Abstract
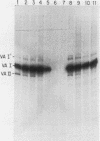
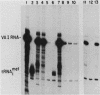
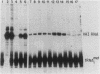
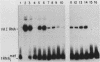
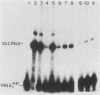
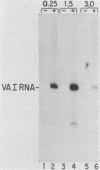
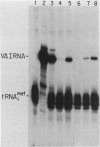
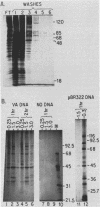
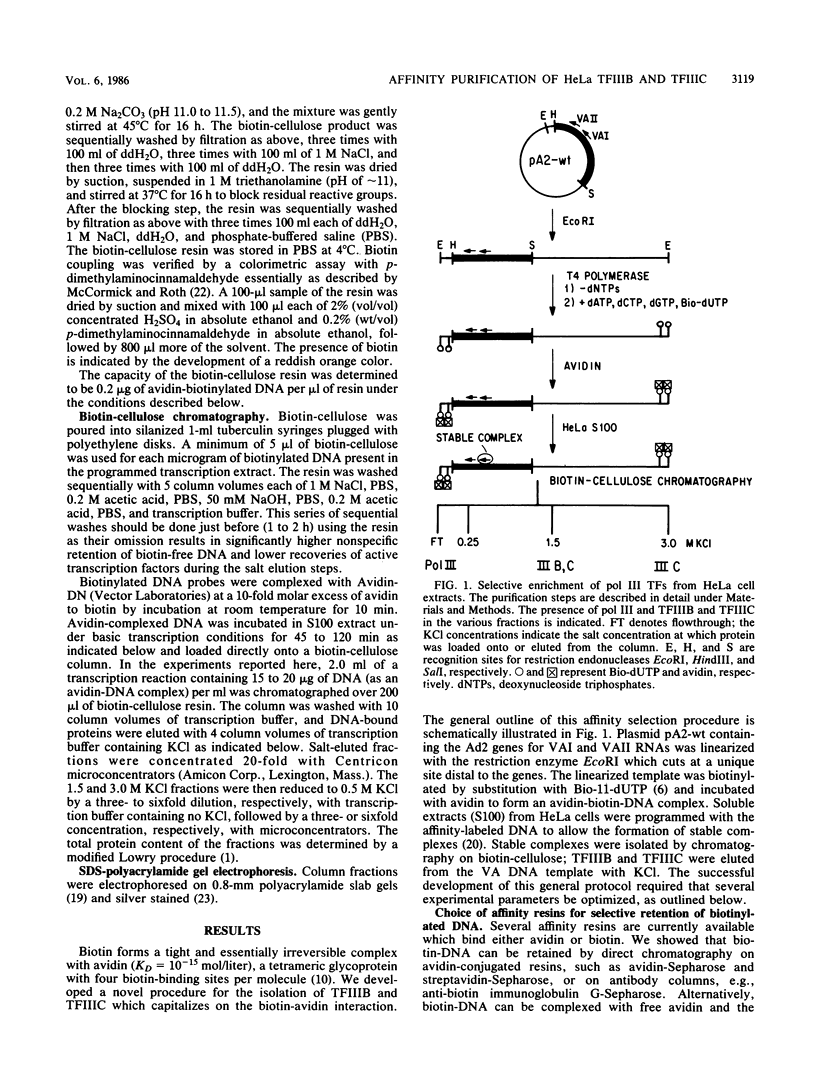
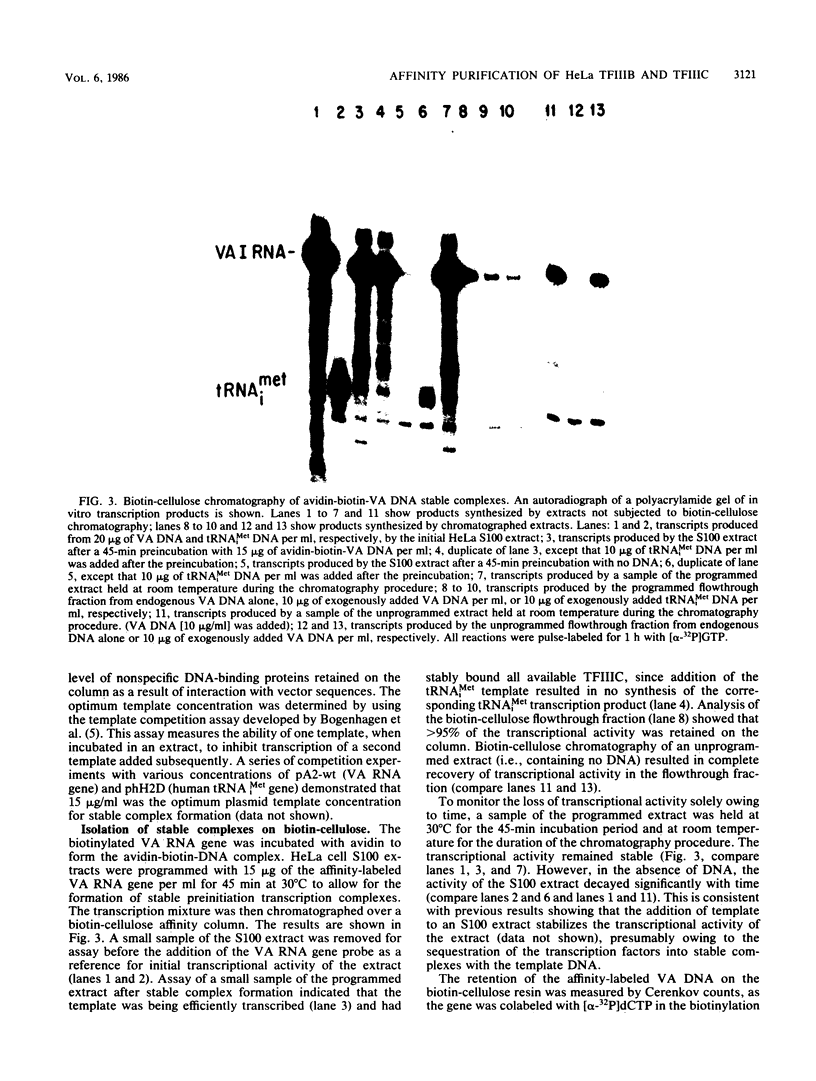
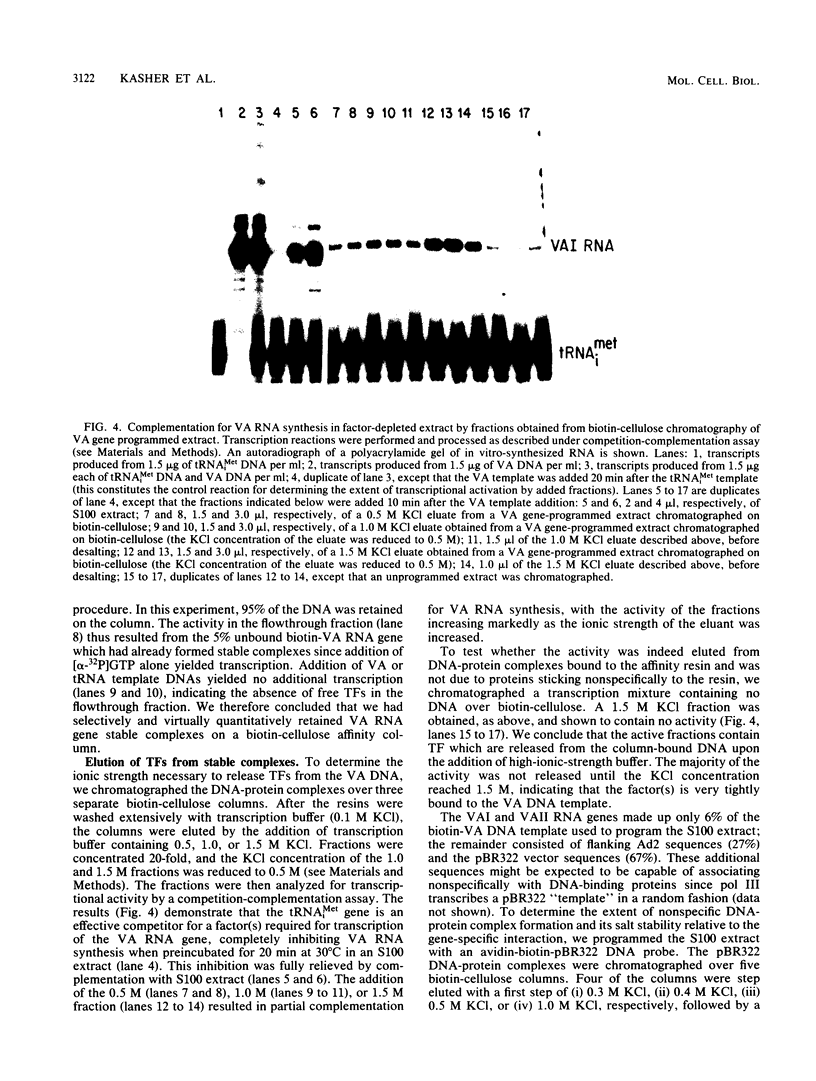
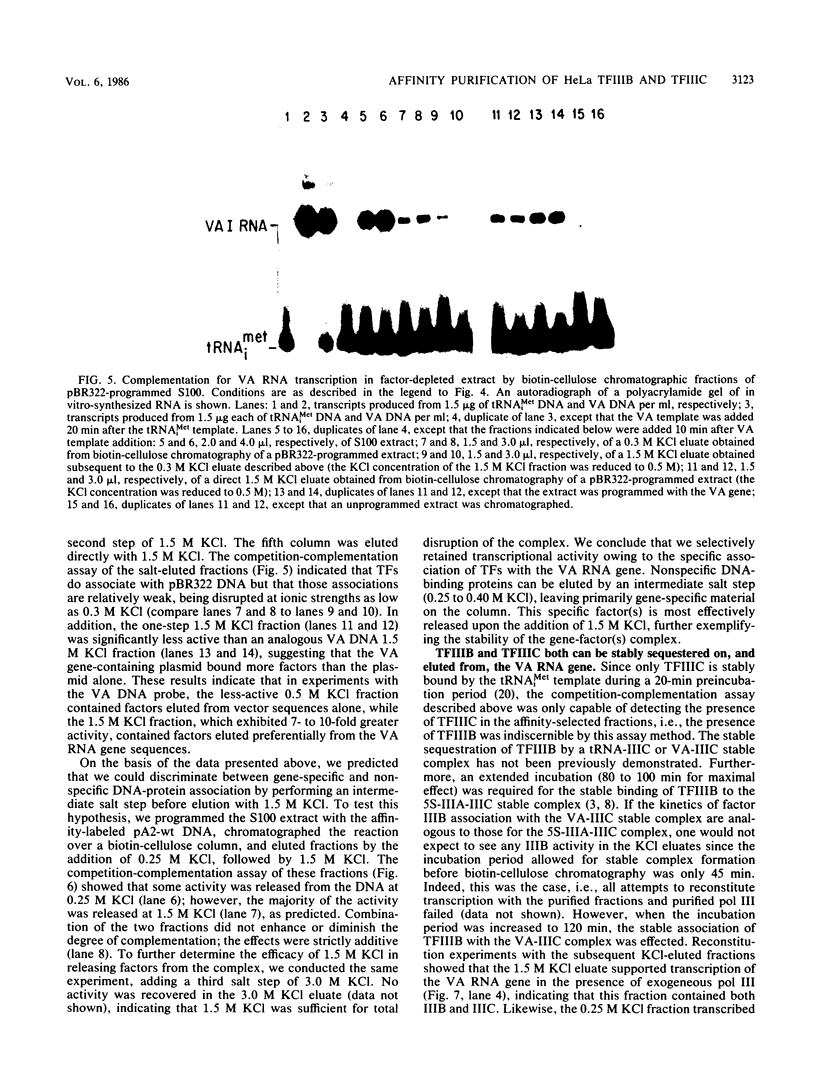
Plasmid DNA containing the adenovirus type 2 genes for VA RNA was linearized at a site distal to the gene, end labeled with a biotin-nucleotide analog of TTP, and incubated with avidin to form an avidin-biotinylated DNA complex. HeLa cell S100 extracts containing crude RNA polymerase III and transcription factors (TFs) IIIB and IIIC were programmed with the avidin-biotin-VA DNA to allow stable complex formation (A.B. Lassar, P.L. Martin, and R.G. Roeder, Science 222:740-748, 1983). Chromatography of the programmed extract over a biotin-cellulose affinity resin resulted in the selective, and virtually quantitative, retention of one of two stable preinitiation complexes, either VA-IIIC or VA-IIIC-IIIB, depending on the length of template incubation in the S100 extract. After washing the resin with 0.10 M and 0.25 M KCl to remove RNA polymerase III and nonspecifically bound proteins, respectively, TFIIIC was eluted from the VA-IIIC complex by the addition of 1.5 M KCl. The VA-IIIC-IIIB complex exhibited a higher salt stability. Most of TFIIIB and some TFIIIC were released by the addition of 1.5 M KCl; however, the majority of TFIIIC