Abstract
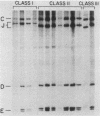
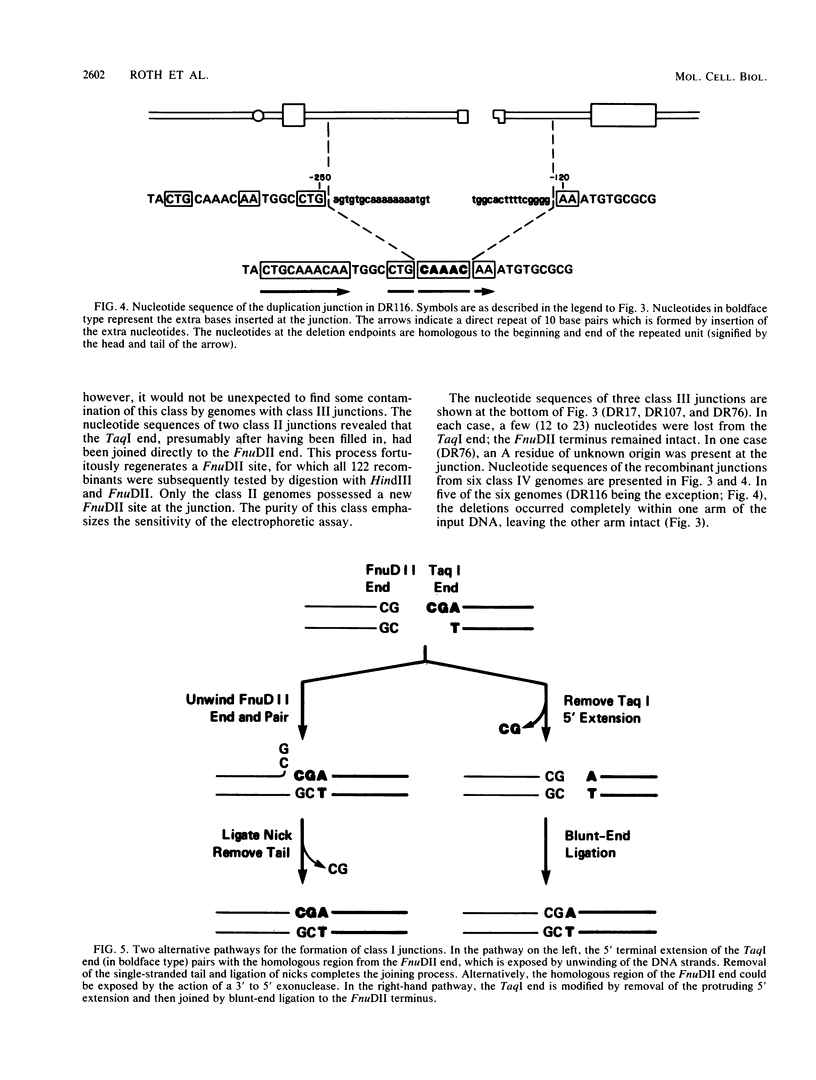
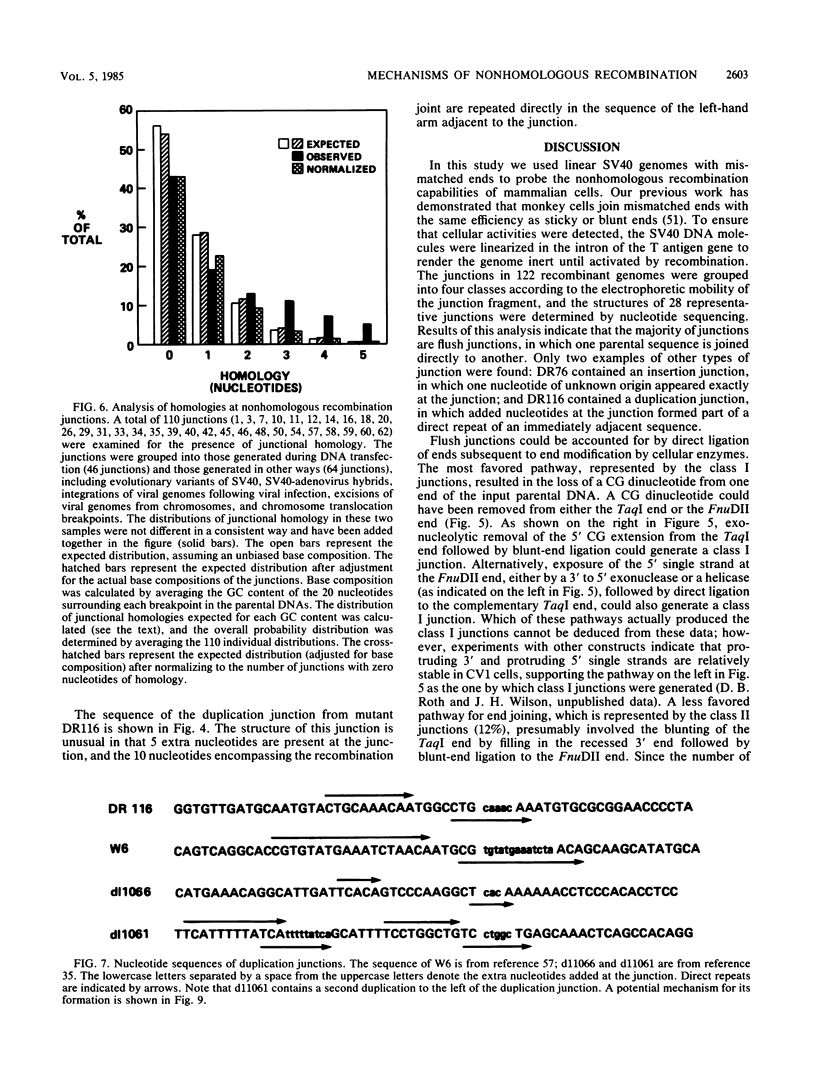
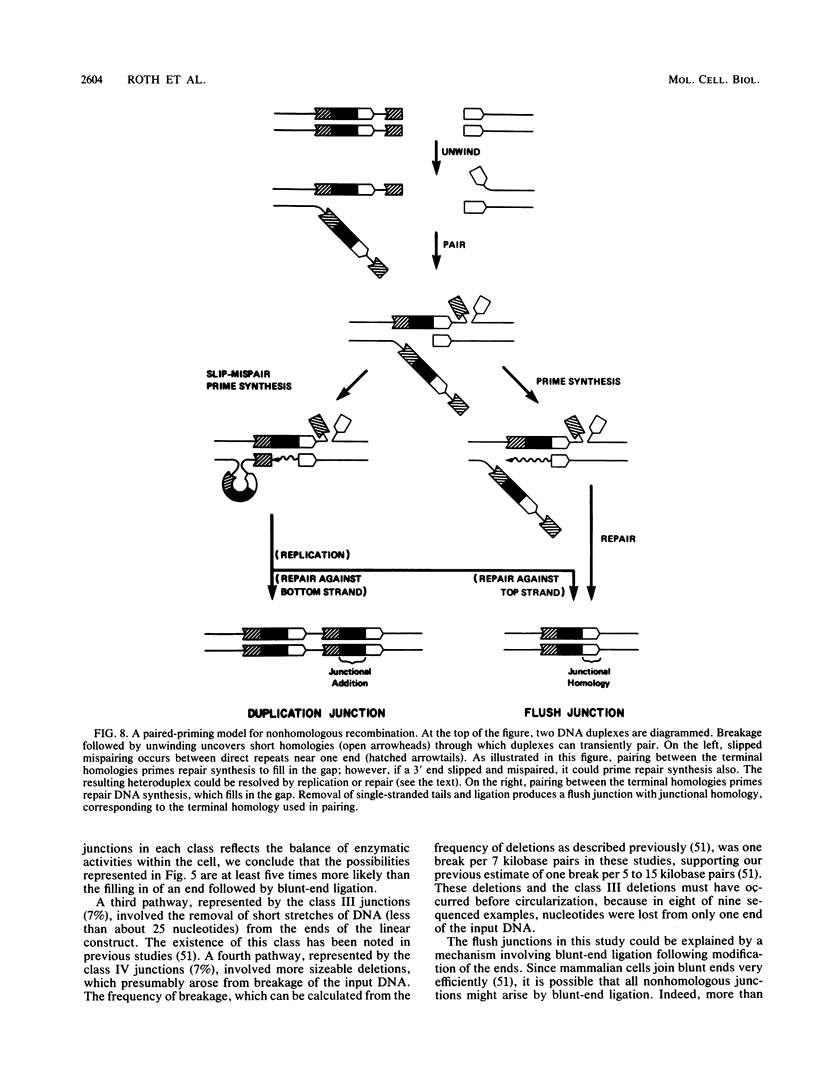
The primary mechanism of nonhomologous recombination in transfected DNA involves breakage followed by end joining. To probe the joining step in more detail, linear simian virus 40 genomes with mismatched ends were transfected into cultured monkey cells, and individual viable recombinants were analyzed. The transfected genomes carried mismatched ends as a result of cleavage with two restriction enzymes, the recognition sites of which are located in the intron of the gene encoding the T antigen. Because the T antigen gene was split by this cleavage, the transfected genomes were inert until activated by cell-mediated end joining. Clonal descendants of the original recombinants were isolated from 122 plaques and were grouped into four classes based on the electrophoretic mobility of the junction fragment. The structures of representative junctions were determined by nucleotide sequencing. The spectrum of nonhomologous junctions analyzed here along with a large number of previously reported junctions suggest that there are two mechanisms for the linkage of DNA molecules: (i) direct ligation of ends and (ii) repair synthesis primed by terminal homologies of a few nucleotides. A paired-priming model of nonhomologous recombination is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Mitchell J., Bernard O., Cory S. Transcriptionally active DNA region that rearranges frequently in murine lymphoid tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6966–6970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Baltimore D. Joining of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene segments: implications from a chromosome with evidence of three D-JH fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4118–4122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Kato S., Camerini-Otero R. D. A pattern of partially homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):206–210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashman C. R., Davidson R. L. High spontaneous mutation frequency in shuttle vector sequences recovered from mammalian cellular DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2266–2272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austerberry C. F., Allis C. D., Yao M. C. Specific DNA rearrangements in synchronously developing nuclei of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7383–7387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L. B., Mount S. M., Weiner A. M. Pseudogenes for human small nuclear RNA U3 appear to arise by integration of self-primed reverse transcripts of the RNA into new chromosomal sites. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P., Forrester W., Botchan M. DNA sequence studies of simian virus 40 chromosomal excision and integration in rat cells. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):55–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90365-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Lebkowski J. S., Botchan M. R. High mutation frequency in DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio S. V., Yancopoulos G. D., Paskind M., Thomas E., Boss M. A., Landau N., Alt F. W., Baltimore D. Insertion of N regions into heavy-chain genes is correlated with expression of terminal deoxytransferase in B cells. