Abstract
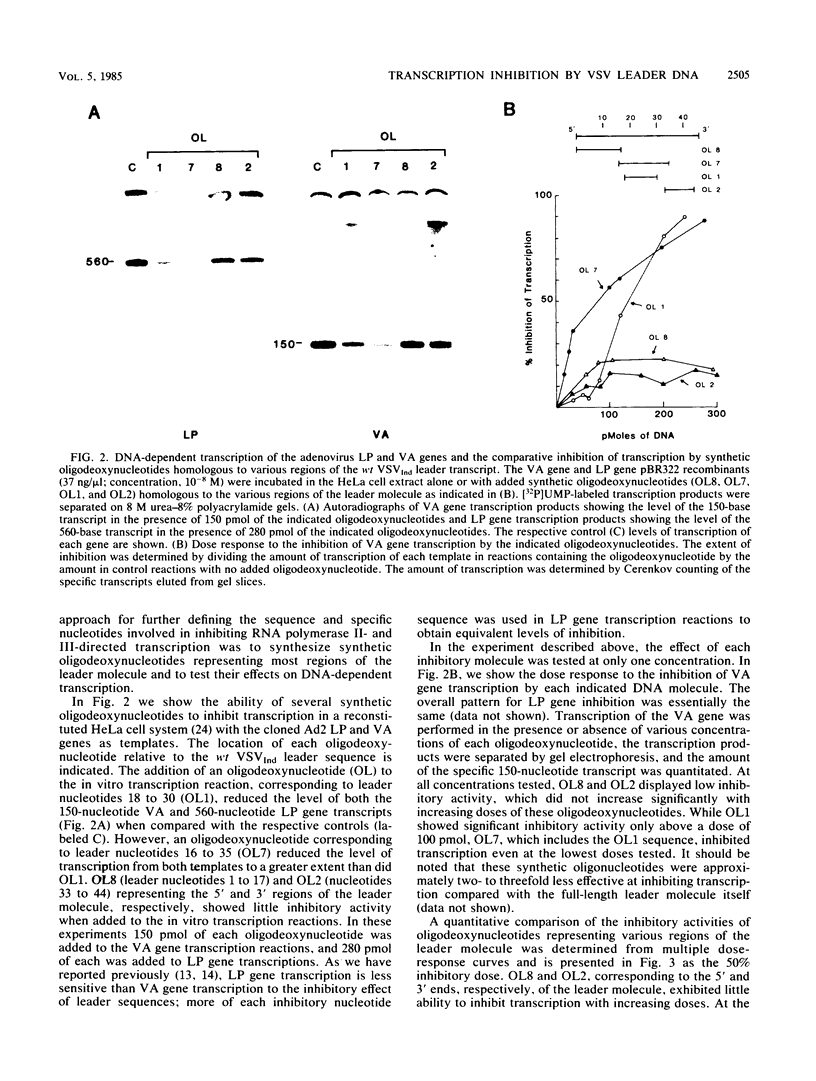
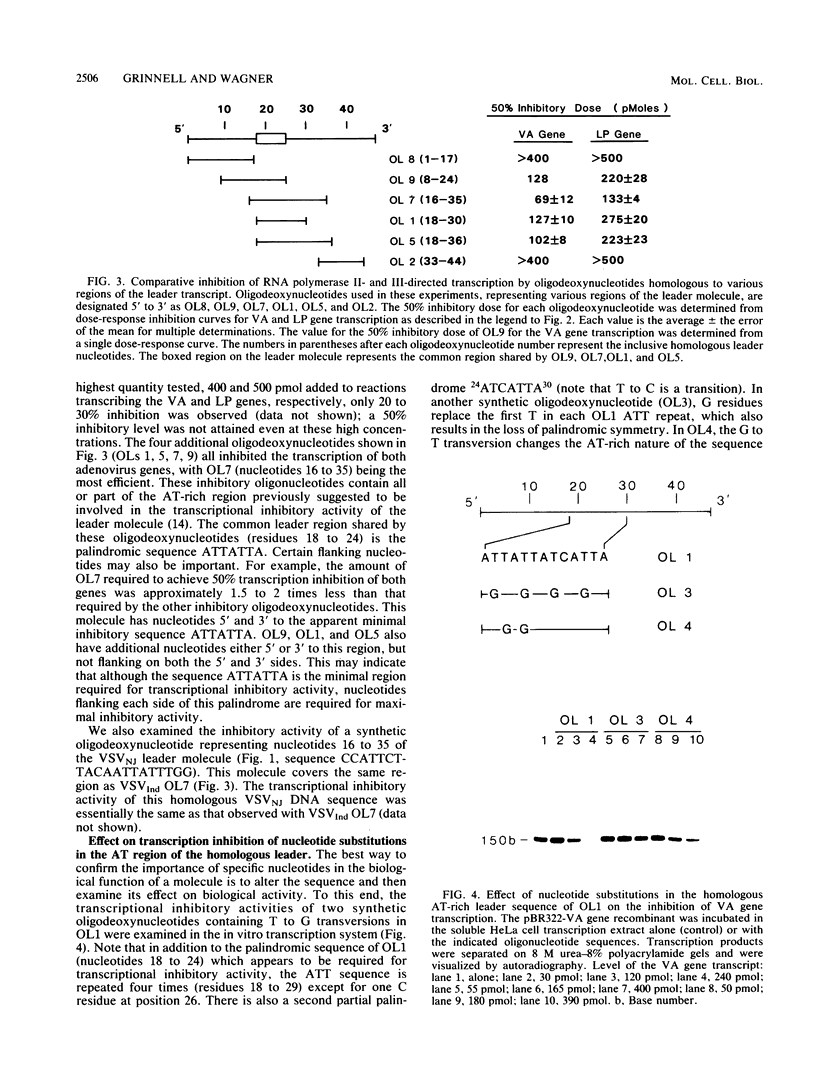
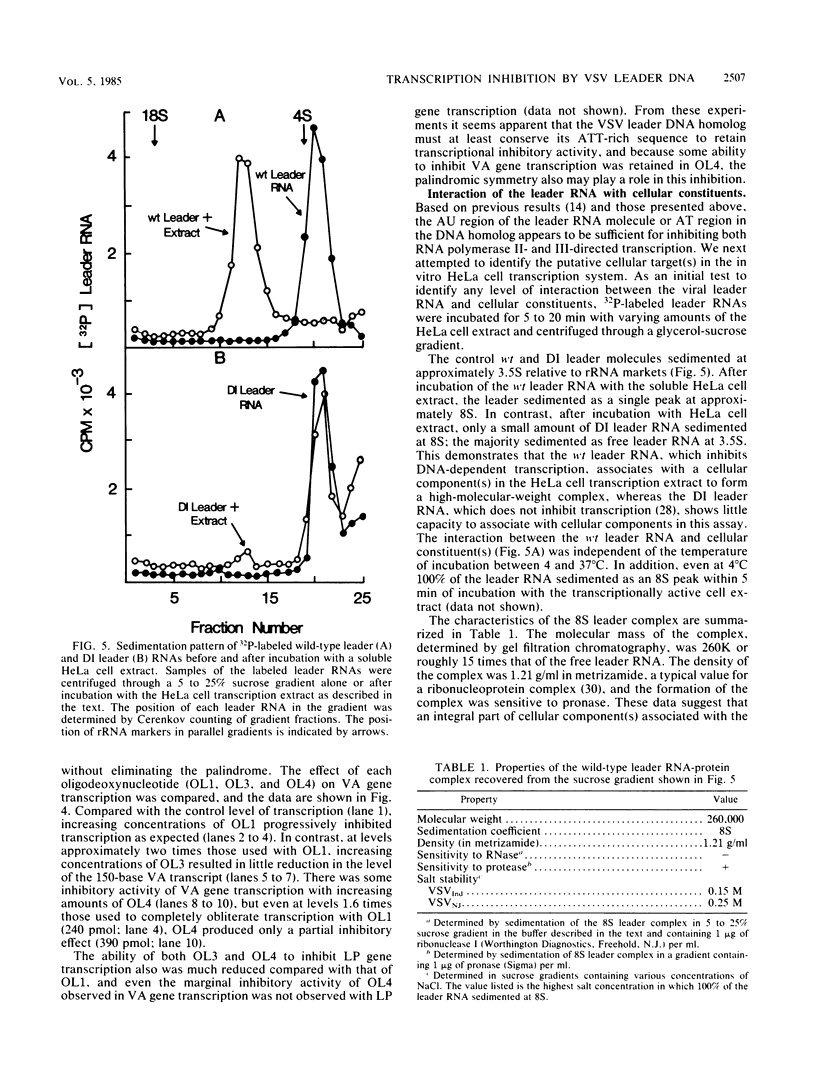
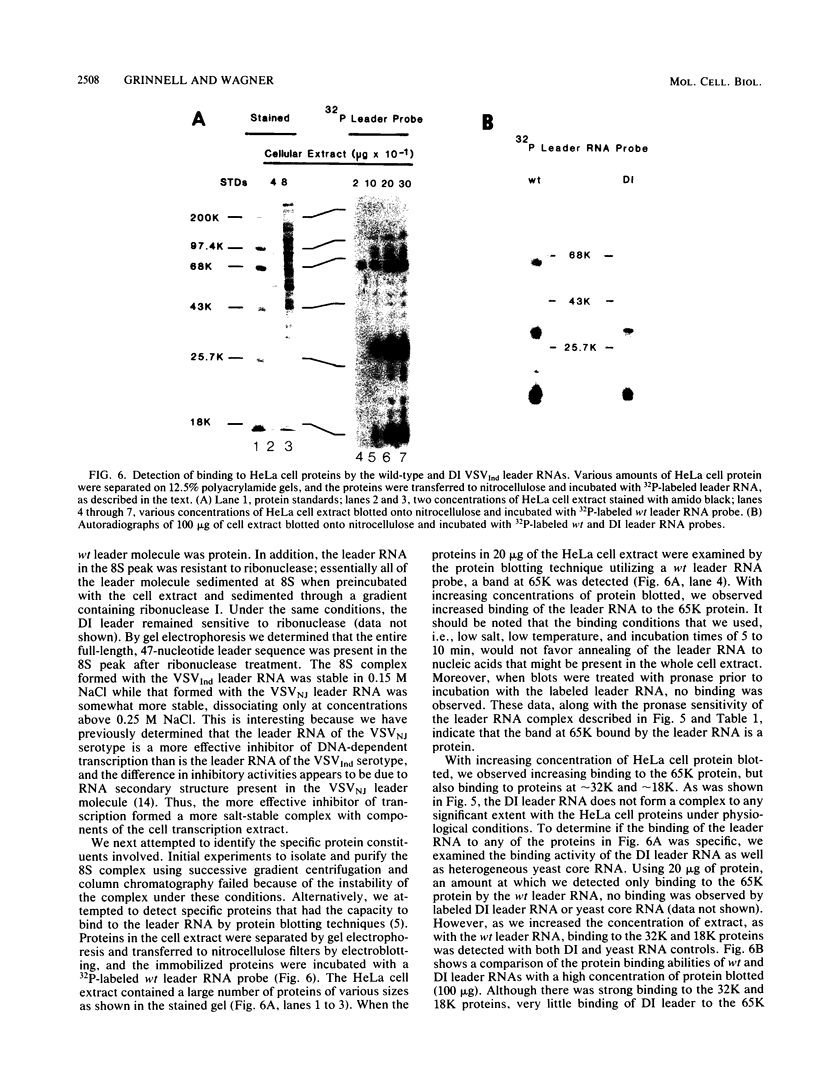
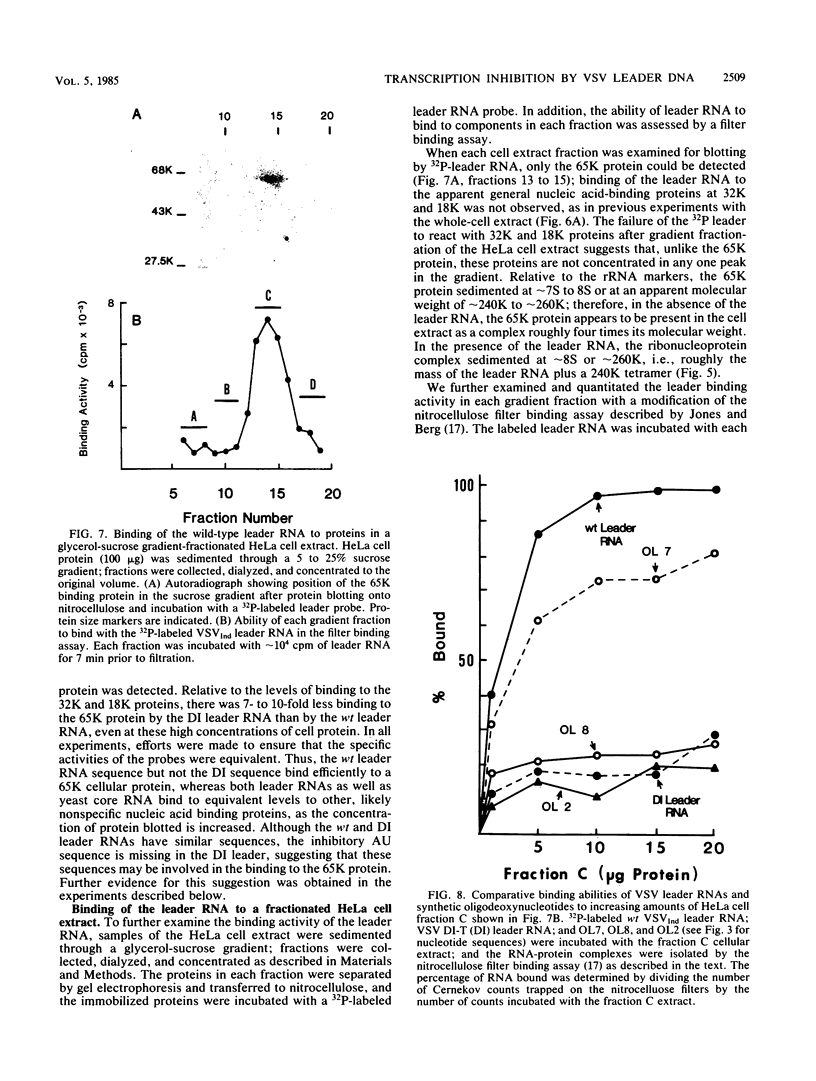
The leader RNA transcript of vesicular stomatitis virus inhibits transcription of the adenovirus major late promoter and virus-associated genes in a soluble HeLa cell transcription system. We examined the specific nucleotide sequence involved and the potential role of leader-protein interactions in this inhibition of RNA polymerase II- and III-directed transcription. Using synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides homologous to regions of the leader RNA molecule, we extend our previous results (B.W. Grinnell and R.R. Wagner, Cell 36:533-543, 1984) that suggest a role for the AU-rich region of the leader RNA or the homologous AT region of a cloned cDNA leader in the inhibition of DNA-dependent transcription. Our results indicate that a short nucleotide sequence (AUUAUUA) or its deoxynucleotide homolog (ATTATTA) appears to be the minimal requirement for the leader RNA to inhibit transcription by both RNA polymerases, but sequences flanking both sides of this region increase the inhibitory activity. Nucleotide changes in the homologous AT-rich region drastically decrease the transcriptional inhibitory activity. Leader RNAs from wild-type virus, but not from a 5'-defective interfering particle, form a ribonuclease-resistant, protease-sensitive ribonucleoprotein complex in the soluble HeLa cell extract. Several lines of evidence suggest that the leader RNA specifically interacts with a 65,000-dalton (65K) cellular protein. In a fractionated cell extract, only those fractions containing this 65K protein could reverse the inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis by the plus-strand