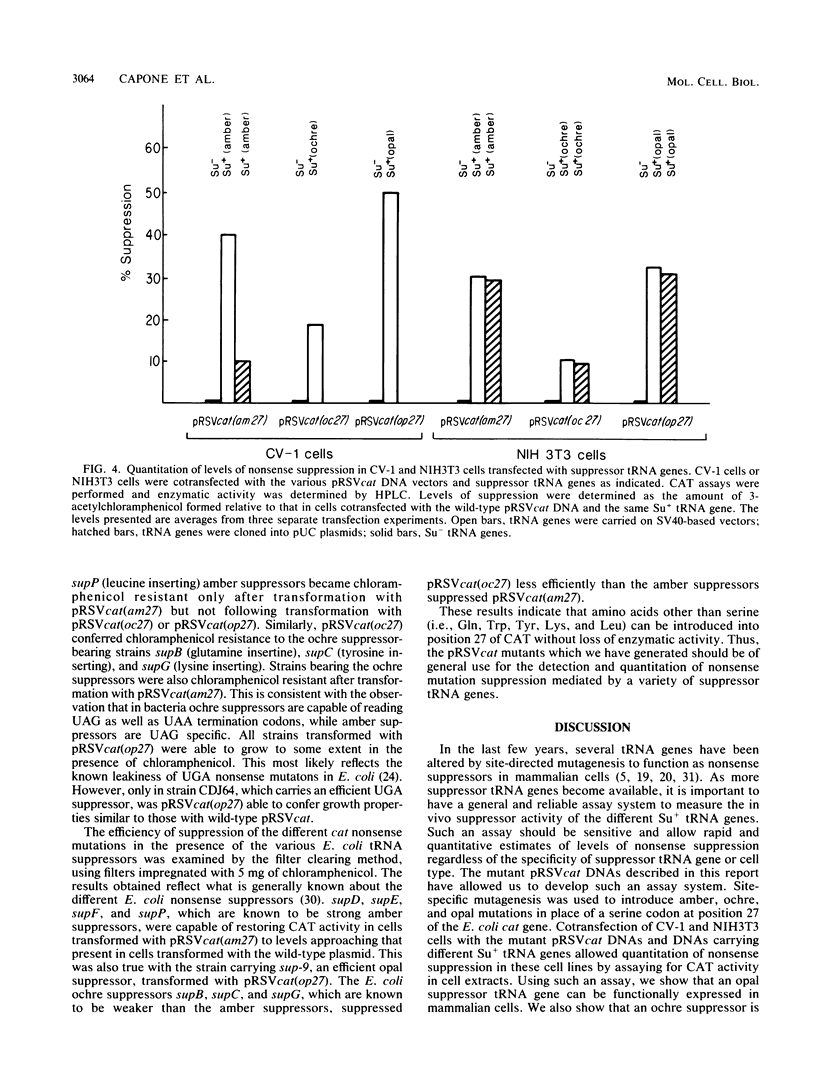
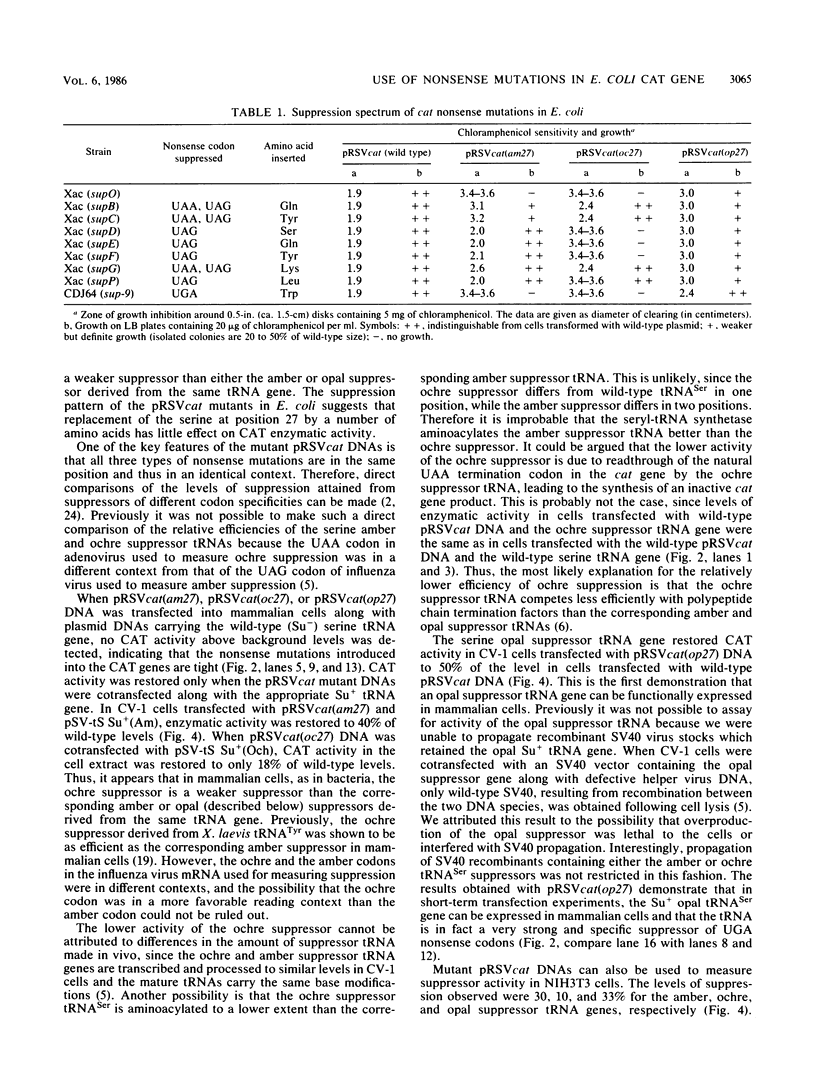
Abstract
We have used oligonucleotide-directed site-specific mutagenesis to convert serine codon 27 of the Escherichia coli chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (cat) gene to UAG, UAA, and UGA nonsense codons. The mutant cat genes, under transcriptional control of the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat, were then introduced into mammalian cells by DNA transfection along with UAG, UAA, and UGA suppressor tRNA genes derived from a human serine tRNA. Assay for CAT enzymatic activity in extracts from such cells allowed us to detect and quantitate nonsense suppression in monkey CV-1 cells and mouse NIH3T3 cells. Using such an assay, we provide the first direct evidence that an opal suppressor tRNA gene is functional in mammalian cells. The pattern of suppression of the three cat nonsense mutations in bacteria suggests that the serine at position 27 of CAT can be replaced by a wide variety of amino acids without loss of enzymatic activity. Thus, these mutant cat genes should be generally useful for the quantitation of suppressor activity of suppressor tRNA genes introduced into cells and possibly for the detection of naturally occurring nonsense suppressors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L. Context effects: translation of UAG codon by suppressor tRNA is affected by the sequence following UAG in the message. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 15;164(1):73–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. F., Mogg A. E. Construction of a vector, pRSVcatamb38, for the rapid and sensitive assay of amber suppression in human and other mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1317–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone J. P., Sharp P. A., RajBhandary U. L. Amber, ochre and opal suppressor tRNA genes derived from a human serine tRNA gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):213–221. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. beta 0 thalassemia, a nonsense mutation in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2886–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond A., Dudock B., Hatfield D. Structure and properties of a bovine liver UGA suppressor serine tRNA with a tryptophan anticodon. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Rich A. A UGA termination suppression tRNATrp active in rabbit reticulocytes. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):41–46. doi: 10.1038/283041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell S. W., Byrne B. J., Subramanian K. N. The simian virus 40 minimal origin and the 72-base-pair repeat are required simultaneously for efficient induction of late gene expression with large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6335–6339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D. L., Dudock B. S., Eden F. C. Characterization and nucleotide sequence of a chicken gene encoding an opal suppressor tRNA and its flanking DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4940–4944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak R. M., Laski F. A., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A., Capecchi M. R. Establishment of mammalian cell lines containing multiple nonsense mutations and