CASE SUMMARY
A 13-year-old girl with no significant previous history was admitted with respiratory failure, managed with endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation for 12 days. Subsequently, she was weaned off in view of clinico-radiological improvement and was discharged from the hospital. Post discharge, within a few days she started having exertional breathlessness, which increased progressively and was associated with noisy breathing. Hence, she was referred to our department for opinion and further management. Clinically her vital signs were stable.
Radiograph of the chest showed normal findings. Spirometry showed a “Box Pattern” on flow volume loop (FVL) [Figure 1] with Empey′s index of 14.6 and the ratio of maximal expiratory flow at 50% of vital capacity and maximal inspiratory flow at 50% of the vital capacity FEF50/FIF50 was 1.19, suggesting fixed upper airway obstruction (UAO).
Figure 1.
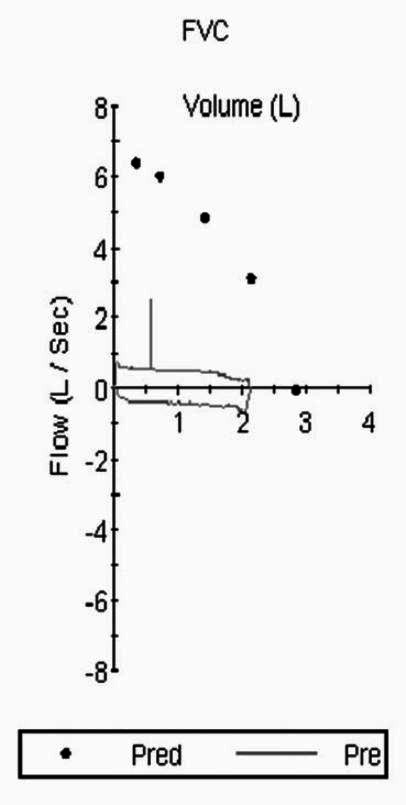
Spirometry with flow volume loop showing “box pattern” suggestive of upper airway obstruction
Computed Tomography (CT) of the neck with 3-D reconstruction [Figure 2 a-b] showed tracheal narrowing for the length of 9 mm at the level of thyroid isthmus, approximately 3.5 cm below the level of the glottis. Antero-posterior diameter at the level of narrowing was 6.5 mm, and the tracheal wall was irregular at this segment.
Figure 2.
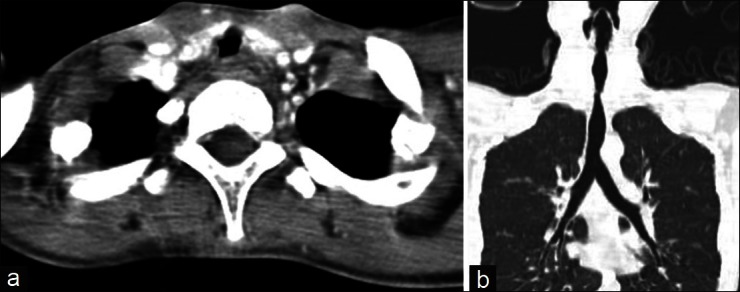
(a-b) Computed tomography of the chest and neck
Based on the above-mentioned findings, the diagnosis of post-intubation tracheal stenosis (PITS) was made. The patient was managed conservatively on an outpatient basis and was referred to the cardiothoracic unit for laser therapy. However, in the intervening period, due to the persistence of symptoms she was hospitalized at another center, where she underwent tracheostomy. Post procedure, she developed severe subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum. Prophylactic intercostal tube insertion was performed to relieve subcutaneous emphysema. However, the condition of the patient deteriorated further and resulted in death due to complications of pneumomediastinum.
Discussion
PITS occur in 10–22% of endotracheal intubation cases and its etiology has not been fully elucidated. Various authors consider mechanical damage to tracheal mucosa, and especially compression and ischemia-associated necrosis of the stenotic segment, to be the main cause of stenosis.[1] Local infections, low blood pressure in the period of intubation, sensitivity of the patient to the employed intubation materials, and chemical agents used to sterilize the intubation tube, as well as an individual idiosyncratic reaction are also suggested.[1] Depending on the site of stenosis, the presentation can vary from dyspnea, inspiratory stridor, dyphonia, and apnea. Patients may present with cough, progressive dyspnea on exertion, with 50–60% reduction in tracheal lumen. Hence, only 1–2% of patients are symptomatic. As the degree of obstruction increases, dyspnea at rest and stridor may be detected. However, these symptoms following endotracheal intubation or tracheostomy should guide as an indicator to the diagnosis of PITS.
