Abstract
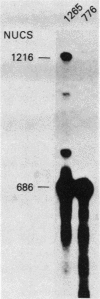
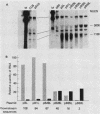
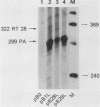
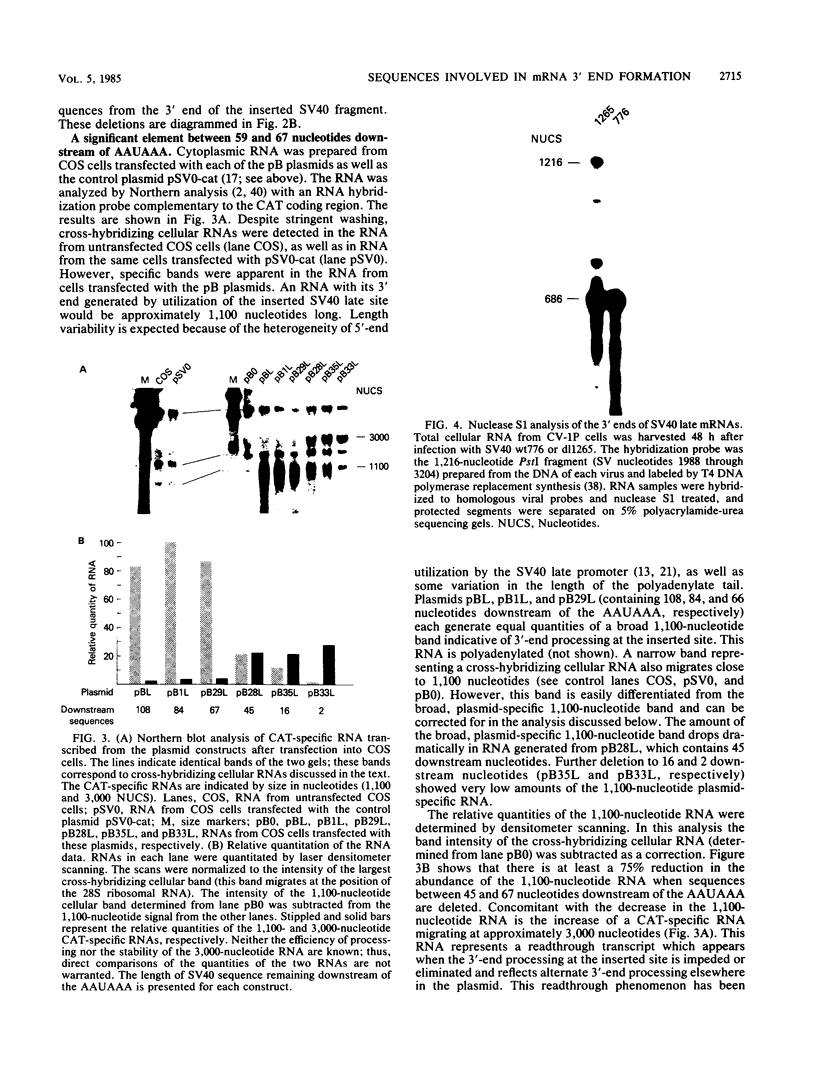
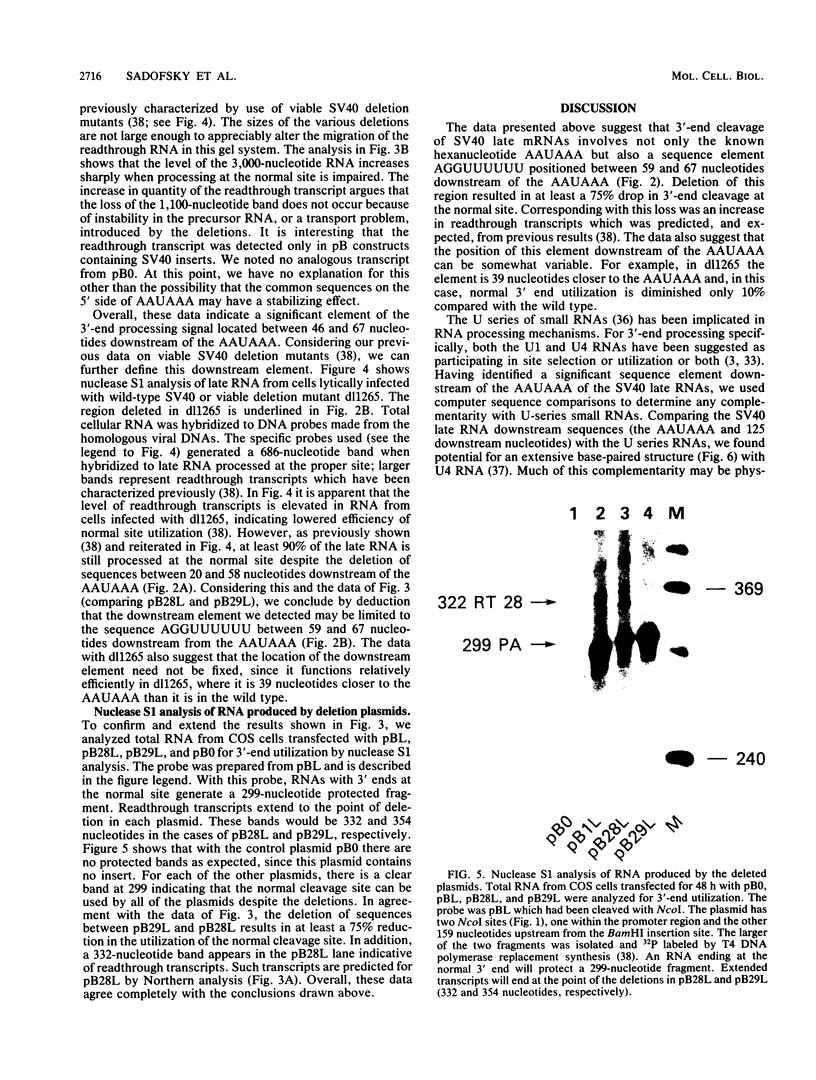
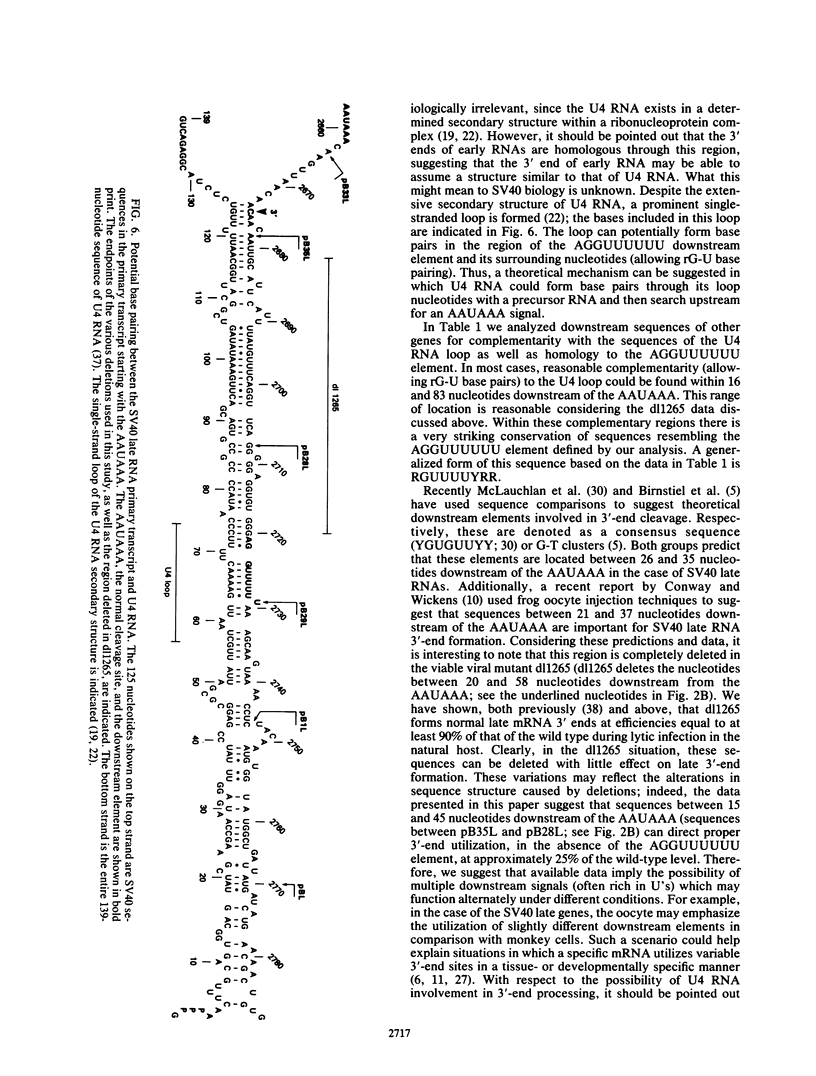
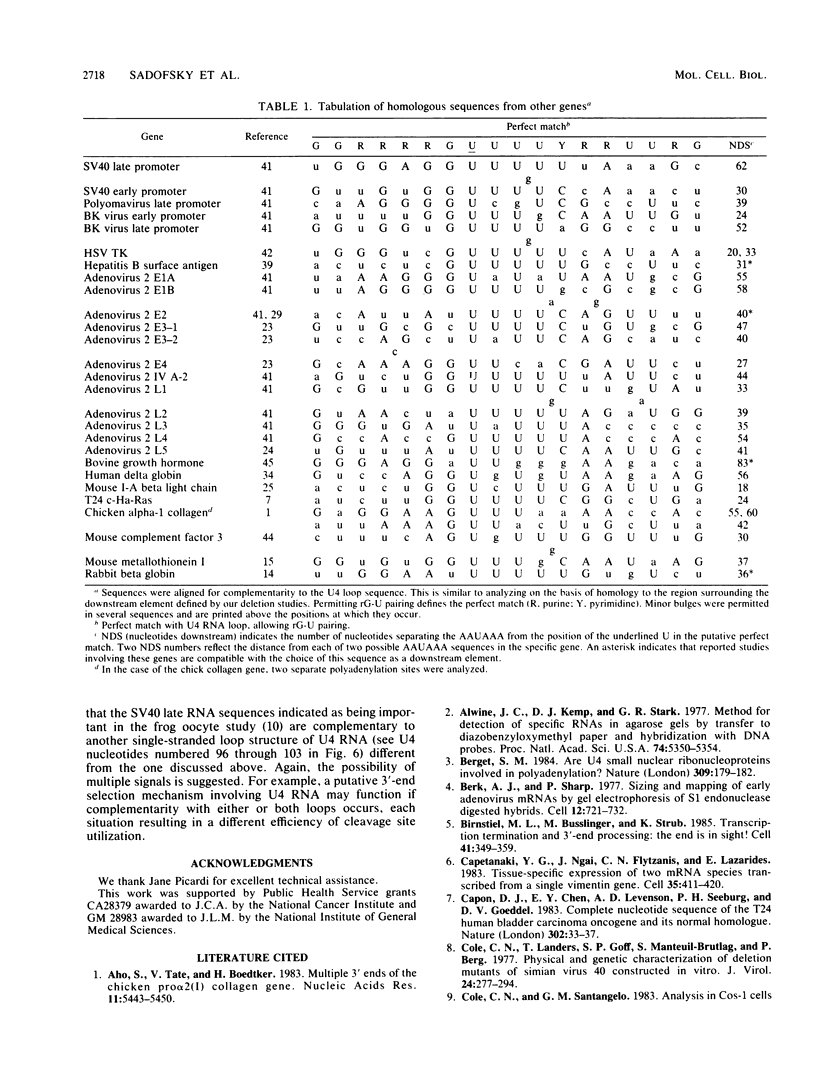
Our previous studies of the 3'-end processing of simian virus 40 late mRNAs indicated the existence of an essential element (or elements) downstream of the AAUAAA signal. We report here the use of transient expression analysis to study a functional element which we located within the sequence AGGUUUUUU, beginning 59 nucleotides downstream of the recognized signal AAUAAA. Deletion of this element resulted in (i) at least a 75% drop in 3'-end processing at the normal site and (ii) appearance of readthrough transcripts with alternate 3' ends. Some flexibility in the downstream position of this element relative to the AAUAAA was noted by deletion analysis. Using computer sequence comparison, we located homologous regions within downstream sequences of other genes, suggesting a generalized sequence element. In addition, specific complementarity is noted between the downstream element and U4 RNA. The possibility that this complementarity could participate in 3'-end site selection is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho S., Tate V., Boedtker H. Multiple 3' ends of the chicken pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5443–5450. