Abstract
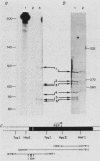
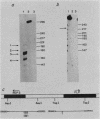
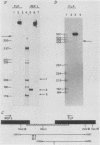
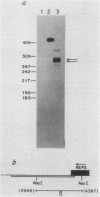
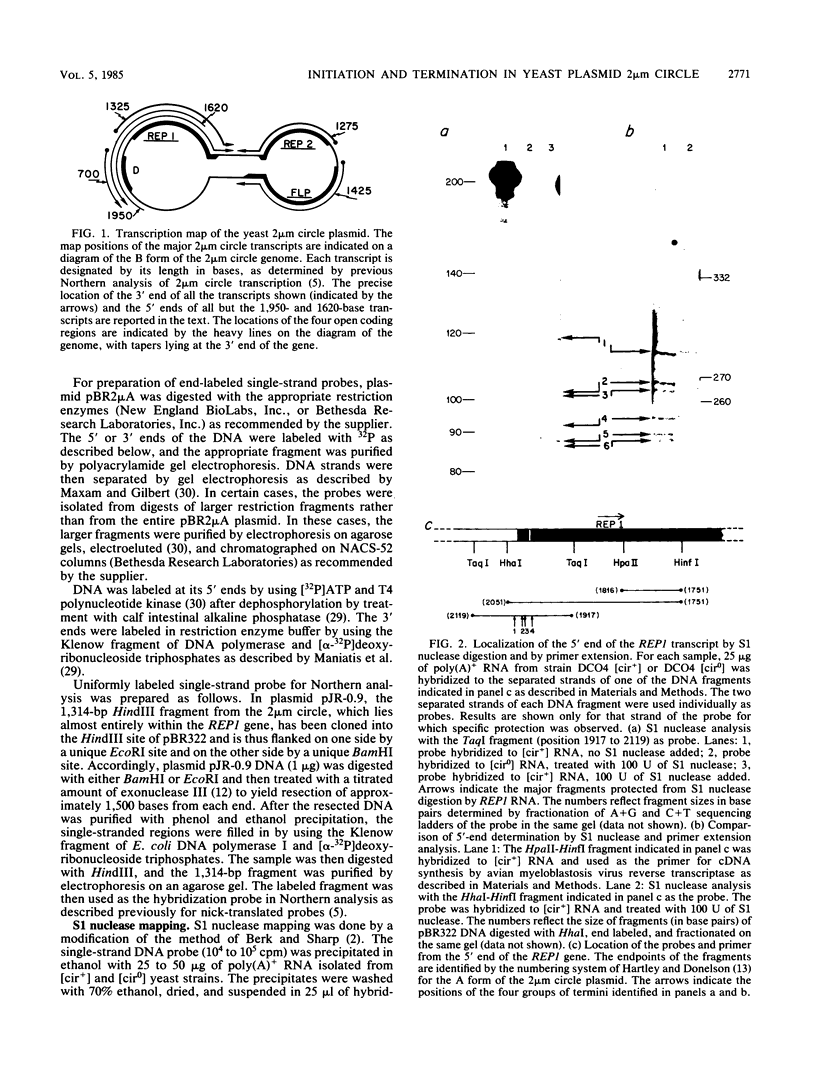
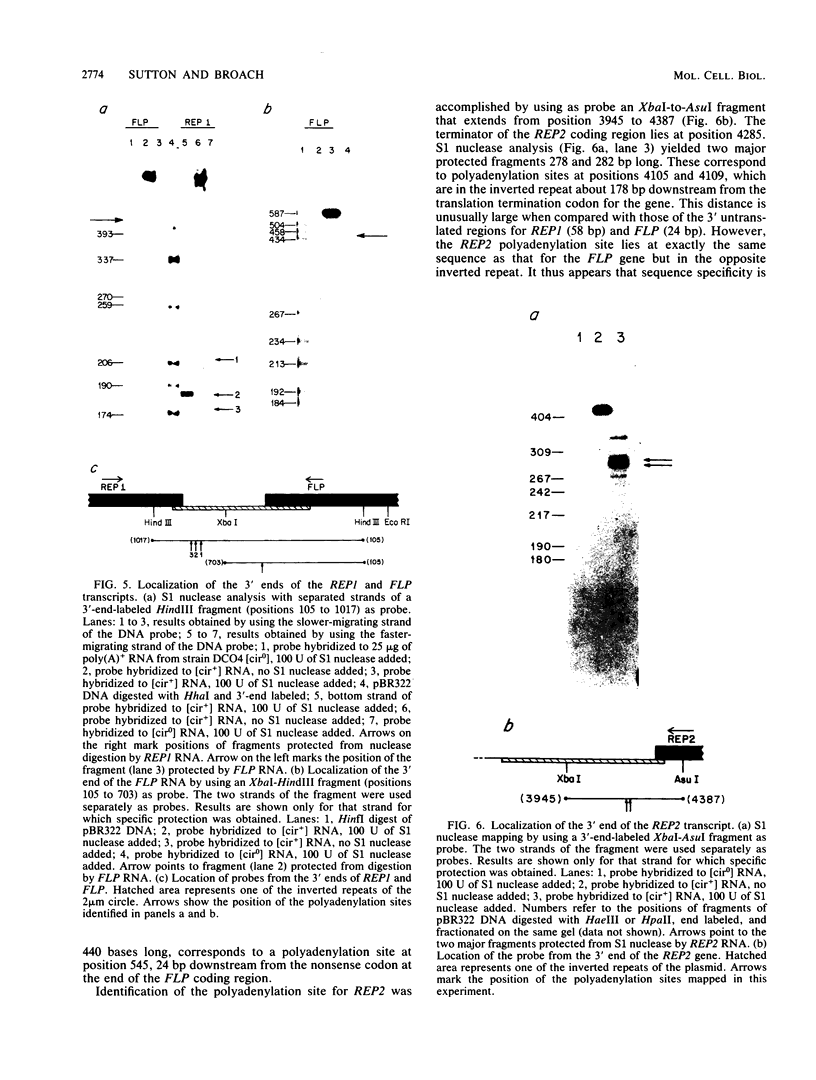
By S1 nuclease protection experiments and primer extension analysis, we determined precisely the cap and polyadenylation sites of transcripts from the four genes of the yeast 2 micron circle plasmid, as well as those of other plasmid transcripts of unknown function. In addition, we used deletion analysis to identify sequences necessary for polyadenylation in plasmid transcripts. Our results indicate that plasmid genes constitute independent transcription units and that plasmid mRNAs are not derived by extensive processing of precursor transcripts. In addition, we found that the D coding region of 2 micron circle is precisely encompassed by a polyadenylated transcript, suggesting that this coding region constitutes a functional plasmid gene. Our identification of the position of plasmid polyadenylation sites and of sequences necessary for polyadenylation provides support for a tripartite signal for polyadenylation as proposed by Zaret and Sherman (K.S. Zaret and F. Sherman, Cell 28:563-573, 1982). Finally, these data highlight salient features of the transcriptional regulatory circuitry that underlies the control of plasmid maintenance in the cell.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Atkins J. F., McGill C., Chow L. Identification and mapping of the transcriptional and translational products of the yeast plasmid, 2mu circle. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):827–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Hicks J. B. Replication and recombination functions associated with the yeast plasmid, 2 mu circle. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90487-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Leung D. W., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Smith M. Deletion mapping of sequences essential for in vivo transcription of the iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futcher A. B., Cox B. S. Copy number and the stability of 2-micron circle-based artificial plasmids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):283–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.283-290.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Rich A. A UGA termination suppression tRNATrp active in rabbit reticulocytes. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):41–46. doi: 10.1038/283041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Wu R. Exonuclease III: use for DNA sequence analysis and in specific deletions of nucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:60–96. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. L., Donelson J. E. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast plasmid. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):860–865. doi: 10.1038/286860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D., Diamond A., Dudock B. Opal suppressor serine tRNAs from bovine liver form phosphoseryl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6215–6219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Cohen E. H. Sequences responsible for transcription termination on a gene segment in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1515–1520. