Abstract
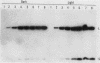
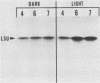
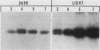
The regulation of expression of the genes encoding the large subunit (LSU) and small subunit (SSU) of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBPCase) was examined in 1- through 8-day-old, dark-grown (etiolated) and light-grown amaranth cotyledons. RuBPCase specific activity in light-grown cotyledons increased during this 8-day period to a level 15-fold higher than in dark-grown cotyledons. Under both growth conditions, the accumulation of the LSU and SSU polypeptides was not coordinated. Initial detection of the SSU occurred 1 and 2 days after the appearance of the LSU in light- and dark-grown cotyledons, respectively. Furthermore, although the levels of the LSU were similar in both light- and dark-grown seedlings, the amount of the SSU followed clearly the changes in enzyme activity. Synthesis of these two polypeptides was dramatically different in etiolated versus light-grown cotyledons. In light the synthesis of both subunits was first observed on day 2 and continued throughout the growth of the cotyledons. In darkness the rate of synthesis of both subunits was much lower than in light and occurred only as a burst between days 2 and 5 after planting. However, mRNAs for both subunits were present in etiolated cotyledons at similar levels on days 4 through 7 (by Northern analysis) and were functional in vitro, despite their apparent inactivity in vivo after day 5. In addition, since both LSU and SSU mRNA levels were lower in dark- than in light-grown seedlings, our results indicate that both transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls modulate RuBPCase production in developing amaranth cotyledons.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews T. J., Abel K. M. Kinetics and subunit interactions of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase from the cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8445–8451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews T. J., Ballment B. The function of the small subunits of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7514–7518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apel K. Phytochrome-induced appearance of mRNA activity for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barraclough R., Ellis R. J. The biosynthesis of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. Uncoupling of the synthesis of the large and small subunits in isolated soybean leaf cells. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 15;94(1):165–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachy R. N. In Vitro Synthesis of the alpha and alpha' Subunits of the 7S Storage Proteins (Conglycinin) of Soybean Seeds. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):990–994. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. Biosynthesis of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Polypeptide turnover in darkness. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):61–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J., Jenkins G. I., Hartley M. R. Differential regulation of the accumulation of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b complex and ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in greening pea leaves. J Cell Biochem. 1984;25(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240250102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry-Lowe S. L., Mc Knight T. D., Shah D. M., Meagher R. B. The nucleotide sequence, expression, and evolution of one member of a multigene family encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in soybean. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):483–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore A. R., Broadhurst M. K., Gray R. E. Cell-free synthesis of leaf protein: Identification of an apparent precursor of the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):655–659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore A. R. Reiteration frequency of the gene coding for the small subunit of ribulose--1,5--bisphosphate carboxylase. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Schmidt G. W. Post-translational transport into intact chloroplasts of a precursor to the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Bedbrook J. R., Bogorad L., Rich A. Maize chloroplast DNA fragment encoding the large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Cashmore A., Chua N. H. Nucleotide sequences of two pea cDNA clones encoding the small subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and the major chlorophyll a/b-binding thylakoid polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1399–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Edwards C., Chua N. H. Tissue-specific and light-regulated expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1671–1679. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criddle R. S., Dau B., Kleinkopf G. E., Huffaker R. C. Differential synthesis of ribulosediphosphate carboxylase subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 9;41(3):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossland L. D., Rodermel S. R., Bogorad L. Single gene for the large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase in maize yields two differentially regulated mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4060–4064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B., Blobel G., Chua N. H. In vitro synthesis and processing of a putative precursor for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1082–1085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D. Physical change in cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoproteins in cells treated with inhibitors of mRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):415–423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmuir P., Smith S., Bedbrook J. A number of different nuclear genes for the small subunit of RuBPCase are transcribed in petunia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4177–4183. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. F., Ellis R. J. Light-stimulated transcription of genes for two chloroplast polypeptides in isolated pea leaf nuclei. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1493–1498. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01345.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geetha V., Mohamed A. H., Gnanam A. Cell-free synthesis of active ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in the mesophyll chloroplasts of Sorghum vulgare. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;606(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johal S., Bourque D. P., Smith W. W., Suh S. W., Eisenberg D. Crystallization and characterization of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from eight plant species. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8873–8880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Miziorko H. M. Carbamate formation on the epsilon-amino group of a lysyl residue as the basis for the activation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase by CO2 and Mg2+. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5321–5328. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H. Ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase: amino acid sequence of a peptide bearing the activator carbon dioxide. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1236–1240. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANS R. J., NOVELLI G. D. A convenient, rapid and sensitive method for measuring the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Nov;3:540–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. E., Jurgenson J. E., Reardon E. M., Price C. A. Plastid translation in organello and in vitro during light-induced development in Euglena. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14478–14484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkind M. L., Schmidt G. W. Posttranscriptional Regulation of Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase Small Subunit Accumulation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jul;72(3):847–854. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.3.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Lorimer G. H. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:507–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T., Brutlag D. Addition of homopolymers to the 3'-ends of duplex DNA with terminal transferase. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:41–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T., Harpster M. H., Mayfield S. P., Taylor W. C. Light-regulated gene expression during maize leaf development. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):558–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nivison H. T., Stocking C. R. Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase synthesis in barley leaves: a developmental approach to the question of coordinated subunit synthesis. Plant Physiol. 1983 Dec;73(4):906–911. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.4.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santel H. J., Apel K. The protochlorophyllide holochrome of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). The effect of light on the NADPH:protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):95–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Ishiye M., Sakihama T., Kamikubo T. Light-induced increase of mRNA activity coding for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2315–2320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J., Kreuzaler F., Schäfer E., Hahlbrock K. Concomitant induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and flavanone synthase mRNAs in irradiated plant cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims T. L., Hague D. R. Light-stimulated increase of translatable mRNA for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in leaves of maize. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8252–8255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Ellis R. J. Light-stimulated accumulation of transcripts of nuclear and chloroplast genes for ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):127–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Incharoensakdi A., Akazawa T. Essentiality of the small subunit (B) in the catalysis of RuBP carboxylase/oxygenase is not related to substrate-binding in the large subunit (A). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):763–769. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Rai A. K., Akazawa T. Interaction of constituent subunits in ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Aphanothece halophytica. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 15;229(1):202–211. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin E. M. Light regulation of specific mRNA species in Lemna gibba L. G-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4749–4753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin E. M., Suttie J. L. Light Effects on the Synthesis of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase in Lemna gibba L. G-3. Plant Physiol. 1980 Apr;65(4):641–647. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin E. M. White Light Effects on the mRNA for the Light-Harvesting Chlorophyll a/b-Protein in Lemna gibba L. G-3. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jun;67(6):1078–1083. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.6.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden R., Leaver C. J. Synthesis of Chloroplast Proteins during Germination and Early Development of Cucumber. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jun;67(6):1090–1096. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.6.1090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. In vitro synthesis of protein in microbial systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:267–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]