The most common risk factors predisposing to the development of PITS are high tracheostomy site, prolonged intubation period, traumatic intubation, and history of previous intubation or previous tracheostomy. Spirometry with FVL remains the most effective way of detecting UAO even before the manifestation of symptoms.[2] Anatomical distribution of the upper airway as extrathoracic and intrathoracic portions helps in spirometric diagnosis. Although the upper airways are relatively rigid conducting passages, changes in airway diameter occur during the normal respiratory cycle. During inspiration, the intrathoracic airways expand; in contrast, the extrathoracic airways diminish in caliber during inspiration due to the decrease in intraluminal pressure compared with atmospheric pressure. The reverse process occurs during expiration [Figures 3a–c].
Figure 3a.
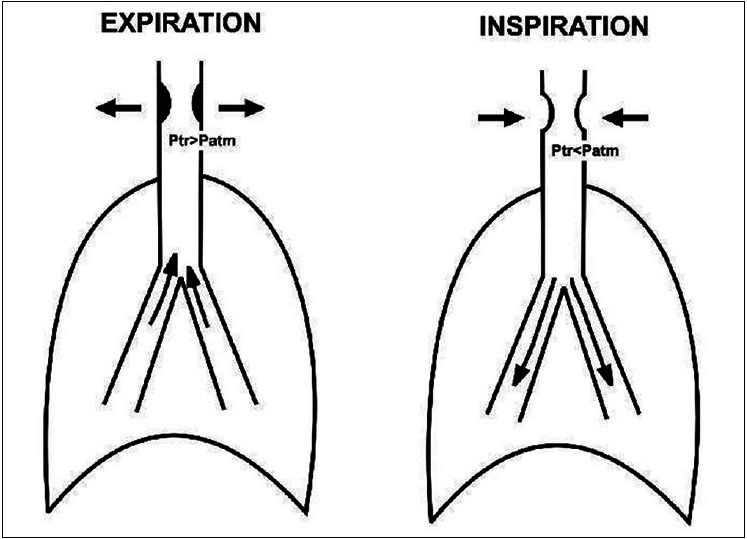
Schematic diagram explaining the mechanism of variable extrathoracic upper airway obstruction
Figure 3c.
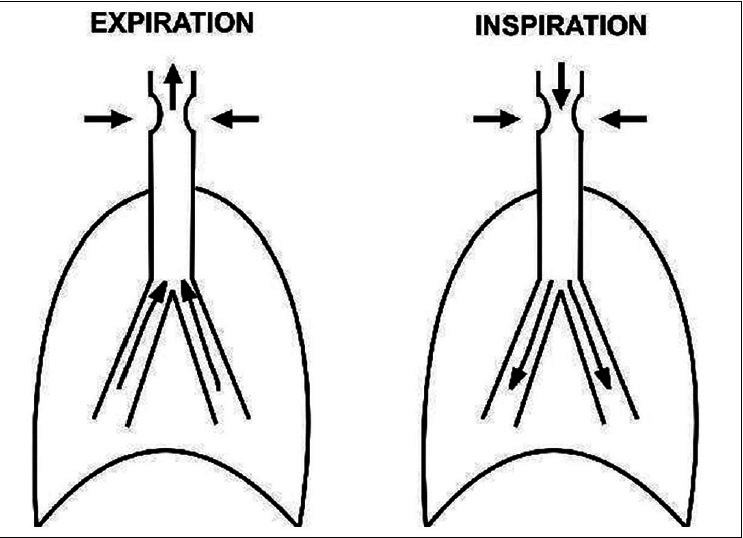
Schematic diagram explaining the mechanism of fixed upper airway obstruction
Figure 3b.