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Kelly J. D., Cohen E. H. Transcription terminates in yeast distal to a control sequence. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer E., Darnell J. E., Jr The primary transcription unit of the mouse beta-major globin gene. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S., Mellstrom K., Kosik E., Tamanoi F., Brugge J. Mutation of a termination codon affects src initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1738–1746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaram M., Li Y. Y., Broach J. R. The yeast plasmid 2mu circle encodes components required for its high copy propagation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y. Yeast plasmid requires a cis-acting locus and two plasmid proteins for its stable maintenance. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Evaluation of the "scanning model" for initiation of protein synthesis in eucaryotes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Mechanism of mRNA recognition by eukaryotic ribosomes during initiation of protein synthesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:81–123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Selection of initiation sites by eucaryotic ribosomes: effect of inserting AUG triplets upstream from the coding sequence for preproinsulin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3873–3893. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Translation of insulin-related polypeptides from messenger RNAs with tandemly reiterated copies of the ribosome binding site. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):971–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90554-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Initiation of translation at internal AUG codons in mammalian cells. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):82–85. doi: 10.1038/309082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Volkert F., Broach J. Components of the site-specific recombination system encoded by the yeast plasmid 2-micron circle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:779–787. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Pedigree analysis of plasmid segregation in yeast. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):961–970. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90553-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Astell C., Smith M. Physical analysis of mating-type loci in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):961–981. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Botstein D. Structure and function of the yeast URA3 gene. Differentially regulated expression of hybrid beta-galactosidase from overlapping coding sequences in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):883–904. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdson D. C., Gaarder M. E., Livingston D. M. Characterization of the transmission during cytoductant formation of the 2 micrometers DNA plasmid from Saccharomyces. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(1):59–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00270139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]