activity was recovered only after a subsequent 3.0 M KCl elution. The specific activity of the TFIIIC in the 3.0 M KCl fraction was 770-fold higher than that in the S100 extract, while the protein content of the 1.5 and 3.0 M KCl fractions was reduced 7,500- and 100,000-fold, respectively.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker J. J., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Formation of a rate-limiting intermediate in 5S RNA gene transcription. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker J. J., Roeder R. G. Physical properties and DNA-binding stoichiometry of a 5 S gene-specific transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6158–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigati D. J., Myerson D., Leary J. J., Spalholz B., Travis S. Z., Fong C. K., Hsiung G. D., Ward D. C. Detection of viral genomes in cultured cells and paraffin-embedded tissue sections using biotin-labeled hybridization probes. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):32–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Raugei G., Costanzo F., Dente L., Cortese R. Common and interchangeable elements in the promoters of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase iii. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Wides R. J., Sollner-Webb B. Eucaryotic transcription complexes are specifically associated in large sedimentable structures: rapid isolation of polymerase I, II, and III transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1582–1590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo G., Razvi F., Worcel A. Assembly of transcriptionally active chromatin in Xenopus oocytes requires specific DNA binding factors. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):511–521. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90506-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Hazuda D. J., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Xenopus transcription factor A requires zinc for binding to the 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14120–14125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. L., Gregori T. J. Cloning multiple copies of a DNA segment. Gene. 1981 May;13(4):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Partial purification and characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor TFIIIB. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2819–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. B., Roth J. A. Specificity, stereochemistry, and mechanism of the color reaction between p-dimethylaminocinnamalhyde and biotin analogs. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:226–236. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Camier S., Smagowicz W., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Isolation of a class C transcription factor which forms a stable complex with tRNA genes. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):343–350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E., Shi X. P., Houpert A., Seifart K. H. Isolation of a transcription complex for ribosomal 5S RNA. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1761–1768. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02043.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]