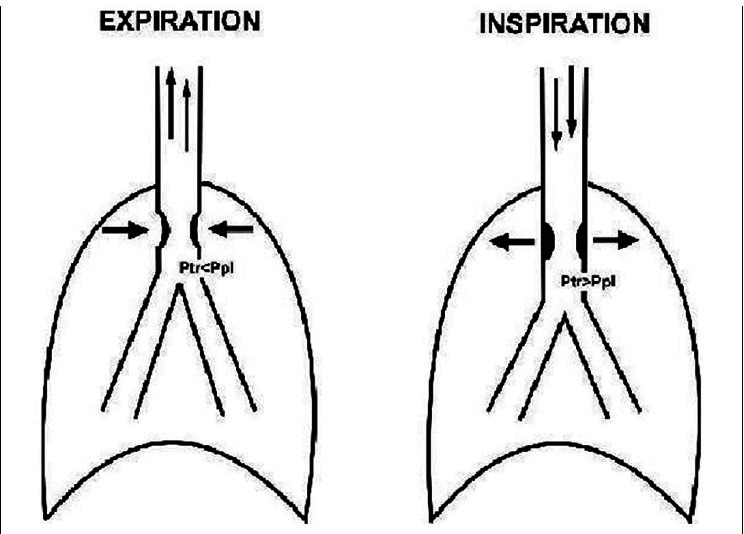
Schematic diagram explaining the mechanism of variable intrathoracic upper airway obstruction
Miller and Hyatt defined three classic patterns of FVL contours [Figure 4]in patients with UAO, depending on the location of the obstruction and depending on whether the obstruction is fixed, variable intrathoracic (VI-UAO) or variable extrathoracic (VE-UAO).[3] In addition, two ratios are calculated: 1) Empey′s index,[4] which is the ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1s (FEV1) and peak expiratory flow (PEF); and 2) Mid-vital capacity ratio, (FEF50/FIF50). Empey′s index greater than 8 suggests the presence of UAO. Furthermore, FEF50/FIF50 greater than 1 indicates VE-UAO, and if it is less than 0.3, it indicates VI-UAO.[5] Fixed UAO is characterized by lack of changes in caliber during inhalation or exhalation and it produces a constant degree of airflow limitation during the entire respiratory cycle. A fixed lesion therefore, whether extrathoracic or intrathoracic, results in the flattening of both the inspiratory and expiratory portions of FLV with “Box Pattern”. Depending on any single ratio or measurement can be misleading.[6] Hence, appearances of the loop as well as upper airway indices should both be taken into consideration for the diagnosis of UAO. Spirometry with FVL in patients with tracheal stomas is also possible with the use of adapters, which fit tightly onto the tracheostomy tubes.
Figure 4.
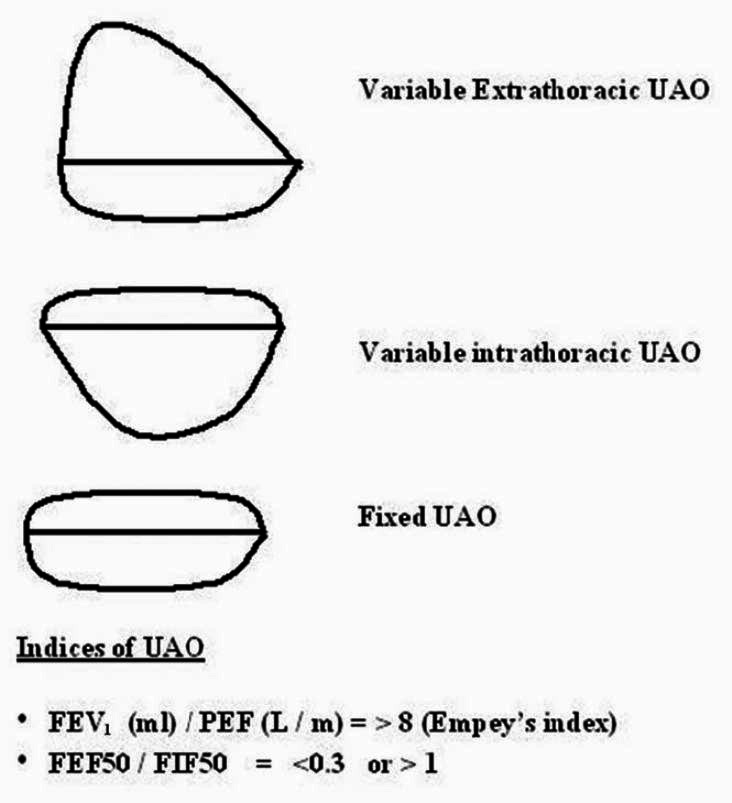
Three classic patterns of flow volume loop contours in patients with upper airway obstruction
PITS can be prevented to a great extent using large-volume, low-pressure cuffs and careful management of stomal tubes.[7] This includes aseptic precautions, maintaining low pressures in the endotracheal tube balloon, and reducing the pressure for 5 minutes every hour. Eletrocautery, cryotherapy,[8] and argon plasma coagulation rigid bronchoscopy with Nd: YAG laser, mechanical dilatation by rigid bronchoscopy,[9] and stent placements[10] are different interventional modalities used for the treatment of tracheal stenosis. Complete resection of the stenosed airway and anastomosis of the normal airway are the most appropriate methods of treatment.[11] In a minority of patients, who have short-segment stenosis and intact cartilage rings, non-surgical procedures such as dilatation, laser therapy, or granulation tissue extraction via bronchoscopy, and local and systemic steroids can be effective. Topical application of Mitomycin-C, an anti-proliferative agent, can be used to treat tracheal stenosis as it can inhibit cell division, as has been described in some studies.[12]
Unnecessary tracheostomies should be avoided in such cases because iatrogenic complications such as subcutaneous emphysema further increase mortality. Pneumomediastinum subsequent to subcutaneous emphysema causes stretching of the mediastinal pleura, leading to rupture and pneumothorax. Prophylactic intercostal tube insertion should not be done as it further increases complications related to the procedure.[13] PITS, when diagnosed and treated appropriately, has gratifying results with complete resolution of symptoms. Prompt recognition of the problem is essential to avoid delay in the institution of measures that relieve the obstruction. The appropriate use of investigative strategies such as spirometry with FVL, which can identify UAO, is crucial to reduce mortality related to PITS.