Abstract
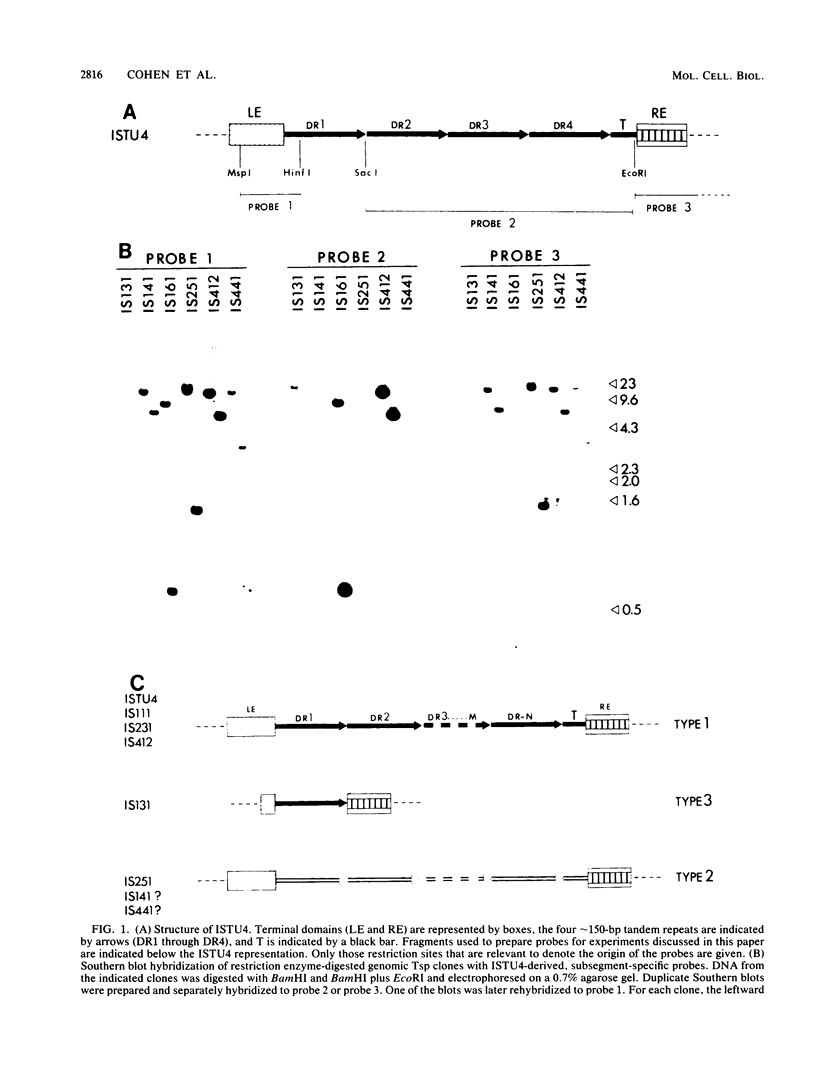
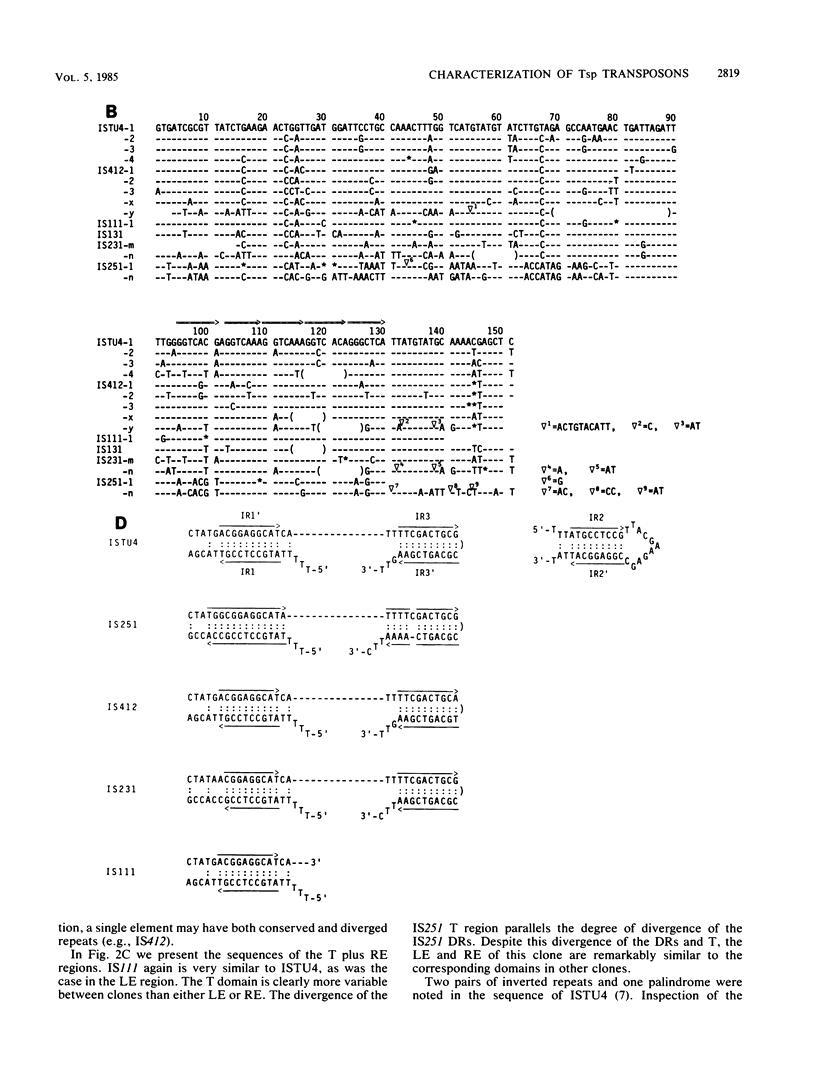
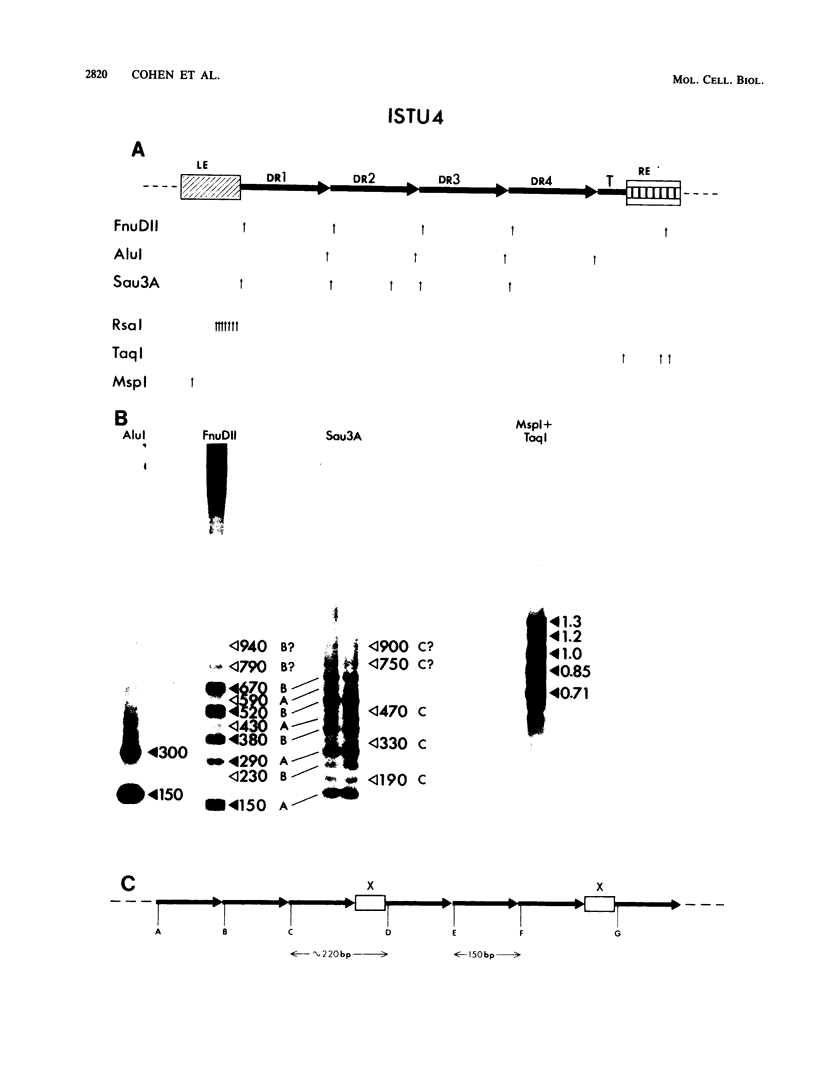
In the preceding paper (J.B. Cohen, B. Hoffman-Liebermann, and L. Kedes, Mol. Cell. Biol., 5:2804-2813, 1985), we described the nucleotide sequence of ISTU4, which is a member of a new family of repetitive sequences, the Tsp family, present in a higher eucaryote, the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. We provided evidence that individual members of this family can act as transposable elements. Here we describe our structural analysis of the Tsp element family, which numbers about 1,000 members per haploid genome. Hybridization and nucleotide sequence analysis of several genomic Tsp clones demonstrate that structurally most Tsp elements resemble ISTU4. Tsp elements range in size up to about 1.3 kilobase pairs, have terminal domains that are conserved between the various examples studied, and contain a central portion of varying size, which may be extensively diverged. Structurally, however, the central portions are very similar and consist of several approximately 150-base-pairs-long, tandemly arranged, imperfect repeats, which are followed by a truncated repeat. The structural analysis is consistent with the possibility that the individual Tsp elements differ by multiples of these 150-base-pair repeats. One variant genomic clone has a solitary repeat and lacks the truncated repeat. The nucleotide sequences of different repeats of a single Tsp element can diverge extensively. The truncated repeat is divergent from most of the repeats, but in one case it is almost identical to a repeat of the same element. Comparison of the sequences from different elements enabled us to determine the boundaries of each structural domain and allows us to propose that each of these domains may be independent units of genetic information. Analysis of the population of Tsp-related sequences in the S. purpuratus genome by genomic blot hybridization suggests that most Tsp family members share the same overall structure. In addition, there is a structural element, about 70 base pairs long, that appears to interrupt the tandem arrangement of the 150-base-pair repeats at regular intervals.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Scheller R. H., Posakony J. W., McAllister L. B., Trabert S. G., Beall C., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequences of the sea urchin genome. Distribution of members of specific repetitive families. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):5–28. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Dreazen O., Klar A., Rechavi G., Ram D., Cohen J. B., Givol D. Activation of the c-mos oncogene in a mouse plasmacytoma by insertion of an endogenous intracisternal A-particle genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7118–7122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Garrett J. E., Lam B. S. Isolated clusters of paired tandemly repeated sequences in the Xenopus laevis genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):254–259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Effron K., Rechavi G., Ben-Neriah Y., Zakut R., Givol D. Simple DNA sequences in homologous flanking regions near immunoglobulin VH genes: a role in gene interaction? Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3353–3370. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Kedes L. Structure and unusual characteristics of a new family of transposable elements in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2804–2813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Lee B. K. Association of the lethal yellow (Ay) coat color mutation with an ecotropic murine leukemia virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):247–249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egner C., Berg D. E. Excision of transposon Tn5 is dependent on the inverted repeats but not on the transposase function of Tn5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. RNA from the yeast transposable element Ty1 has both ends in the direct repeats, a structure similar to retrovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Ish-Horowicz D. Extrachromosomal circular copies of the eukaryotic transposable element copia in cultured Drosophila cells. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):591–595. doi: 10.1038/292591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Davis M. A., Roberts D. E., Takeshita K., Kleckner N. Genetic organization of transposon Tn10. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Shulman M. J., Hozumi N. Transposition of two different intracisternal A particle elements into an immunoglobulin kappa-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2565–2572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D., Kedes L. H., Cohen S. N. TU elements: a heterogeneous family of modularly structured eucaryotic transposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):991–1001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzir N., Rechavi G., Cohen J. B., Unger T., Simoni F., Segal S., Cohen D., Givol D. "Retroposon" insertion into the cellular oncogene c-myc in canine transmissible venereal tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1054–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebermann D., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Weinthal J., Childs G., Maxson R., Mauron A., Cohen S. N., Kedes L. An unusual transposon with long terminal inverted repeats in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):342–347. doi: 10.1038/306342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Fulton S. M., Dobson M. J., Wilson W., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. A retrovirus-like strategy for expression of a fusion protein encoded by yeast transposon Ty1. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):243–246. doi: 10.1038/313243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D., Kleckner N. Transposase promotes double strand breaks and single strand joints at Tn10 termini in vivo. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. DNA sequence of a foldback transposable element in Drosophila. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):201–204. doi: 10.1038/297201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba T., Saigo K. Retrovirus-like particles containing RNA homologous to the transposable element copia in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):119–124. doi: 10.1038/302119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Origin of retroviruses from cellular moveable genetic elements. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Jones R. S., Potter S. S. Unusual structure of the FB family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Ortiz S. Retroviruses as mutagens: insertion and excision of a nontransforming provirus alter expression of a resident transforming provirus. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Kleckner N. Essential sites at transposon Tn 10 termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Rotter V. Inactivation of p53 gene expression by an insertion of Moloney murine leukemia virus-like DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1402–1410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]