Abstract
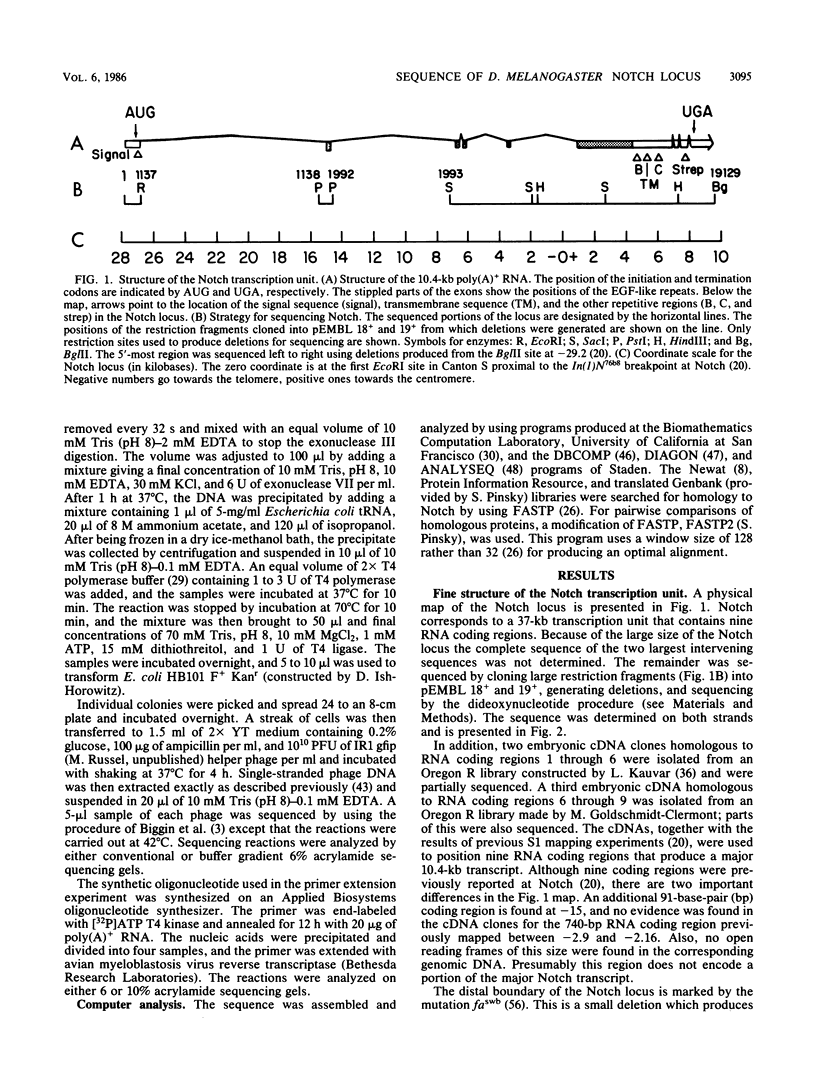
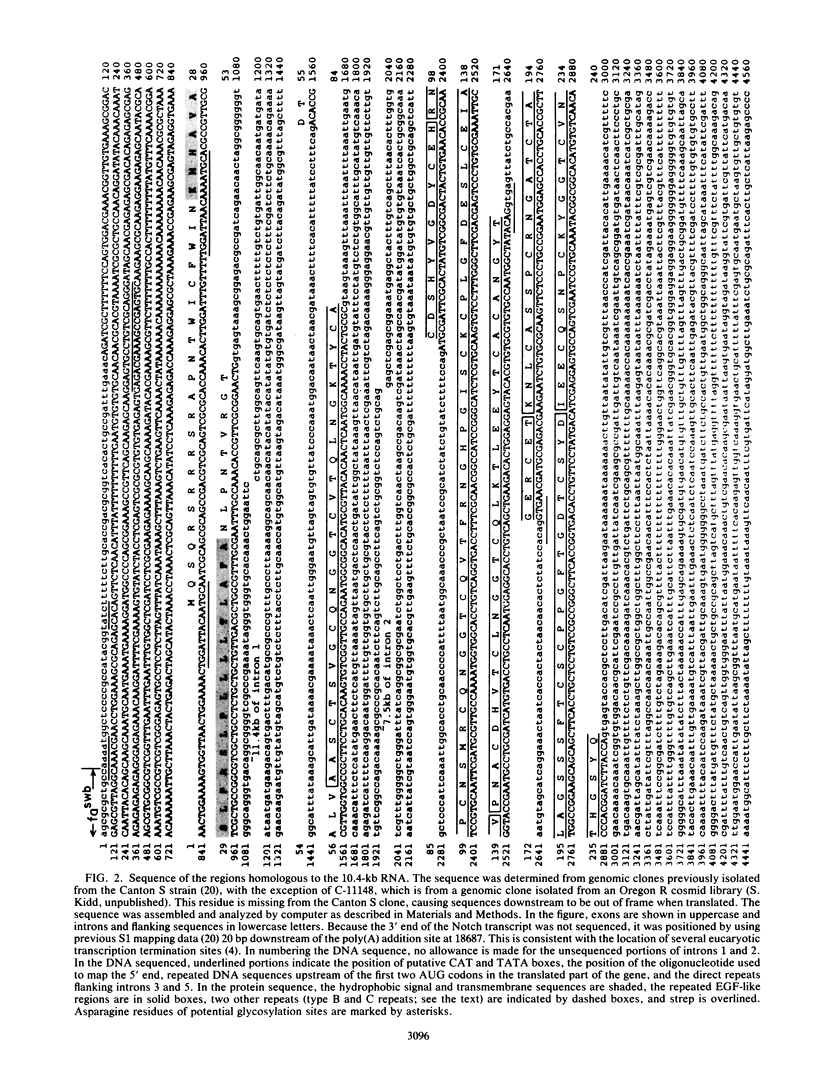
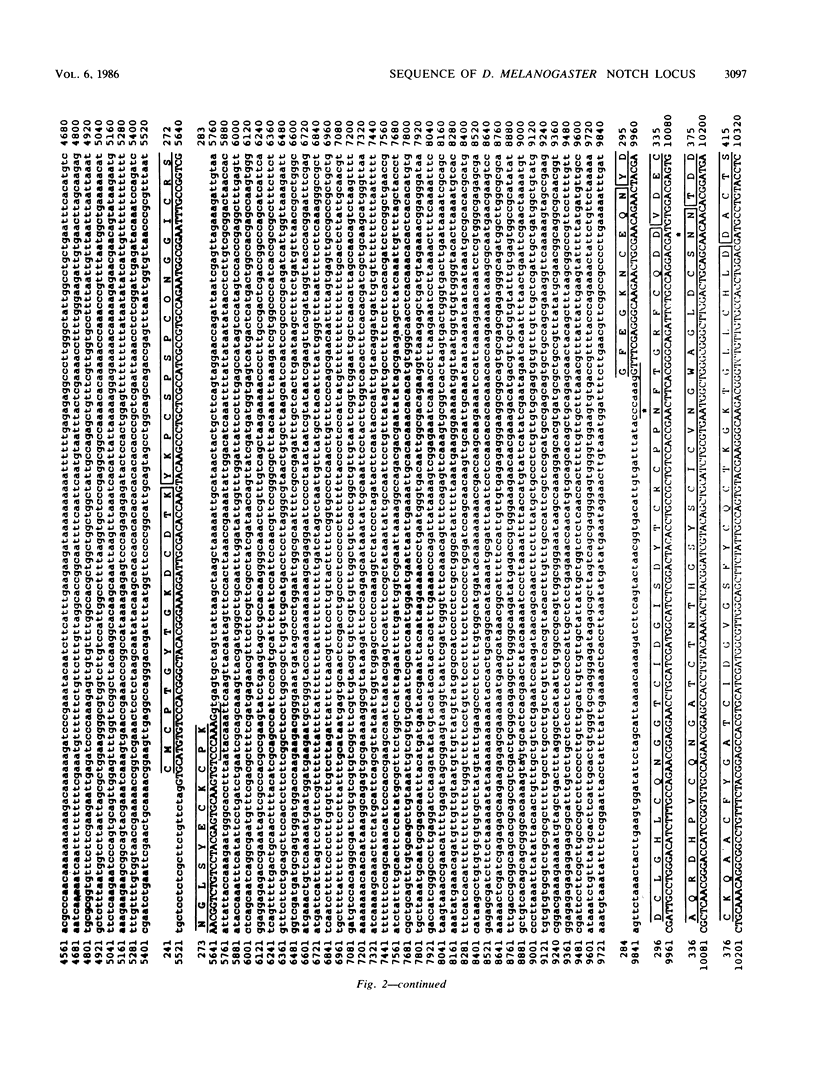
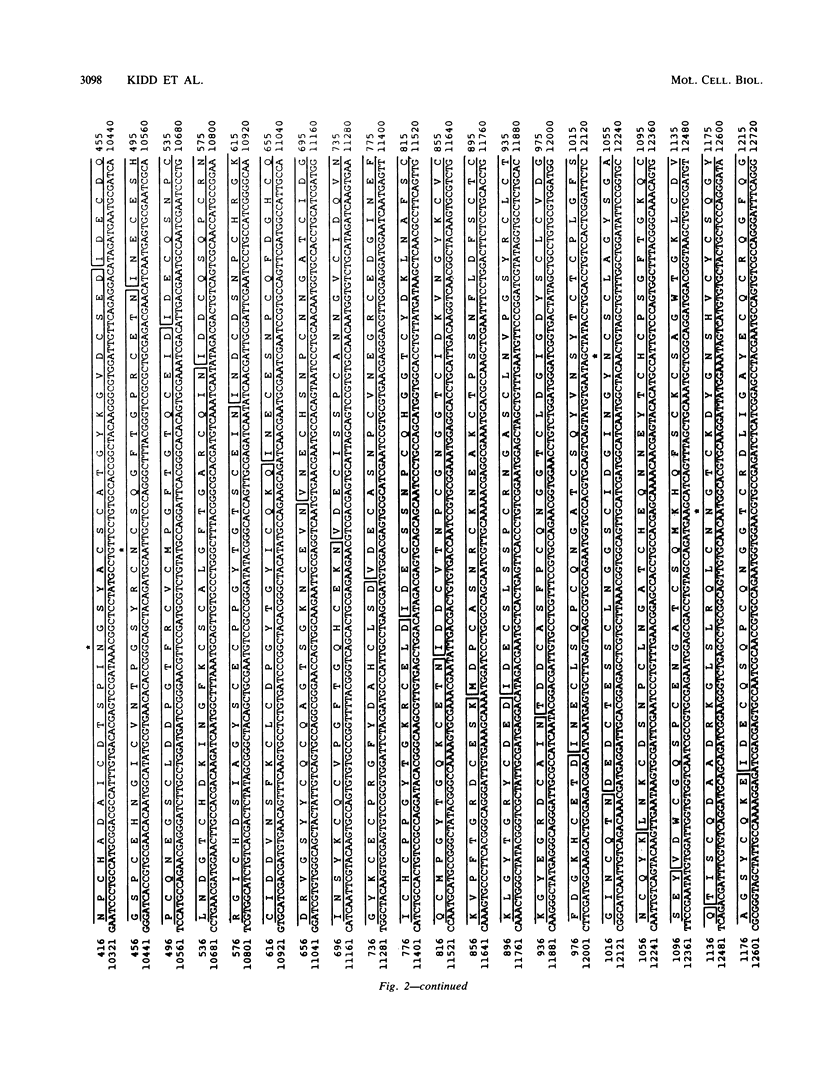
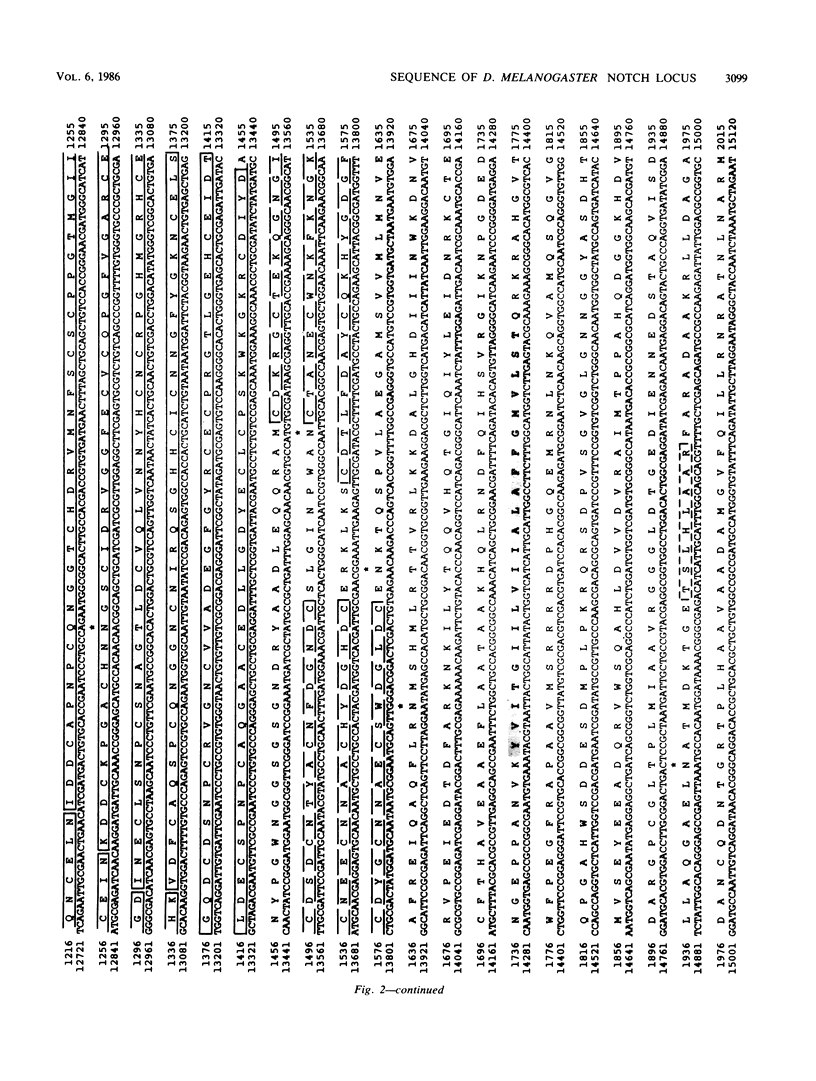
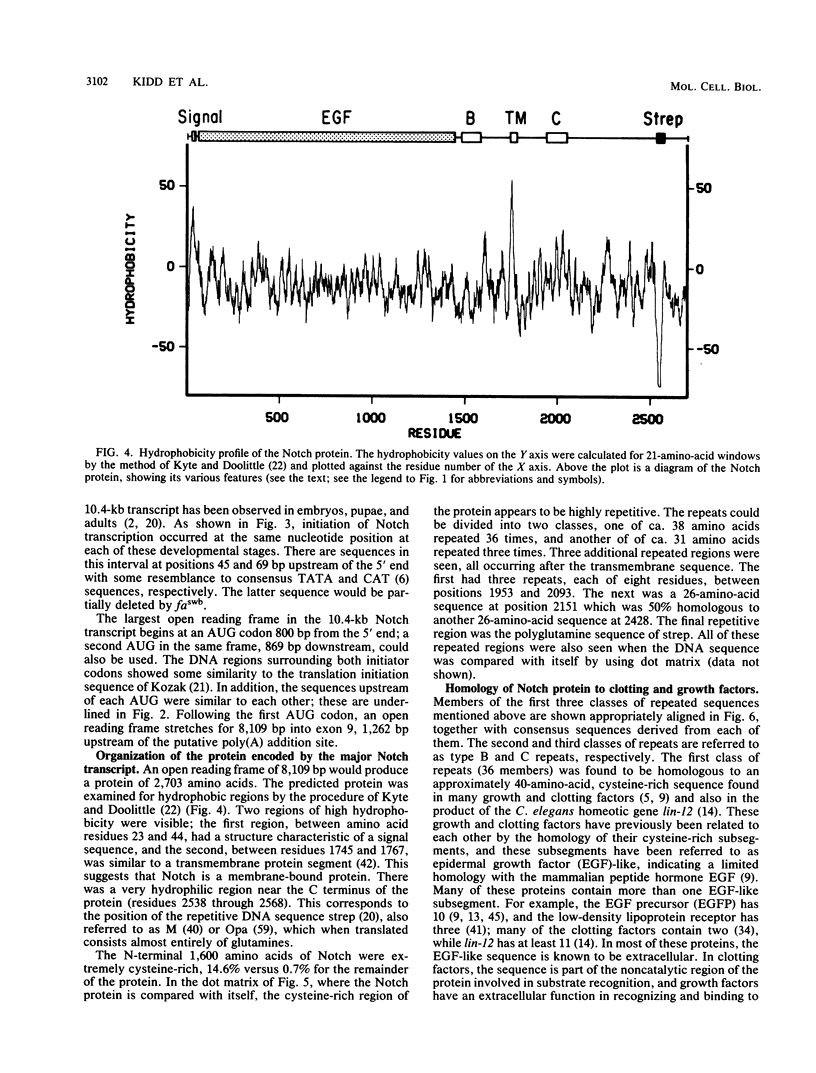
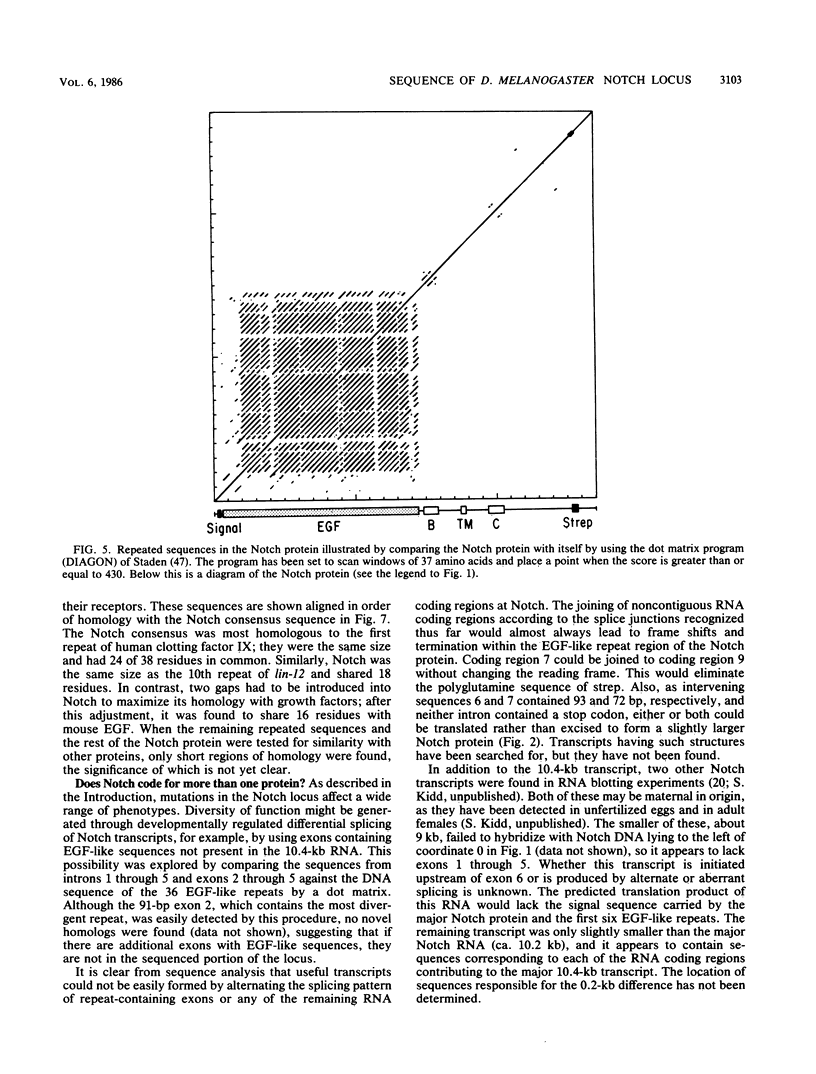
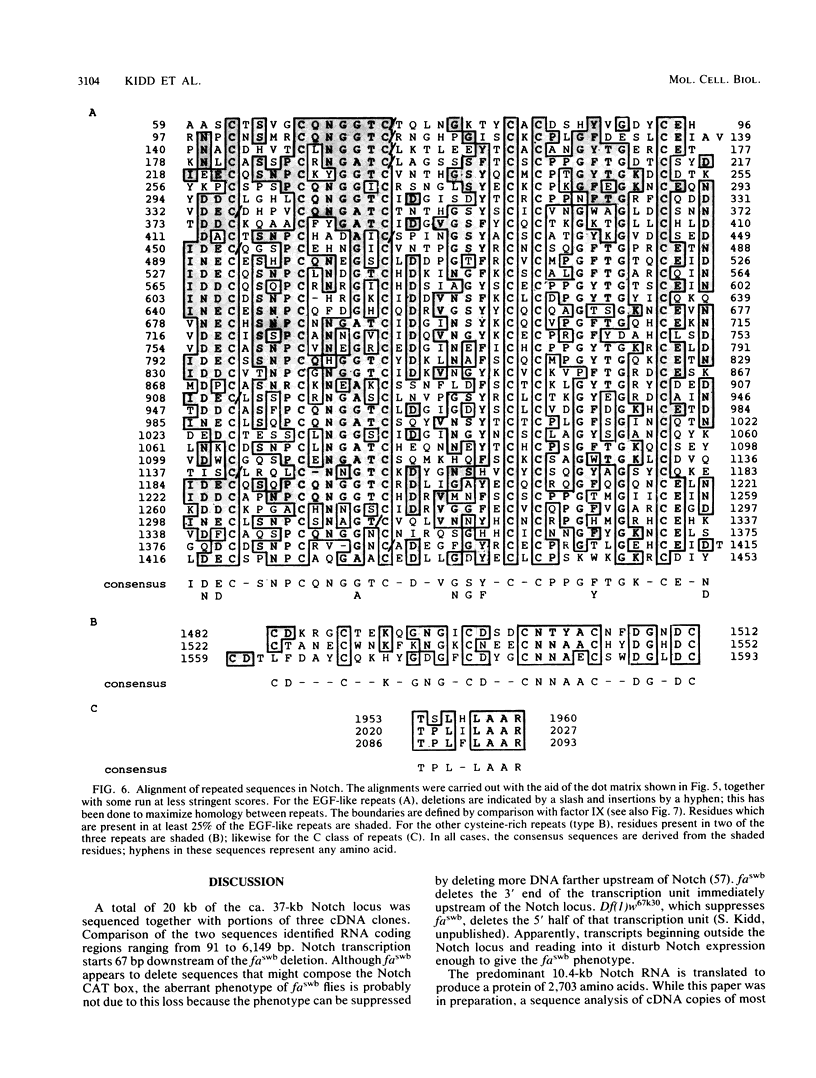
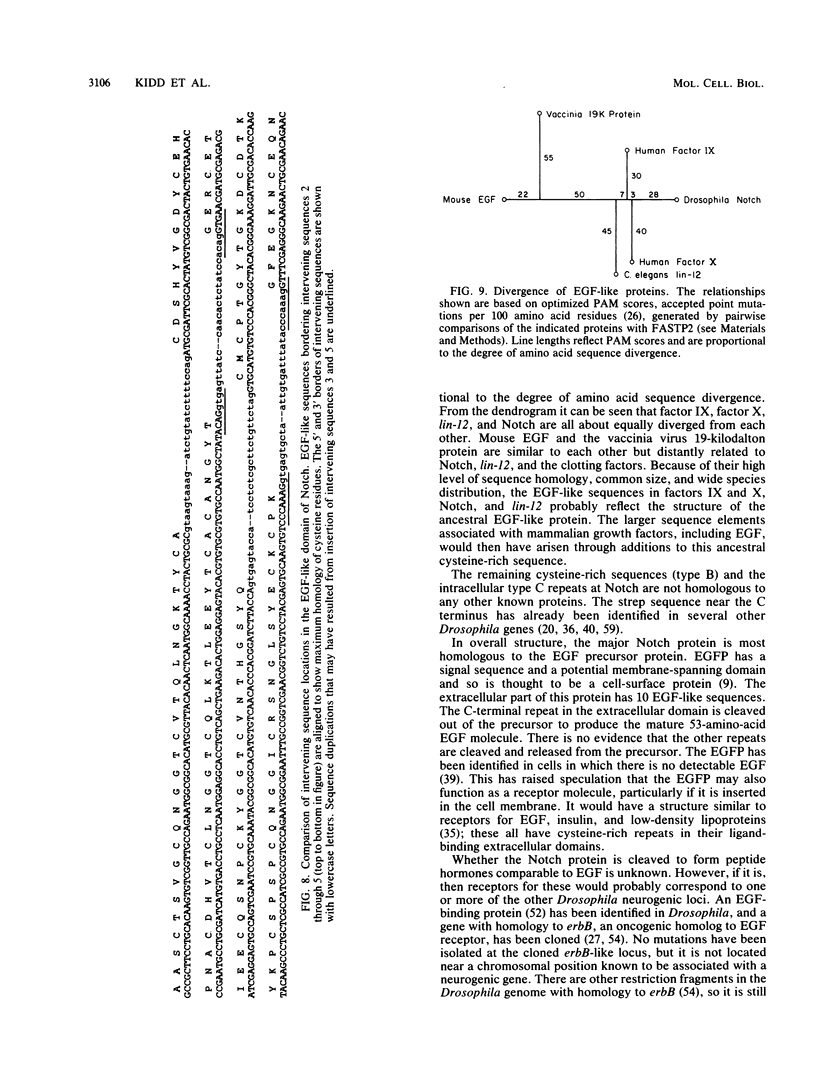
The Notch locus is essential for proper differentiation of the ectoderm in Drosophila melanogaster. Notch corresponds to a 37-kilobase transcription unit that codes for a major 10.4-kilobase polyadenylated RNA. The DNA sequence of this transcription unit is presented, except for portions of the two largest intervening sequences. DNA sequences also were obtained from three Notch cDNA clones, allowing the 5' and 3' ends of the gene to be mapped, and the structures and locations of nine RNA coding regions to be determined. The major Notch transcript encodes a protein of 2,703 amino acids. The protein is probably associated with cell surfaces and carries an extracellular domain composed of 36 cysteine-rich repeating units, each of about 38 amino acids. The gene appears to have evolved by repeated tandem duplications of the DNA coding for the 38-amino-acid-long protein