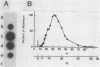
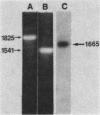
Abstract
We have determined the sequence of cloned cDNAs derived from a 1,665-nucleotide mRNA which transiently accumulates during Xenopus laevis embryogenesis. Computer analysis of the deduced amino acid sequence revealed that this mRNA encodes a 47-kilodalton type I intermediate filament subunit, i.e., a cytokeratin. As is common to all intermediate filament subunits so far examined, the predicted polypeptide, named XK70, contains N- and C-terminal domains flanking a central alpha-helical rod domain. The overall amino acid homology between XK70 and a human 50-kilodalton type I keratin is 47%; homology within the alpha-helical domain is 57%. The N-terminal domain, which is not completely contained in our cDNAs, is basic, contains 42% serine plus alanine, and includes five copies of a six-amino-acid repeating unit. The C-terminal domain has a high alpha-helical content and contains a region with sequence homology to the C-terminal domains of other type I and type III intermediate filament proteins. We suggest that different keratin filament subtypes may have different functional roles during amphibian oogenesis and embryogenesis.
Full text
PDF
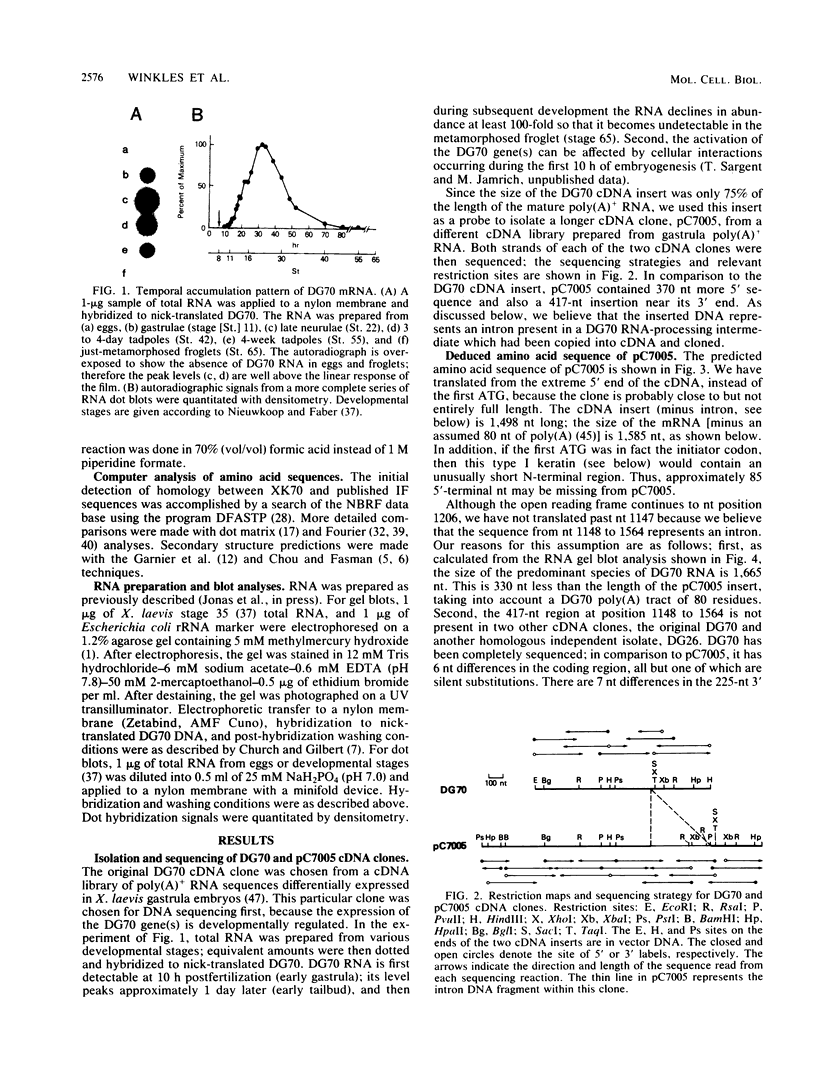





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks-Schlegel S. P. Keratin alterations during embryonic epidermal differentiation: a presage of adult epidermal maturation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):551–559. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz J. K., Gall L., Williams M. A., Picheral B., Franke W. W. Intermediate-size filaments in a germ cell: Expression of cytokeratins in oocytes and eggs of the frog Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6254–6258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Proteinchemical characterization of three structurally distinct domains along the protofilament unit of desmin 10 nm filaments. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Comparison of the proteins of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filaments by amino acid sequence analysis: desmin and vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4120–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs A. J., McIntyre G. A. The diagram, a method for comparing sequences. Its use with amino acid and nucleotide sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godsave S. F., Wylie C. C., Lane E. B., Anderton B. H. Intermediate filaments in the Xenopus oocyte: the appearance and distribution of cytokeratin-containing filaments. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1984 Oct;83:157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a Type II cytoskeletal keratin reveals constant and variable structural domains among keratins. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a human epidermal keratin: divergence of sequence but conservation of structure among intermediate filament proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W., Franz J. K. Amino acid sequence of the carboxy-terminal part of an acidic type I cytokeratin of molecular weight 51 000 from Xenopus laevis epidermis as predicted from the cDNA sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1301–1306. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. D., Idler W. W., Zhou X. M., Roop D. R., Steinert P. M. Structure of a gene for the human epidermal 67-kDa keratin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1896–1900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorcano J. L., Magin T. M., Franke W. W. Cell type-specific expression of bovine keratin genes as demonstrated by the use of complementary DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 15;176(1):21–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90380-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorcano J. L., Rieger M., Franz J. K., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Franke W. W. Identification of two types of keratin polypeptides within the acidic cytokeratin subfamily I. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 25;179(2):257–281. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Rheinwald J. G., Fuchs E. V. Tissue specificity of epithelial keratins: differential expression of mRNAs from two multigene families. