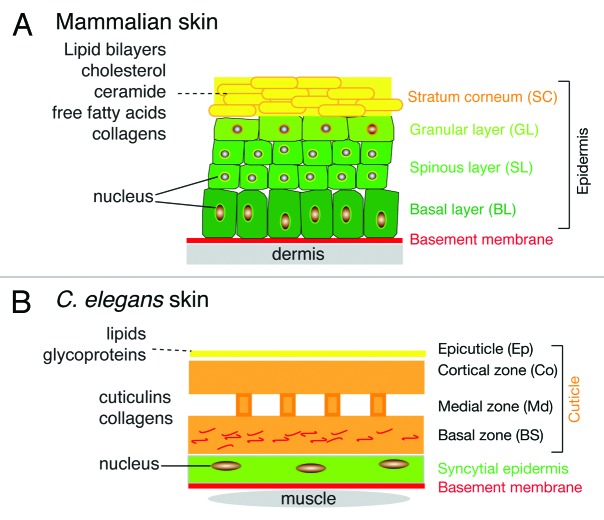
Figure 1. Comparison of mammalian and C. elegans skin layers. (A) Mammalian skin consists of the epidermis and dermis, separated by a basement membrane. The epidermis is composed of several cell layers, including the basal layer (BL) resting on the basement membrane, and the differentiated cell layers of the spinous layer (SL), granular layer (GL) and the stratum corneum (SC). The SC is a lipid-rich layer composed of cholesterol, free fatty acids, ceramides and collagen, which together provide the permeability barrier function of the skin. (B) C. elegans skin consists of the epidermis and cuticle. The epidermis is a simple epithelium whose basal surface rests on a basement membrane. The apical surface of the epidermal epithelium secretes the cuticle, a collagenous extracellular matrix. The cuticle is a flexible barrier layer that is composed predominantly of cross-linked collagens. External to the cuticle is a lipid rich epicuticle that may also function in the permeability barrier.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.