Abstract
According to International Diabetes Federation (IDF), India has 62.4 million people with diabetes and by 2030 it is predicted that the number will rise to 100 million. Studies claim that there are around 410 experimentally proven Indian medicinal plants which have anti-diabetic activity, of which the mechanism of action of 109 plants has been elucidated or reported. So, the need of the hour is to explore the claims of Indian medicinal flora and open up the facets of many Indian plants which are being examined for their beneficial role in diabetes. So, we created a database (InDiaMed) of Indian medicinal plants that captures their role in anti-diabetic activity. InDiaMed's features include chemical, pharmacological, biochemical and geographical information of the medicinal plant, scientifically relevant information of the plant, and the coherent research done on it in the field of diabetes. The database also includes the list of poly-herbal formulations which are used for treatment of diabetes in India.
Availability
Keywords: Diabetes, Database, Medicinal Plants, Poly-herbal formulations, active constituents
Background
Diabetes is a progressive metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycaemia that may result from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The problem of diabetes is increasing worldwide, predominantly in developing countries. The reasons are complex, but are largely accredited to lifestyle changes like diet causing rapid increase in weight (obesity) and physical inactivity [1]. The chronic hyperglycaemia of diabetes is often associated with macro and micro vascular complications [2]. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus is growing rapidly worldwide and is reaching epidemic proportions. It is estimated that there are currently 285 million people with diabetes worldwide and this number is set to increase to 438 million by the year 2030 [3].
Many Indian plants are being examined for their beneficial use in diabetes and reports occur in numerous scientific journals of the merits of using such plants. Previous efforts were made to compile the information of the reported medicinal plants and develop a database exclusively for diabetes but such efforts were not comprehensive. Hence, the basic objective in compiling the InDiaMed database of the Indian medicinal plants is to provide a single source of comprehensive literature about the conventional medicinal plants used for the treatment of diabetes. Extensive literature survey on Indian flora with potential anti-diabetic activity was undertaken and, attempt made to compile all the relevant data for later scientific use. Additionally, of late, many strategies have been evaluated for combating the menace of diabetes and the use of poly-herbal ayurvedic formulations has shown substantial promise as the adjuvant therapy for diabetes. The information on such poly herbal formulation is the elite feature of this database. We expect that this database to be an important tool to researchers worldwide. One can easily identify plants of interest, and find the scientific details to further knowledge and understanding.
Methodology
Data Collection:
Data of anti-diabetic plants were collected from literature sources such as PubMed [4], Science Direct [5], Biomed Central [6], Wiley journals [7], Journal of Ethanopharmacology [8], and through collection of folklore medicinal usage. Currently, information on 407 Indian medicinal plants have been collected and curated in the database. The information regarding the poly-herbal formulations are collected from the products website, or from the published literature of the formulation (see supplementary material).
Database Design:
The Database was constructed using ASP.NET as the front-end and MS ACCESS as the back end. It is a user-friendly web based application and connects to the database of the comprehensive Indian Diabetic Medicinal Plants. The web application has been built with a simple and advanced search options. In simple search mode, one can search for a plant by using its botanical name while in advanced search extensive and boolean search options have been built. The detailed flow schema of the database and its access is shown in the (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
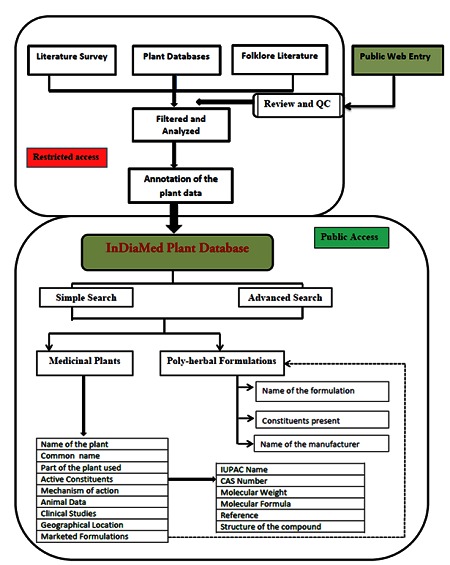
A detailed flow schema of the InDiaMed database
Software:
Asp.Net was used for User Interface Design, C#.Net for Application Development and MYSQL for backend with all the development carried out on a Windows OS-7.0 platform.
Database Features and Utility
The InDiaMed database resides as an open access, public domain web database. All the plants of the database are classified into six groups based on the quantum of research done and are subsequently assigned a color code. The color code is given according to number of citations for the plant in google scholar which provides a basis for the scientific community and industries for a quick and informative conclusion on these anti-diabetic plants. There is also a provision for the researchers to add a new plant data of their interest which they claim to have anti-diabetic property.
The record entry in the database contains the following information about the plant (a) Scientific Name (b) Common name (c) Local name (d) Part of the plant identified for diabetes activity (e) Active constituents (This section further has sub sections viz.Name of the compound, IUPAC name, CAS number, Molecular weight, Molecular formula and structure of the compound) (f) Mechanism of action (g) Animal Data (h) Clinical studies (i) Geographical distribution. The database also includes information regarding the most widely used polyherbal formulations for diabetes as a separate field. Apart from the technical information, the database also provides the current state of the epidemiological status of diabetes in India. A snap shot of the home page of InDiaMed database webpage is shown in (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
A snap shot of the home page of InDiaMed database webpage.
Future Development
As a part of future development releases, we plan to update comprehensive botanical and taxonomical data of all the medicinal plants in the database. Various biochemical pathways pertaining to glucose metabolism and the active constituents of the plants which alter the enzymes will be presented in the database as links. Information regarding 60 genes which are responsible for diabetes and their respective enzymes which are altered by various medicinal plants will be updated as ongoing research continues.
Conflicts of Interests
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgments
The Support of National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER), Hyderabad to Indian Institute of Biotechnology, Hyderabad is gratefully acknowledged.
Footnotes
Citation:Tota et al, Bioinformation 9(7): 378-380 (2013)
References
- 1. http://www.who.int/diabetes/action_online/basics/en/i ndex.html.
- 2.Fowler J. Clinical Diabetes. 2008;26:2. doi:10.2337/diaclin.26.2.77. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anjana R, et al. Indian J Med Res. 2011;133:369. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/PubMed/
- 5. http://www.sciencedirect.com.
- 6. http://www.biomedcentral.com.
- 7. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/home.
- 8. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/03788741.


