Abstract
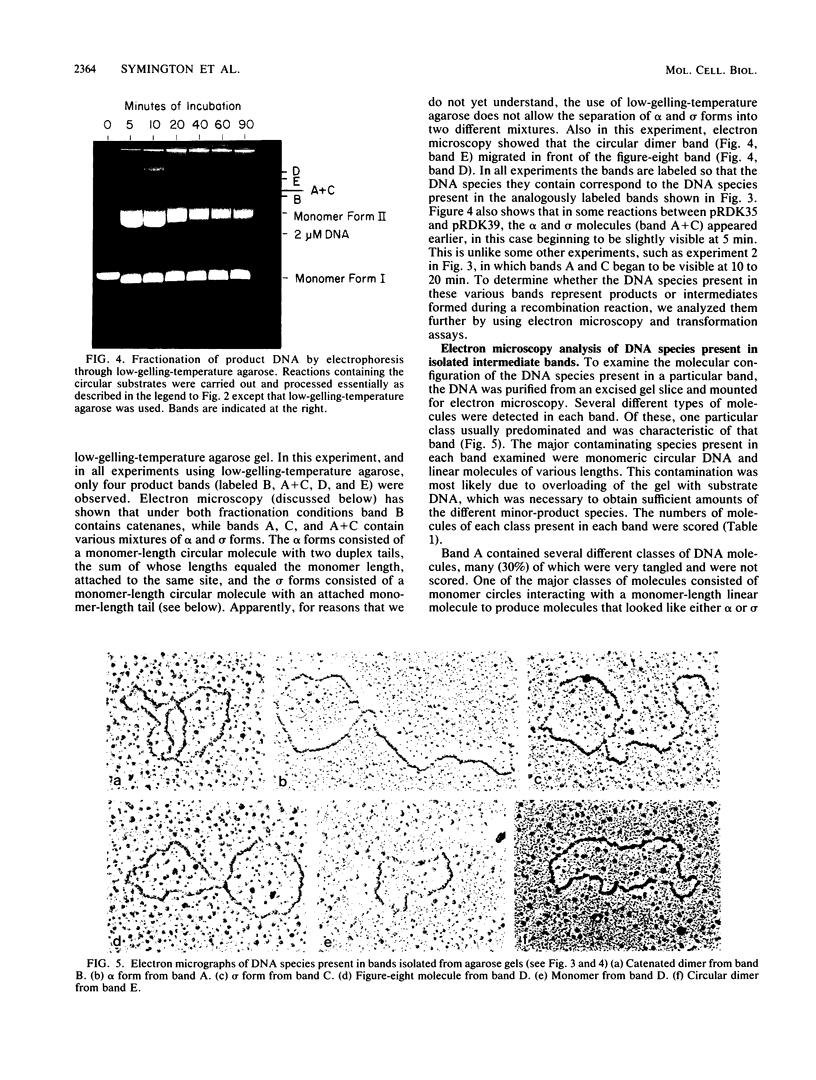
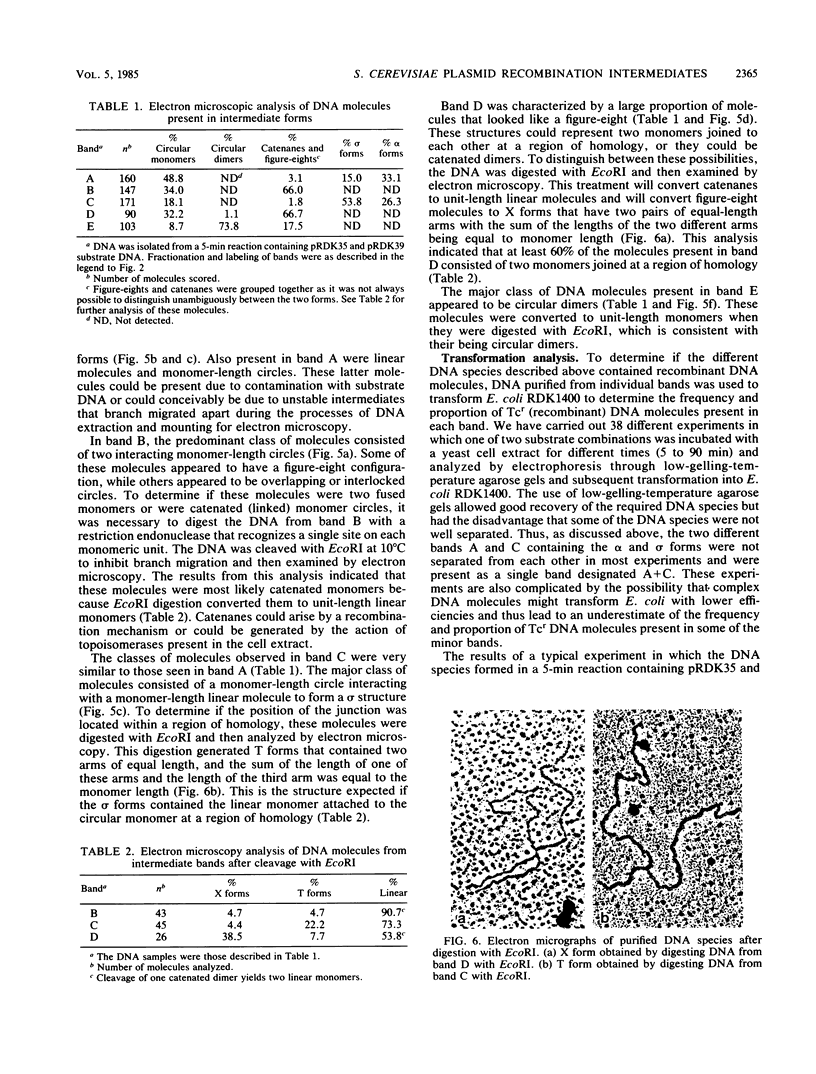
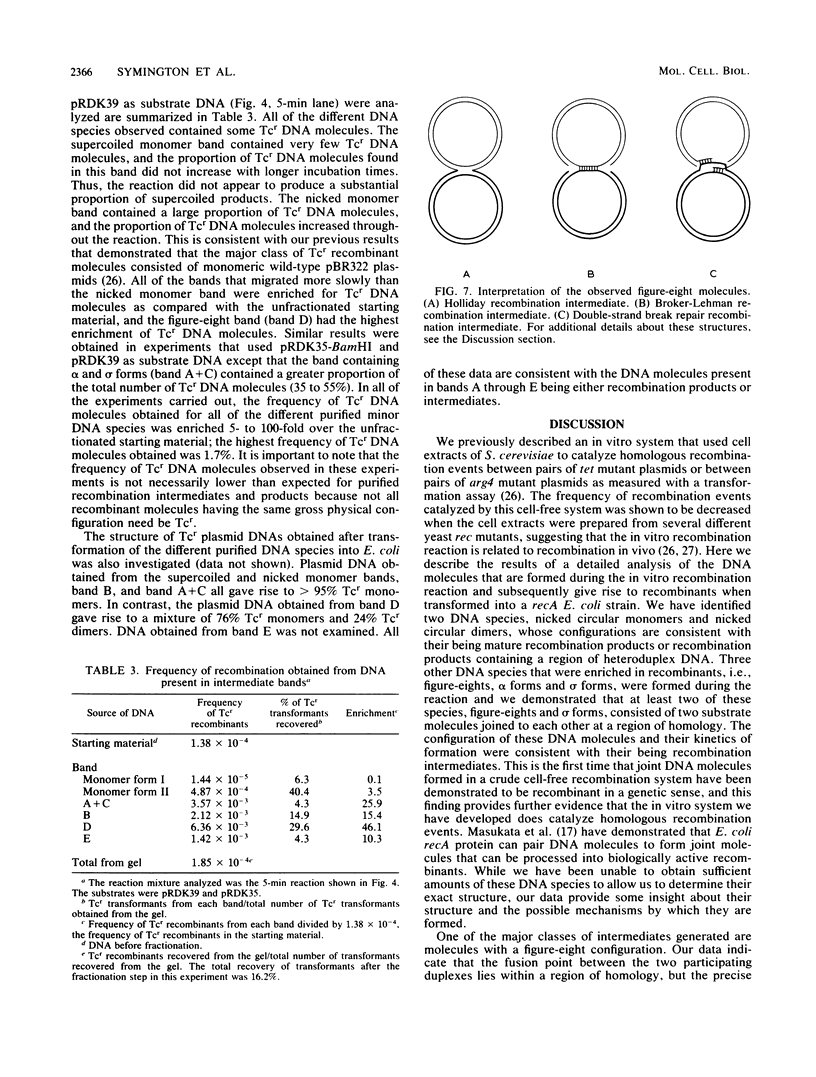
We have developed an assay utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell extracts to catalyze recombination in vitro between homologous plasmids containing different mutant alleles of the tet gene. Electrophoretic analysis of product DNA indicated that a number of novel DNA species were formed during the reaction. These species migrated through agarose gels as distinct bands with decreased electrophoretic mobility compared with the substrate DNA. The DNA from each individual band was purified and shown to be enriched 5- to 100-fold for tetracycline-resistant recombinants by using a transformation assay. The structure of the DNA molecules present in these bands was determined by electron microscopy. Recombination between circular substrates appeared to involve the formation and processing of figure-eight molecules, while recombination between circular and linear substrates involved the formation of molecules in which a circular monomer had a monomer-length linear tail attached at a region of homology.
