Abstract
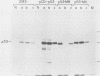
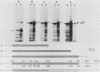
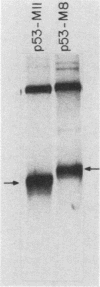
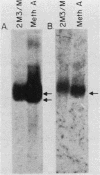
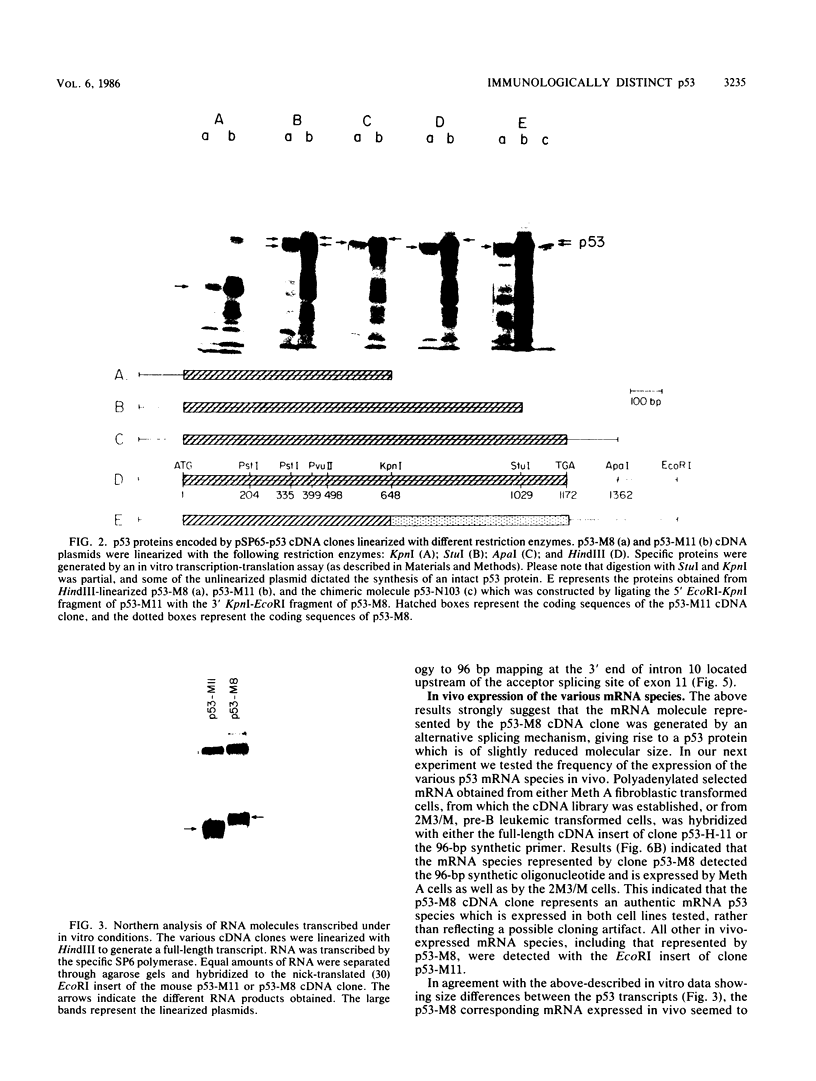
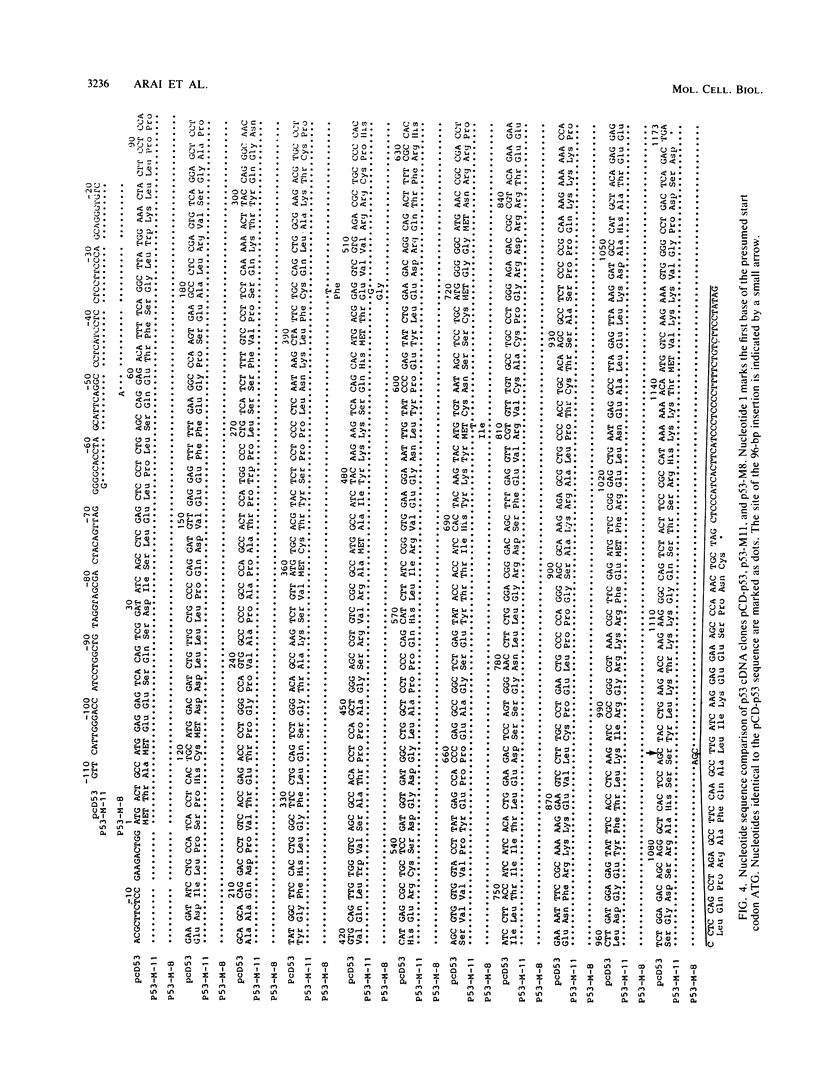
Transfection of a functional cloned p53 gene into an L12 p53 nonproducer cell line efficiently reconstituted p53 expression. The p53 protein synthesized in these clones was indistinguishable from that occurring naturally in tumor cells. When a p53 cDNA clone was used instead, we observed that the L12-derived clones exhibited a distinct immunological profile. In the present experiments we compared the immunological epitopes of p53 proteins encoded by several full-length cDNA clones. Immunoprecipitation of p53 proteins generated by in vitro transcription and translation of the various cDNA clones indicated variations in the content of immunological epitopes. Basically, two p53 protein species were detected. Both species contained the same antigenic determinants except the PAb421-PAb122 site, which was present in proteins encoded by p53-M11 and pcD-p53, but not in the p53 protein encoded by the p53-M8 cDNA clone. Sequence analysis of the various cDNA clones indicated the existence of a 96-base-pair (bp) insert in clone p53-M8 as compared with clone p53-M11 or pCD-p53. The 96-bp insert contained a termination signal which caused the premature termination of the protein, leading to the generation of a p53 product 9 amino acids shorter than usual. The existence of this insert also accounted for the lack of the PAb421-PAb122 epitope which was mapped to the 3' end of the cDNA clone, following the 96-bp insert. This insert shared complete homology with the p53 intron 10 sequences mapping 96 bp upstream of the 5' acceptor splicing site of p53 exon 11. It was therefore concluded that the different cDNA clones represented p53 mRNA species which were generated by an alternative splicing mechanism. Differential hybridization of the mRNA population of transformed fibroblastic or lymphoid cells with either the 96-bp synthetic oligonucleotide or the p53-M11 cDNA indicated that the various mRNA species are expressed in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benchimol S., Pim D., Crawford L. Radioimmunoassay of the cellular protein p53 in mouse and human cell lines. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1055–1062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01296.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz B., Zakut-Houri R., Givol D., Oren M. Analysis of the gene coding for the murine cellular tumour antigen p53. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2179–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayberger C., Dekruyff R. H., Aisenberg J., Cantor H. Hapten-reactive inducer T cells. I. Definition of two classes of hapten-specific inducer cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1906–1919. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes B cells and B cell precursors in mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):269–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Weissman S. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:315–462. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippold W. G., Jay G., DeLeo A. B., Khoury G., Old L. J. p53 transformation-related protein: detection by monoclonal antibody in mouse and human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1695–1699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Williamson N. M., Ralston R., Helfman D. M., Adams T. E. Molecular cloning and in vitro expression of a cDNA clone for human cellular tumor antigen p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1601–1610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley W. S., Stump K. H. A rapid procedure for isolation of large quantities of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I utilizing a lambdapolA transducing phage. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3206–3210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Lamb P., Pim D., Peacock J., Crawford L., Benchimol S. Isolation and characterization of a human p53 cDNA clone: expression of the human p53 gene. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3257–3262. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Nelson D., DeLeo A. B., Old L. J., Baserga R. Microinjection of monoclonal antibody to protein p53 inhibits serum-induced DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6309–6312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. Different forms of p53 detected by monoclonal antibodies in non-dividing and dividing lymphocytes. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):143–145. doi: 10.1038/310143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Milner S. SV40-53K antigen: a possible role for 53K in normal cells. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):785–788. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora P. T., Chandrasekaran K., McFarland V. W. An embryo protein induced by SV40 virus transformation of mouse cells. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):722–724. doi: 10.1038/288722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Post-translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):101–110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten P., Yokota T., Rothbard J., Chien Y., Arai K., Davis M. M. Structure, expression and divergence of T-cell receptor beta-chain variable regions. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):40–46. doi: 10.1038/312040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):199–201. doi: 10.1038/308199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Boss M. A., Baltimore D. Increased concentration of an apparently identical cellular protein in cells transformed by either Abelson murine leukemia virus or other transforming agents. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):336–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.336-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade-Evans A., Jenkins J. R. Precise epitope mapping of the murine transformation-associated protein, p53. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):699–706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Goldfinger N., Rotter V. Isolation of a full-length mouse cDNA clone coding for an immunologically distinct p53 molecule. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):127–132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Rotter V. Reconstitution of p53 expression in a nonproducer Ab-MuLV-transformed cell line by transfection of a functional p53 gene. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Laver-Rudich Z., Rotter V. In vitro expression of human p53 cDNA clones and characterization of the cloned human p53 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1887–1893. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Rotter V. Inactivation of p53 gene expression by an insertion of Moloney murine leukemia virus-like DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1402–1410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut-Houri R., Oren M., Bienz B., Lavie V., Hazum S., Givol D. A single gene and a pseudogene for the cellular tumour antigen p53. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):594–597. doi: 10.1038/306594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]