lethal mutation in collagen I gene of mice is associated with an altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90521-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Messing A., van Dyke T., Levine A. J., Palmiter R. D. Transgenic mice harboring SV40 T-antigen genes develop characteristic brain tumors. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90367-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V., Forrester L., Sanford J., Hastie N., Rossant J. Cell lineage-specific undermethylation of mouse repetitive DNA. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):284–286. doi: 10.1038/307284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov I., Stuhlmann H., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Cloning of two genetically transmitted Moloney leukemia proviral genomes: correlation between biological activity of the cloned DNA and viral genome activation in the animal. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1088–1098. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1088-1098.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N. Eukaryotic DNA methylation. Hum Genet. 1983;64(4):315–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00292363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautsch J. W., Wilson M. C. Delayed de novo methylation in teratocarcinoma suggests additional tissue-specific mechanisms for controlling gene expression. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):32–37. doi: 10.1038/301032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzburg W. H., Groner B. The chromosomal integration site determines the tissue-specific methylation of mouse mammary tumour virus proviral genes. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1129–1135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01941.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Microinjection of cloned retroviral genomes into mouse zygotes: integration and expression in the animal. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):540–542. doi: 10.1038/293540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Kuehn M., Delius H., Jaenisch R. Insertion of retrovirus into the first intron of alpha 1(I) collagen gene to embryonic lethal mutation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1504–1508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Schnieke A., Stuhlmann H., Jaenisch R. Infectivity and structure of molecular clones obtained from two genetically transmitted Moloney leukemia proviral genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2521–2537. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Schnieke A., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. DNA methylation and gene expression: endogenous retroviral genome becomes infectious after molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann J. W., Steffen D., Gusella J., Tabin C., Bird S., Cowing D., Weinberg R. A. DNA methylation affecting the expression of murine leukemia proviruses. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):144–157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.144-157.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Harbers K., Schnieke A., Löhler J., Chumakov I., Jähner D., Grotkopp D., Hoffmann E. Germline integration of moloney murine leukemia virus at the Mov13 locus leads to recessive lethal mutation and early embryonic death. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90511-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Jähner D. Methylation, expression and chromosomal position of genes in mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 15;782(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Jähner D., Nobis P., Simon I., Löhler J., Harbers K., Grotkopp D. Chromosomal position and activation of retroviral genomes inserted into the germ line of mice. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Schnieke A., Harbers K. Treatment of mice with 5-azacytidine efficiently activates silent retroviral genomes in different tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R., Weissman I. L., Early P., Cole J., Hood L. Organization of kappa light chain genes in germ-line and somatic tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Esty A. C., Subramani S., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. Elements in the long terminal repeat of murine retroviruses enhance stable transformation by thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1855–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra J., Reudelhuber T. L., Oudet P., Benoist C., Chae C. B., Jeltsch J. M., Mathis D. J., Chambon P. Induction of altered chromatin structures by simian virus 40 enhancer and promoter elements. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):708–714. doi: 10.1038/307708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Integration of Moloney leukaemia virus into the germ line of mice: correlation between site of integration and virus activation. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):456–458. doi: 10.1038/287456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Retrovirus-induced de novo methylation of flanking host sequences correlates with gene inactivity. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):594–597. doi: 10.1038/315594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Stuhlmann H., Jaenisch R. Conformation of free and of integrated Moloney leukemia virus proviral DNA in preleukemic and leukemic BALB/Mo mice. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):111–123. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Stuhlmann H., Stewart C. L., Harbers K., Löhler J., Simon I., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation and expression of retroviral genomes during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):623–628. doi: 10.1038/298623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Vanin E., deLange T., Flavell R. A., Grosveld F. G. Beta-globin gene inactivation by DNA translocation in gamma beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):662–666. doi: 10.1038/306662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Roberts S., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Costantini F. D. A foreign beta-globin gene in transgenic mice: integration at abnormal chromosomal positions and expression in inappropriate tissues. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Davis B., Overhauser J., Chao E., Fan H. Non-function of a Moloney murine leukaemia virus regulatory sequence in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):470–472. doi: 10.1038/308470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Teratocarcinomas and mammalian embryogenesis. Science. 1980 Aug 15;209(4458):768–776. doi: 10.1126/science.6250214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA contains Z-DNA segments within transcriptional enhancer sequences. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):674–679. doi: 10.1038/303674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Norstedt G., Gelinas R. E., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L. Metallothionein-human GH fusion genes stimulate growth of mice. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):809–814. doi: 10.1126/science.6356363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Enhancers and ribosomal gene spacers. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roan J. G., Dunaway M. Spacer regulation of Xenopus ribosomal gene transcription: competition in oocytes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reudelhuber T. A step closer to the principles of eukaryotic transcriptional control. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):301–301. doi: 10.1038/311301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Sager R. Tissue specificity and clustering of methylated cystosines in bovine satellite I DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3584–3588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnieke A., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Embryonic lethal mutation in mice induced by retrovirus insertion into the alpha 1(I) collagen gene. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):315–320. doi: 10.1038/304315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W., Groudine M. Alteration of c-myc chromatin structure by avian leukosis virus integration. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):702–708. doi: 10.1038/307702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Wagner H., Werner E., Jaenisch R. Retrovirus genomes methylated by mammalian but not bacterial methylase are non-infectious. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):275–277. doi: 10.1038/304275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J., Roberts-Ems J., Luthardt F. W., Riggs A. D. Methylation of DNA in mouse early embryos, teratocarcinoma cells and adult tissues of mouse and rabbit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2369–2385. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Gruenbaum Y., Pollack Y., Razin A., Cedar H. Clonal inheritance of the pattern of DNA methylation in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):61–65. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. L., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation, expression, and infectivity of retroviral genomes introduced into embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4098–4102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Pattengale P. K., Leder P. Spontaneous mammary adenocarcinomas in transgenic mice that carry and express MTV/myc fusion genes. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Infectivity and methylation of retroviral genomes is correlated with expression in the animal. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90305-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Function of the retrovirus long terminal repeat. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90367-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. Form and function of retroviral proviruses. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):812–820. doi: 10.1126/science.6177038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weischet W. O., Glotov B. O., Schnell H., Zachau H. G. Differences in the nuclease sensitivity between the two alleles of the immunoglobulin kappa light chain genes in mouse liver and myeloma nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3627–3645. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M. H. The inheritance of methylation patterns in vertebrates. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):285–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]