Full text
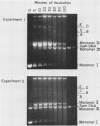
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell L. R., Byers B. Homologous association of chromosomal DNA during yeast meiosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):829–840. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L., Byers B. Occurrence of crossed strand-exchange forms in yeast DNA during meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3445–3449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbow R. M., Krauss M. R. Recombinant DNA formation in a cell-free system from Xenopus laevis eggs. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):191–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbow R. M., Zuccarelli A. J., Sinsheimer R. L. Recombinant DNA molecules of bacteriophage phi chi174. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):235–239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broker T. R., Lehman I. R. Branched DNA molecules: intermediates in T4 recombination. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90453-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Renaturation of complementary single-stranded DNA circles: complete rewinding facilitated by the DNA untwisting enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5328–5332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., DasGupta C., Shibata T., Radding C. M. Homologous pairing in genetic recombination: recA protein makes joint molecules of gapped circular DNA and closed circular DNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):223–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90250-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty M. J., Morrison P. T., Kolodner R. Genetic recombination of bacterial plasmid DNA. Physical and genetic analysis of the products of plasmid recombination in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):539–560. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniger J., Warner R. C., Tessma I. Role of circular dimer DNA in the primary recombination mechanism of bacteriophage S13. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 7;242(114):9–12. doi: 10.1038/newbio242009a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel S., Mortimer R., Lusnak K., Tavares F. Meiotic gene conversion: a signal of the basic recombination event in yeast. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1325–1341. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. A., Morrison P. T., Kolodner R. Genetic recombination of bacterial plasmid DNA. Analysis of the effect of recombination-deficient mutations on plasmid recombination. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 25;160(3):411–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Ikeda H. Double Holliday structure: a possible in vivo intermediate form of general recombination in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(2):213–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00334816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R. Genetic recombination of bacterial plasmid DNA: electron microscopic analysis of in vitro intramolecular recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4847–4851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masukata H., Fujii T., Ogawa T., Ogawa H. Biologically active recombinant formed through DNA pairing by purified recA protein in vitro. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(2):226–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00337809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Kemper B., Hays J., Weisberg R. A. T4 endonuclease VII cleaves holliday structures. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Dressler D. Biochemical assay designed to detect formation of recombination intermediates in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1084–1088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Chow T., Nitiss J., Game J. Changes in the chromosomal DNA of yeast during meiosis in repair mutants and the possible role of a deoxyribonuclease. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:639–649. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B., Abraham J. A., Ivy J. M., Nasmyth K. A., McGill C. Homothallic switching of yeast mating type cassettes is initiated by a double-stranded cut in the MAT locus. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington L. S., Fogarty L. M., Kolodner R. Genetic recombination of homologous plasmids catalyzed by cell-free extracts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington L. S., Morrison P. T., Kolodner R. Genetic recombination catalyzed by cell-free extracts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:805–814. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson B. J., Camien M. N., Warner R. C. Kinetics of branch migration in double-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2299–2303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson B. J., Escarmis C., Parker B., Slater W. C., Doniger J., Tessman I., Warner R. C. Figure-8 configuration of dimers of S13 and phiX174 replicative form DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 5;91(4):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuring R. W., Sanders J. P., Borst P. A freeze-squeeze method for recovering long DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela M. S., Inman R. B. Visualization of a novel junction in bacteriophage lambda DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3024–3028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner R. C., Fishel R. A., Wheeler F. C. Branch migration in recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):957–968. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C., Countryman J. K., Howard-Flanders P. Enzymatic formation of biparental figure-eight molecules from plasmid DNA and their resolution in E. coli. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. A simple method to recover intact high molecular weight RNA and DNA after electrophoretic separation in low gelling temperature agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Hsu M. T. Visualization of genetic recombination intermediates of human adenovirus type 2 DNA from infected HeLa cells. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):168–171. doi: 10.1038/287168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Studier F. W., Dorgai L., Appelbaum E., Weisberg R. A. Enzymes and sites of genetic recombination: studies with gene-3 endonuclease of phage T7 and with site-affinity mutants of phage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:715–726. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]