segments, followed by insertion of intervening sequences. These repeating protein segments are quite homologous to portions of mammalian clotting factors IX and X and to the product of the Caenorhabditis elegans developmental gene lin-12. They are also similar to mammalian growth hormones, typified by epidermal growth factor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anson D. S., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Giannelli F., Gould K., Huddleston J. A., Brownlee G. G. The gene structure of human anti-haemophilic factor IX. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1053–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Muskavitch M. A., Yedvobnick B. Molecular cloning of Notch, a locus affecting neurogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist M. C., Hunt L. T., Barker W. C. Vaccinia virus 19-kilodalton protein: relationship to several mammalian proteins, including two growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7363–7367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S. Computer-based characterization of epidermal growth factor precursor. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):558–560. doi: 10.1038/307558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster G. G. Negative complementation at the notch locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1975 Sep;81(1):99–120. doi: 10.1093/genetics/81.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Hay C. W., MacGillivray R. T. Characterization of an almost full-length cDNA coding for human blood coagulation factor X. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3591–3595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I. lin-12, a nematode homeotic gene, is homologous to a set of mammalian proteins that includes epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90230-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory H., Preston B. M. The primary structure of human urogastrone. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977;9(2):107–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1977.tb03470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzler W. A., Steffens G. J., Otting F., Kim S. M., Frankus E., Flohé L. The primary structure of high molecular mass urokinase from human urine. The complete amino acid sequence of the A chain. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982 Oct;363(10):1155–1165. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1982.363.2.