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Papla B, Dyduch G, Frasik W, Olechnowicz H. Post-intubation tracheal stenosis-Morphological-clinical investigations. Pol J Pathol. 2003;54:261–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kapteijns EF, Kwakkel-van Erp JM, Vos PJ, van den Elshout FJ. Dyspnoea caused by upper-airway obstruction: Simple diagnosis by establishing a flow-volume loop. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2006;150:993–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Miller RD, Hyatt RE. Evaluation of obstructing lesions of the trachea and larynx by flow-volume loops. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973;108:475–81. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.3.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Empey DW. Assessment of upper airways obstruction. Br Med J. 1972;3:503–5. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5825.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kryger M, Bode F, Antic R, Anthonisen N. Diagnosis of obstruction of the upper and central airways. Am J Med. 1976;61:85–93. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Modrykamien AM, Gudavalli R, McCarthy K, Liu X, Stoller JK. Detection of upper airway obstruction with spirometry results and the flow-volume loop: A comparison of quantitative and visual inspection criteria. Respir Care. 2009;54:474–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Grillo HC, Cooper JD, Geffin B, Pontoppidan H. A low-pressure cuff for tracheostomy tubes to minimize tracheal injury. A comparative clinical trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1971;62:898–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fernando HC, Dekeratry D, Downie G, Finley D, Sullivan V, Sarkar S, et al. Feasibility of spray cryotherapy and balloon dilation for non-malignant strictures of the airway. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;40:1177–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2011.02.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chhajed PN, Malouf MA, Glanville AR. Bronchoscopic dilatation in the management of benign (non-transplant) tracheobronchial stenosis. Intern Med J. 2001;31:512–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1445-5994.2001.00135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Charokopos N, Foroulis CN, Rouska E, Sileli MN, Papadopoulos N, Papakonstantinou C. The management of post-intubation tracheal stenoses with self-expandable stents: Early and long-term results in 11 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;40:919–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2010.12.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nandakumar R, Jagdish C, Prathibha CB, Shilpa C, Sreenivas V, Balasubramanya AM, et al. Tracheal resection with end-to-end anastomosis for post-intubation cervical tracheal stenosis: Study of 14 cases. J Laryngol Otol. 2011;125:958–61. doi: 10.1017/S002221511100137X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rahbar R, Shapshay SM, Healy GB. Mitomycin: Effects on laryngeal and tracheal stenosis, benefits, and complications. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001;110:1–6. doi: 10.1177/000348940111000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Maunder RJ, Pierson DJ, Hudson LD. Subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Arch Intern Med. 1984;144:1447–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


