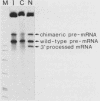
Abstract
We isolated a chromosomal protein fraction derived from chromatin of sea urchin embryos which specifically stimulated the expression of the histone H2B gene by a factor of 5- to 10-fold when the complete sea urchin histone gene repeat h22 was injected in Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei. Gene manipulation experiments revealed the existence of two different target sites in the H2B gene which appear to mediate the response to injection of the stimulatory sea urchin chromatin-associated proteins; both are located downstream of the transcription initiation site. The first sequence element which is shown to be implicated is within, or at least includes, the H2B 5' untranslated leader sequence between nucleotides 11 and 76. The second element resides within an H2B DNA segment located near the 3' end of the gene, extending from 90 base pairs upstream of the mRNA 3' terminus to 140 base pairs in the spacer sequences downstream.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Folk W., Birnstiel M. L. The terminal RNA stem-loop structure and 80 bp of spacer DNA are required for the formation of 3' termini of sea urchin H2A mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Generation of authentic 3' termini of an H2A mRNA in vivo is dependent on a short inverted DNA repeat and on spacer sequences. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Bucher P., Strub K., Birnstiel M. L. Transcription of a cloned Xenopus laevis H4 histone gene in the homologous frog oocyte system depends on an evolutionary conserved sequence motif in the -50 region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8641–8657. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Biochemical complementation with RNA in the Xenopus oocyte: a small RNA is required for the generation of 3' histone mRNA termini. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):823–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O., Birnstiel M. L. The conserved CAAGAAAGA spacer sequence is an essential element for the formation of 3' termini of the sea urchin H3 histone mRNA by RNA processing. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):481–489. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O., Mous J., Birnstiel M. L. Processing and nucleo-cytoplasmic transport of histone gene transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8539–8551. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K., Probst E., Schaffner W., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of Psammechinus miliaris: I. Fractionation and identification of five individual histone mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):455–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of far upstream sequences required for maximal in vitro transcription of an H2A histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Probst E., Birnstiel M. L. Transcriptional fidelity of histone genes injected into Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):100–102. doi: 10.1038/288100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration and clustering of DNA sequences complementary to histone messenger RNA. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 7;230(14):165–169. doi: 10.1038/newbio230165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. D., Marks A. R., Buckley D. I., Kapler G., Payvar F., Goodman H. M. The first intron of the human growth hormone gene contains a binding site for glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):699–702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newrock K. M., Cohen L. H., Hendricks M. B., Donnelly R. J., Weinberg E. S. Stage-specific mRNAs coding for subtypes of H2A and H2B histones in the sea urchin embryo. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst E., Kressmann A., Birnstiel M. L. Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):709–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelsberg T. C., Hnilica L. S. Deoxyribonucleoproteins and the tissue-specific restriction of the deoxyribonucleic acid in chromatin. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):435–437. doi: 10.1042/bj1200435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Galli G., Busslinger M., Birnstiel M. L. The cDNA sequences of the sea urchin U7 small nuclear RNA suggest specific contacts between histone mRNA precursor and U7 RNA during RNA processing. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2801–2807. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Bioassay for components regulating eukaryotic gene expression: a chromosomal factor involved in the generation of histone mRNA 3' termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6201–6204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Rosenthal A., Flavell R., Grosveld F. DNA sequences required for regulated expression of beta-globin genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90548-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]