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capetanaki Y. G., Ngai J., Flytzanis C. N., Lazarides E. Tissue-specific expression of two mRNA species transcribed from a single vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Landers T., Goff S. P., Manteuil-Brutlag S., Berg P. Physical and genetic characterization of deletion mutants of simian virus 40 constructed in vitro. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):277–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.277-294.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Santangelo G. M. Analysis in Cos-1 cells of processing and polyadenylation signals by using derivatives of the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):267–279. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L., Wickens M. A sequence downstream of A-A-U-A-A-A is required for formation of simian virus 40 late mRNA 3' termini in frog oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3949–3953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Structure of mouse metallothionein-I gene and its mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):267–269. doi: 10.1038/292267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. U4 and U6 RNAs coexist in a single small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3283–3293. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Lamb J., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Proudfoot N. J. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a polyadenylation signal mutation. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):398–400. doi: 10.1038/306398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Branlant C., Lazar E., Gallinaro H., Jacob M. Primary and secondary structures of chicken, rat and man nuclear U4 RNAs. Homologies with U1 and U5 RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2699–2716. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Moullec J. M., Akusjärvi G., Stålhandske P., Pettersson U., Chambraud B., Gilardi P., Nasri M., Perricaudet M. Polyadenylic acid addition sites in the adenovirus type 2 major late transcription unit. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):127–134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.127-134.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Hunkapiller T., Hood L. Nucleotide sequence of a light chain gene of the mouse I-A subregion: A beta d. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):750–754. doi: 10.1126/science.6410508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Inhibition of RNA cleavage but not polyadenylation by a point mutation in mRNA 3' consensus sequence AAUAAA. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):600–605. doi: 10.1038/305600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Site-specific polyadenylation in a cell-free reaction. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Schwartz E., Ballantine M., Surrey S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the delta beta-globin gene region in humans. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11599–11609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Busch H. Small nuclear RNAs and RNA processing. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;30:127–162. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60685-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Busch H. The primary nucleotide sequence of U4 RNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3532–3538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Alwine J. C. Sequences on the 3' side of hexanucleotide AAUAAA affect efficiency of cleavage at the polyadenylation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Analysis of processing and polyadenylation signals of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene by using simian virus 40-hepatitis B virus chimeric plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2250–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Sharp J. A., Summers W. C. Nucleotide sequence of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebauer K., Domdey H., Diggelmann H., Fey G. Isolation and analysis of genomic DNA clones encoding the third component of mouse complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7077–7081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Lyons R. H., Post L., Rottman F. M. Requirement for the 3' flanking region of the bovine growth hormone gene for accurate polyadenylylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3944–3948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]