Abstract
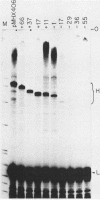
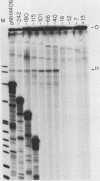
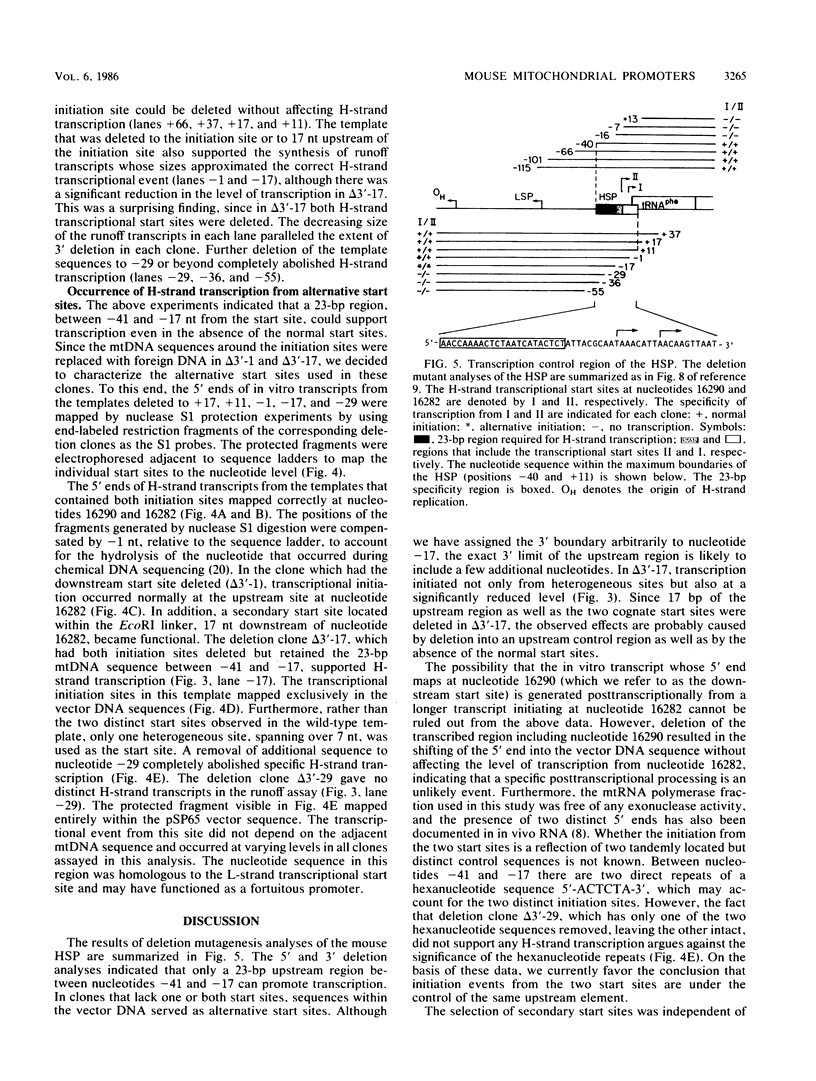
Transcription of the heavy strand of mouse mitochondrial DNA starts from two closely spaced, distinct sites located in the displacement loop region of the genome. We report here an analysis of regulatory sequences required for faithful transcription from these two sites. Data obtained from in vitro assays demonstrated that a 51-base-pair region, encompassing nucleotides -40 to +11 of the downstream start site, contains sufficient information for accurate transcription from both start sites. Deletion of the 3' flanking sequences, including one or both start sites to -17, resulted in the initiation of transcription by the mitochondrial RNA polymerase from alternative sites within vector DNA sequences. This feature places the mouse heavy-strand promoter uniquely among other known mitochondrial promoters, all of which absolutely require cognate start sites for transcription. Comparison of the heavy-strand promoter with those of other vertebrate mitochondrial DNAs revealed a remarkably high rate of sequence divergence among species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Van Etten R. A., Wright C. T., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas T. K., Edwards J. C., Rabinowitz M., Getz G. S. Characterization of a yeast mitochondrial promoter by deletion mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1954–1958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Applegate E. F., Yoza B. K. Identification of a promoter for transcription of the heavy strand of human mtDNA: in vitro transcription and deletion mutagenesis. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1105–1113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Identification of primary transcriptional start sites of mouse mitochondrial DNA: accurate in vitro initiation of both heavy- and light-strand transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1446–1453. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Precise assignment of the light-strand promoter of mouse mitochondrial DNA: a functional promoter consists of multiple upstream domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3253–3261. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Precise identification of individual promoters for transcription of each strand of human mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Priming of human mitochondrial DNA replication occurs at the light-strand promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):351–355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Hauswirth W. W., Clayton D. A. Replication priming and transcription initiate from precisely the same site in mouse mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1559–1567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T., Rabinowitz M. Identification of multiple transcriptional initiation sites on the yeast mitochondrial genome by in vitro capping with guanylyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14025–14033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Raugei G., Costanzo F., Dente L., Cortese R. Common and interchangeable elements in the promoters of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase iii. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Replication of animal mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):693–705. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Transcription of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:573–594. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Clayton D. A. A transcription factor required for promoter recognition by human mitochondrial RNA polymerase. Accurate initiation at the heavy- and light-strand promoters dissected and reconstituted in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11330–11338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Clayton D. A. Initiation of transcription from each of the two human mitochondrial promoters requires unique nucleotides at the transcriptional start sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2660–2664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. A component of Drosophila RNA polymerase I promoter lies within the rRNA transcription unit. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):179–181. doi: 10.1038/304179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. Transcription of cloned Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA microinjected into Xenopus oocytes, and the identification of an RNA polymerase I promoter. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner J. A., Ohrlein A., Grummt I. In vitro mutagenesis and transcriptional analysis of a mouse ribosomal promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2137–2141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Wilkinson J. A., Roan J., Reeder R. H. Nested control regions promote Xenopus ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerville J. RNA polymerase I promoters and transcription factors. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):189–190. doi: 10.1038/310189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkley C. S., Keller M. J., Jaehning J. A. A multicomponent mitochondrial RNA polymerase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14214–14223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto O., Takakusa N., Mishima Y., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Determination of the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene by an in vitro transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):299–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]