vesicular stomatitis virus leader RNA or by homologous DNA. In studies with synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides homologous to leader RNA sequences, only those oligonucleotides containing the inhibitory sequence were able to bind to a gradient fraction containing the 65K protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Banerjee A. K. Sequential transcription of the genes of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1504–1508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A., White C. N. Order of transcription of genes of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt B., Bablanian R. Mechansims of vesicular stomatitis virus-induced cytopathic effects. II. Inhibition of macromolecular synthesis induced by infectious and defective-interfering particles. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
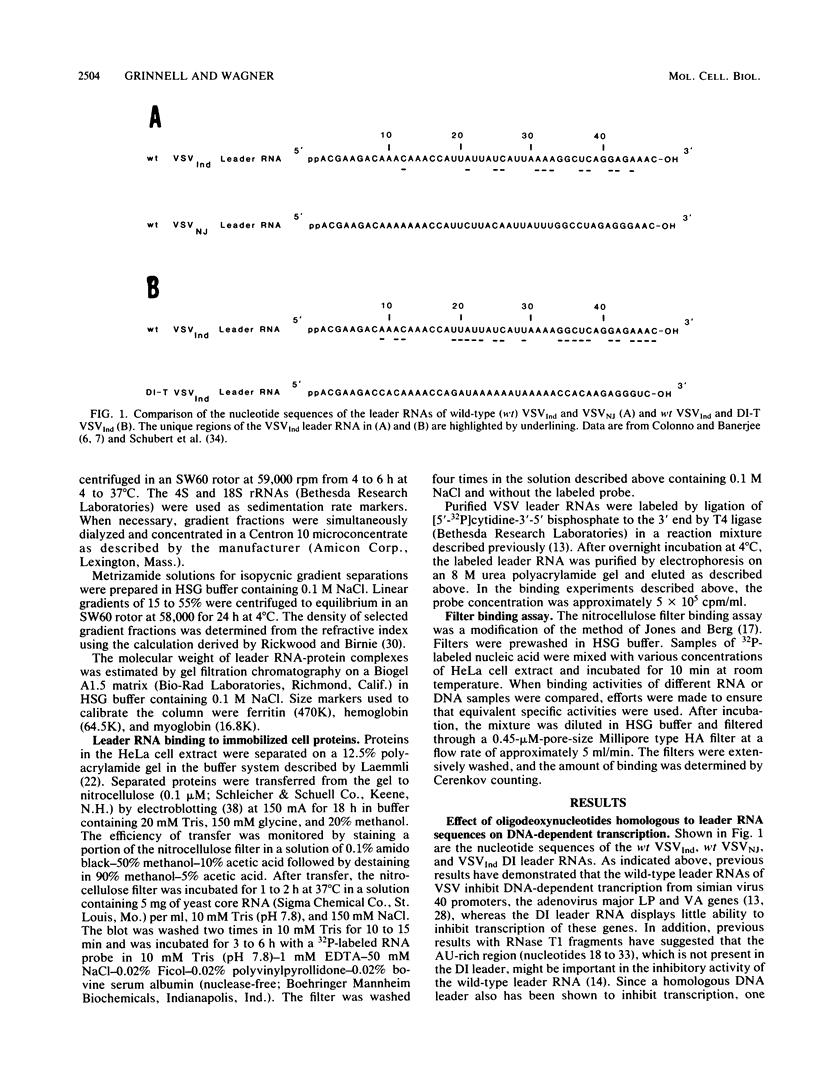
- Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the leader RNA synthesized in vitro by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K. Nucleotide sequence of the leader RNA of the New Jersey serotype of vesicular stomatitis virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4165–4176. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio J. M., Bagshaw J. C. DNA-dependent RNA polymerases from Artemia salina. Characterization of a protein factor from developing embryos that stimulates artemia RNA polymerase II. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Dierks P. M., Parsons J. T. In vitro synthesis of a unique RNA species by a T particle of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.708-716.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi C., Blumberg B., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the (+) leader RNA regions of the vesicular stomatitis virus Chandipura, Cocal, and Piry serotype genomes. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):125–130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.125-130.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Wagner R. R. Comparative inhibition of cellular transcription by vesicular stomatitis virus serotypes New Jersey and Indiana: role of each viral leader RNA. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):88–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.88-101.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Wagner R. R. Nucleotide sequence and secondary structure of VSV leader RNA and homologous DNA involved in inhibition of DNA-dependent transcription. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):533–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Manley J. L. DNA sequence required for initiation of transcription in vitro from the major late promoter of adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones O. W., Berg P. Studies on the binding of RNA polymerase to polynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Schubert M., Lazzarini R. A. Intervening sequence between the leader region and the nucleopcapsid gene of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):789–794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.789-794.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Specific transcription of homologous class III genes in yeast-soluble cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8432–8441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. The leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus is bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90541-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Piwnica-Worms H., Keene J. D. Rapid and transient localization of the leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus in the nuclei of infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5240–5244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister P. E., Wagner R. R. Differential inhibition of host protein synthesis in L cells infected with RNA - temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):550–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.550-558.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. J., Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. The plus-strand leader RNA of VSV inhibits DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus and SV40 genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Alterations in the protein synthetic apparatus of Friend erythroleukemia cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus or herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):422–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.422-426.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickwood D., Birnie G. D. Metrizamide, a new density-gradient medium. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):102–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80467-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Steitz J. A. Precursor molecules of both human 5S ribosomal RNA and transfer RNAs are bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Iverson L. Nucleotide sequences from the 3'-ends of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA's as determined from cloned DNA. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):404–411. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.404-411.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Keene J. D., Lazzarini R. A., Emerson S. U. The complete sequence of a unique RNA species synthesized by a DI particle of VSV. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Nakanishi Y., Mizuno D., Natori S. Purification and preparation of antibody to RNA polymerase II stimulatory factors from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1582–1588. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., Kops L. E., Minghetti P. P., O'Malley B. W. Transcription factors from oviduct and HeLa cells are similar. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13055–13059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Carroll A. R., Shattuck D. M., Wagner R. R. Use of UV irradiation to identify the genetic information of vesicular stomatitis virus responsible for shutting off cellular RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):746–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.746-753.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Wagner R. R. Inhibition of RNA synthesis in mouse myeloma cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):770–780. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.770-780.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Wagner R. R. Transcription of vesicular stomatitis virus is required to shut off cellular RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):410–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.410-413.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Wagner R. R. Vesicular stomatitis virus infection reduces the number of active DNA-dependent RNA polymerases in myeloma cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5430–5434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F. S., Lucas-Lenard J. M. Inhibition of ribonucleic acid accumulation in mouse L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus requires viral ribonucleic acid transcription. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):804–810. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]