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Højrup P., Jensen M. S., Petersen T. E. Amino acid sequence of bovine protein Z: a vitamin K-dependent serine protease homolog. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 20;184(2):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80633-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S., Lockett T. J., Young M. W. The Notch locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):421–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Rose T. M., Webb N. R., Todaro G. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for rat transforming growth factor-alpha. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):489–491. doi: 10.1038/313489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Glazer L., Segal D., Schlessinger J., Shilo B. Z. The Drosophila EGF receptor gene homolog: conservation of both hormone binding and kinase domains. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long G. L., Belagaje R. M., MacGillivray R. T. Cloning and sequencing of liver cDNA coding for bovine protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5653–5656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez H. M. An efficient method for finding repeats in molecular sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4629–4634. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen B. A., Fujikawa K. Amino acid sequence of the heavy chain of human alpha-factor XIIa (activated Hageman factor). J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5328–5341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Elgh F., Lund B. The structure of the human tissue-type plasminogen activator gene: correlation of intron and exon structures to functional and structural domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5355–5359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L. Evolution of the proteases of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis by assembly from modules. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):657–663. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S., Ullrich A. Epidermal growth factor. Is the precursor a receptor? Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):184–184. doi: 10.1038/313184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Kauvar L. M., Drees B., Kornberg T. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: structural analysis of an embryonic transcript. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portin P. Allelic negative complementation at the Abruptex locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1975 Sep;81(1):121–133. doi: 10.1093/genetics/81.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Scott J., Bell G. I., Crawford R. J., Penschow J. D., Niall H. D., Coghlan J. P. Mouse prepro-epidermal growth factor synthesis by the kidney and other tissues. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):228–231. doi: 10.1038/313228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regulski M., Harding K., Kostriken R., Karch F., Levine M., McGinnis W. Homeo box genes of the Antennapedia and bithorax complexes of Drosophila. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Schneider W. J., Yamamoto T., Luskey K. L., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Domain map of the LDL receptor: sequence homology with the epidermal growth factor precursor. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90388-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Fong N., Selby M., Rutter W. J., Bell G. I. Structure of a mouse submaxillary messenger RNA encoding epidermal growth factor and seven related proteins. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):236–240. doi: 10.1126/science.6602382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Graphic methods to determine the function of nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):521–538. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Kocher H. P., Luzio J. P., Jackson P., Tschopp J. The sequence and topology of human complement component C9. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):375–382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03639.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):815–822. doi: 10.1126/science.2988123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Sanchez-Pescador R., Bell G. I. Cassette of eight exons shared by genes for LDL receptor and EGF precursor. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):893–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3873704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. L., Decker S. J., Rosner M. R. Identification of a novel receptor in Drosophila for both epidermal growth factor and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8443–8447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Gershowitz A., Moss B. Complete nucleotide sequences of two adjacent early vaccinia virus genes located within the inverted terminal repetition. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):637–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.637-646.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S. C., Vincent W. S., 3rd, Bilodeau-Wentworth D. A Drosophila genomic sequence with homology to human epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):178–180. doi: 10.1038/314178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welshons W. J. Genetic basis for two types of recessive lethality at the notch locus of Drosophila. Genetics. 1971 Jun;68(2):259–268. doi: 10.1093/genetics/68.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welshons W. J., Keppy D. O. Intragenic deletions and salivary band relationships in Drosophila. Genetics. 1975 May;80(1):143–155. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welshons W. J., Welshons H. J. Suppression of the facet-strawberry position effect in Drosophila by lesions adjacent to notch. Genetics. 1985 Jul;110(3):465–477. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Yedvobnick B., Finnerty V. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. opa: a novel family of transcribed repeats shared by the Notch locus and other developmentally regulated loci in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]