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):752–755. doi: 10.1038/311752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Cold-sensitive regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):129–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W., Gahlmann R., Stabel S., Deuring R., Lichtenberg U., Schulz M., Eick D., Leisten R. On the mechanism of recombination between adenoviral and cellular DNAs: the structure of junction sites. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;109:193–228. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69460-8_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick W., Rabbitts T. H., Milstein C. An immunoglobulin deletion mutant with implications for the heavy-chain switch and RNA splicing. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):669–675. doi: 10.1038/286669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K., Thomas K., Capecchi M. R. Analysis of homologous recombination in cultured mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:123–138. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerondakis S., Cory S., Adams J. M. Translocation of the myc cellular oncogene to the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in murine plasmacytomas is an imprecise reciprocal exchange. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutai M. W., Nathans D. Evolutionary variants of simian virus 40: Cellular DNA sequences and sequences at recombinant joints of substituted variants. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90363-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Cohen D. I., Nielsen E. A., Davis M. M. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding T cell-specific membrane-associated proteins. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):149–153. doi: 10.1038/308149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan A., Faust E. A. Short direct repeats mediate spontaneous high-frequency deletions in DNA of minute virus of mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2239–2242. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T. Immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:499–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Hayward S. D. Organization of the Epstein-Barr virus DNA molecule. III. Location of the P3HR-1 deletion junction and characterization of the NotI repeat units that form part of the template for an abundant 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced mRNA transcript. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):135–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.135-148.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Barkan A., Mertz J. E. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the recombinant joints in 16 naturally arising deletion mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1982 Dec;123(2):464–469. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Jahn C. L., Prescott D. M. Internal sequences are eliminated from genes during macronuclear development in the ciliated protozoan Oxytricha nova. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1045–1055. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopchick J. J., Stacey D. W. Differences in intracellular DNA ligation after microinjection and transfection. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):240–246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., DuBridge R. B., Antell E. A., Greisen K. S., Calos M. P. Transfected DNA is mutated in monkey, mouse, and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1951–1960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Recombination in mouse L cells between DNA introduced into cells and homologous chromosomal sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1391–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling L. E., Manos M. M., Gluzman Y. Sequence of the junction in adenovirus 2-SV40 hybrids: examples of illegitimate recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8099–8112. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Clayton C. E., Murphy D., Rigby P. W., Smith A. E., Chaudry F. Structure and synthesis of a simian virus 40 super T-antigen. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):963–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.963-973.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Minard K., Mjolsness S., Kronenberg M., Goverman J., Hunkapiller T., Prystowsky M. B., Yoshikai Y., Fitch F., Mak T. W. Mouse T cell antigen receptor: structure and organization of constant and joining gene segments encoding the beta polypeptide. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Oda K. Two types of deletion within integrated viral sequences mediate reversion of simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):479–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.479-489.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Structure of simian virus 40 recombinants that contain both host and viral DNA sequences. II. The structure of variant 1103 and its comparison to variant CVPS/1P2 (EcoRI res). J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3592–3597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. K., Temin H. M. High-efficiency ligation and recombination of DNA fragments by vertebrate cells. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):606–609. doi: 10.1126/science.6301012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Calabi F. Reciprocal chromosome translocation between c-myc and immunoglobulin gamma 2b genes. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):240–243. doi: 10.1038/305240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup D. J., Ink B. S., Parsons B. L., Hu W., Joklik W. K. Spontaneous deletions and duplications of sequences in the genome of cowpox virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6817–6821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razzaque A., Chakrabarti S., Joffee S., Seidman M. Mutagenesis of a shuttle vector plasmid in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razzaque A., Mizusawa H., Seidman M. M. Rearrangement and mutagenesis of a shuttle vector plasmid after passage in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Relative rates of homologous and nonhomologous recombination in transfected DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3355–3359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E., Fried M. Clustered illegitimate recombination events in mammalian cells involving very short sequence homologies. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):181–184. doi: 10.1038/304181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. A rapid enzymatic DNA sequencing technique: determination of sequence alterations in early simian virus 40 temperature sensitive and deletion mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2225–2240. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheflin L., Celeste A., Woodworth-Gutai M. Recombination in simian virus 40-infected cells. Structure of naturally arising variants ev-2114, ev-2102, and ev-1110. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14315–14321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Koralewski M. A., Song K. Y., Kucherlapati R. S. Homologous recombination with DNA introduced into mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:161–170. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R. DNA sequence homology and chromosomal deletion at a site of SV40 DNA integration. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):363–366. doi: 10.1038/296363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Berg P. Homologous and nonhomologous recombination in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1040–1052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swimmer C., Shenk T. A viable simian virus 40 variant that carries a newly generated sequence reiteration in place of the normal duplicated enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6652–6656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylla B. S., Huberdeau D., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D., Bourgaux P. Site-specific excision of integrated polyoma DNA. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):661–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90398-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamiya T., McCutchan T., Rosenberg M., Singer M. Structure of simian virus 40 recombinants that contain both host and viral DNA sequences. I. The structure of variant CVPS/1/P2 (EcoRI res). J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3584–3591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Gudewicz T., Porter T., White A., Wilson J. H. How damaged is the biologically active subpopulation of transfected DNA? Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):387–398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Vernaleone F., Wilson J. H. Topological requirements for homologous recombination among DNA molecules transfected into mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2080–2089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal H. Genomic arrangement of an adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrid virus, Ad2+ND4del. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):526–532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.526-532.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Berget P. B., Pipas J. M. Somatic cells efficiently join unrelated DNA segments end-to-end. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H. Genetic analysis of host range mutant viruses suggests an uncoating defect in simian virus 40-resistant monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3503–3507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H. Interference in SV40 DNA infections: a possible basis for cellular competence. Virology. 1978 Dec;91(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth-Gutai M. Recombination in SV40-infected cells: nucleotide sequences at viral-viral recombinant joints in naturally arising variants. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth-Gutai M. Recombination in SV40-infected cells: viral DNA sequences at sites of circularization of transfecting linear DNA. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi Y., Yoshikai Y., Leggett K., Clark S. P., Aleksander I., Mak T. W. A human T cell-specific cDNA clone encodes a protein having extensive homology to immunoglobulin chains. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):145–149. doi: 10.1038/308145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain B. S., Roberts R. J. Characterization and sequence analysis of a recombination site in the hybrid virus Ad2+ND. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):13–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]