functional suppressor tRNA genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo I., Leineweber M., RajBhandary U. L. Site-specific mutagenesis on cloned DNAs: generation of a mutant of Escherichia coli tyrosine suppressor tRNA in which the sequence G-T-T-C corresponding to the universal G-T-pseudouracil-C sequence of tRNAs is changed to G-A-T-C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4753–4757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Belagaje R., Hudziak R. M., Capecchi M. R., Norton G. P., Palese P., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A. Synthesis of an ochre suppressor tRNA gene and expression in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2445–2452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Belagaje R., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A. An amber suppressor tRNA gene derived by site-specific mutagenesis: cloning and function in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5813–5817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Internalization-defective LDL receptors produced by genes with nonsense and frameshift mutations that truncate the cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):735–743. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K. M., Jones S. S., Hackett N. R., Khorana H. G. Specific amino acid substitutions in bacterioopsin: Replacement of a restriction fragment in the structural gene by synthetic DNA fragments containing altered codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Albertini A. M. Effects of surrounding sequence on the suppression of nonsense codons. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 15;164(1):59–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Andersson P., Olshevsky U., Weinberg R., Baltimore D., Gesteland R. Translation of MuLV and MSV RNAs in nuclease-treated reticulocyte extracts: enhancement of the gag-pol polypeptide with yeast suppressor tRNA. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase: enzymology and molecular biology. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;14(1):1–46. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Packman L. C., Burleigh B. D., Dell A., Morris H. R., Hartley B. S. Primary structure of a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase specified by R plasmids. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):870–872. doi: 10.1038/282870a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple G. F., Dozy A. M., Roy K. L., Kan Y. W. Construction of a functional human suppressor tRNA gene: an approach to gene therapy for beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):537–540. doi: 10.1038/296537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaka Y., Katoh I., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S. Murine leukemia virus protease is encoded by the gag-pol gene and is synthesized through suppression of an amber termination codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1618–1622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. F., Capecchi M., Laski F. A., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A., Palese P. Measurement of suppressor transfer RNA activity. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):873–875. doi: 10.1126/science.6308765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]