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):495–502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments: a chemically heterogeneous, developmentally regulated class of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:219–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Balcarek J. M., Krek V., Shelanski M., Cowan N. J. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein: structural conservation of intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2743–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., McCrohon S., Fuchs E. Complete sequence of a gene encoding a human type I keratin: sequences homologous to enhancer elements in the regulatory region of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., McCrohon S., Fuchs E. Remarkable conservation of structure among intermediate filament genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):491–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M. The 14-fold periodicity in alpha-tropomyosin and the interaction with actin. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 15;103(2):271–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Moll I., Wiest W. Changes in the pattern of cytokeratin polypeptides in epidermis and hair follicles during skin development in human fetuses. Differentiation. 1982;23(2):170–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Traub P. Proteolysis of vimentin and desmin by the Ca2+-activated proteinase specific for these intermediate filament proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1146–1156. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A. Analysis of the primary sequence of alpha-tropomyosin from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):519–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Crewther W. G., Fraser R. D., MacRae T. P. Structure of alpha-keratin: structural implication of the amino acid sequences of the type I and type II chain segments. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 25;113(2):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax-Jeuken Y. E., Quax W. J., Bloemendal H. Primary and secondary structure of hamster vimentin predicted from the nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3548–3552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., van den Heuvel R., Egberts W. V., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. Intermediate filament cDNAs from BHK-21 cells: demonstration of distinct genes for desmin and vimentin in all vertebrate classes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5970–5974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Shiokawa K., Yamana K. A study on the steady-state population of poly(A)+RNA during early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1980 Jun 15;77(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90486-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus laevis 18S ribosomal RNA inferred from gene sequence. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):205–208. doi: 10.1038/291205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Dawid I. B. Differential gene expression in the gastrula of Xenopus laevis. Science. 1983 Oct 14;222(4620):135–139. doi: 10.1126/science.6688681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M. Regional biosynthetic markers in the early amphibian embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1984 Apr;80:289–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Parry D. A., Racoosin E. L., Idler W. W., Steven A. C., Trus B. L., Roop D. R. The complete cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of a type II mouse epidermal keratin of 60,000 Da: analysis of sequence differences between type I and type II keratins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5709–5713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rice R. H., Roop D. R., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Complete amino acid sequence of a mouse epidermal keratin subunit and implications for the structure of intermediate filaments. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):794–800. doi: 10.1038/302794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M. Structure of the three-chain unit of the bovine epidermal keratin filament. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 25;123(1):49–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]