Abstract
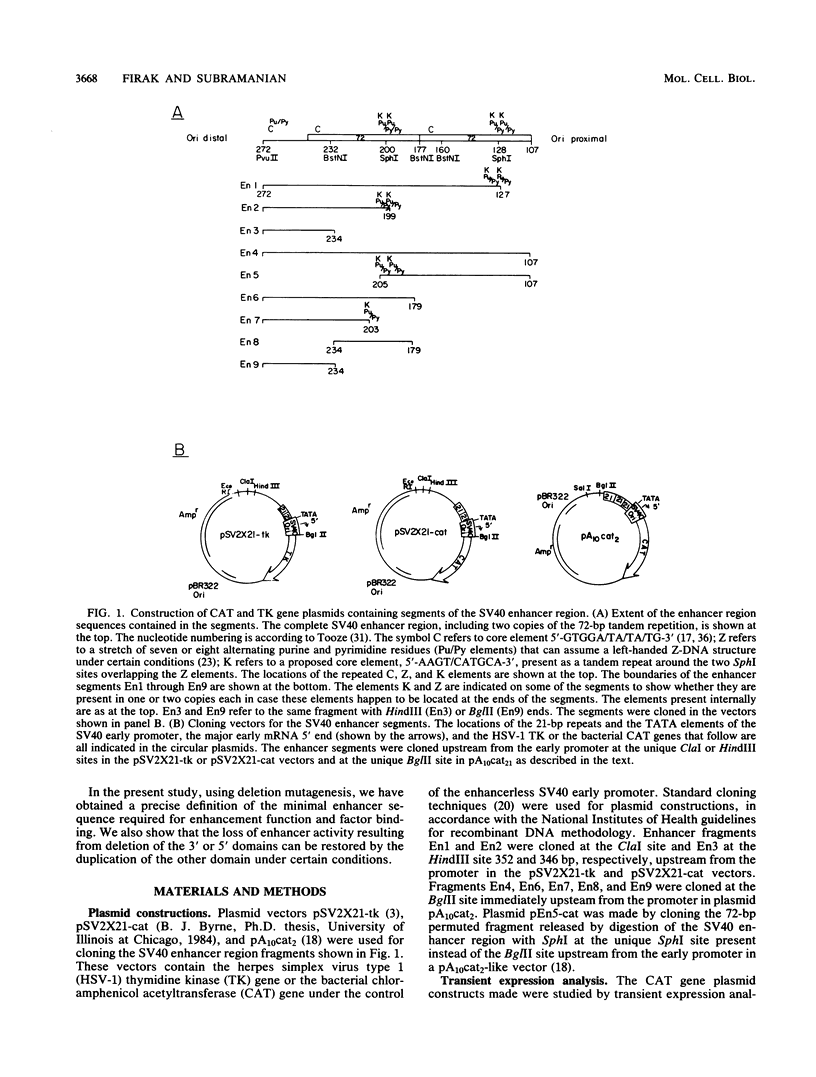
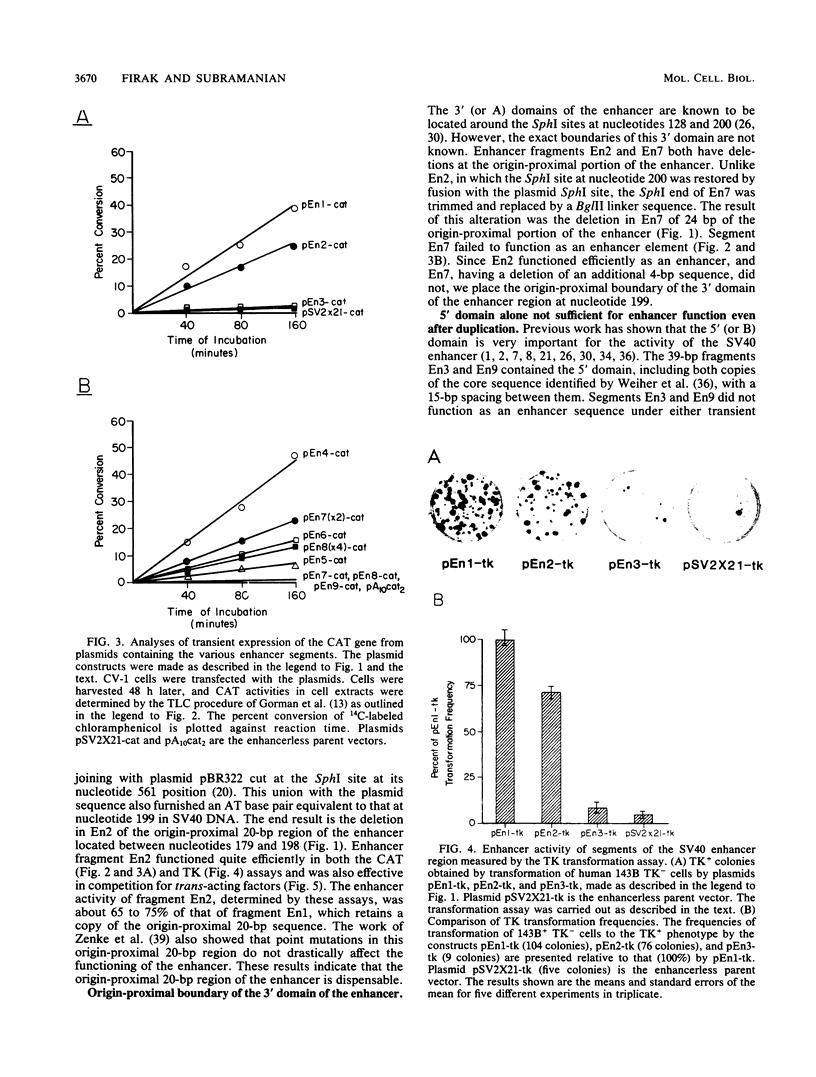
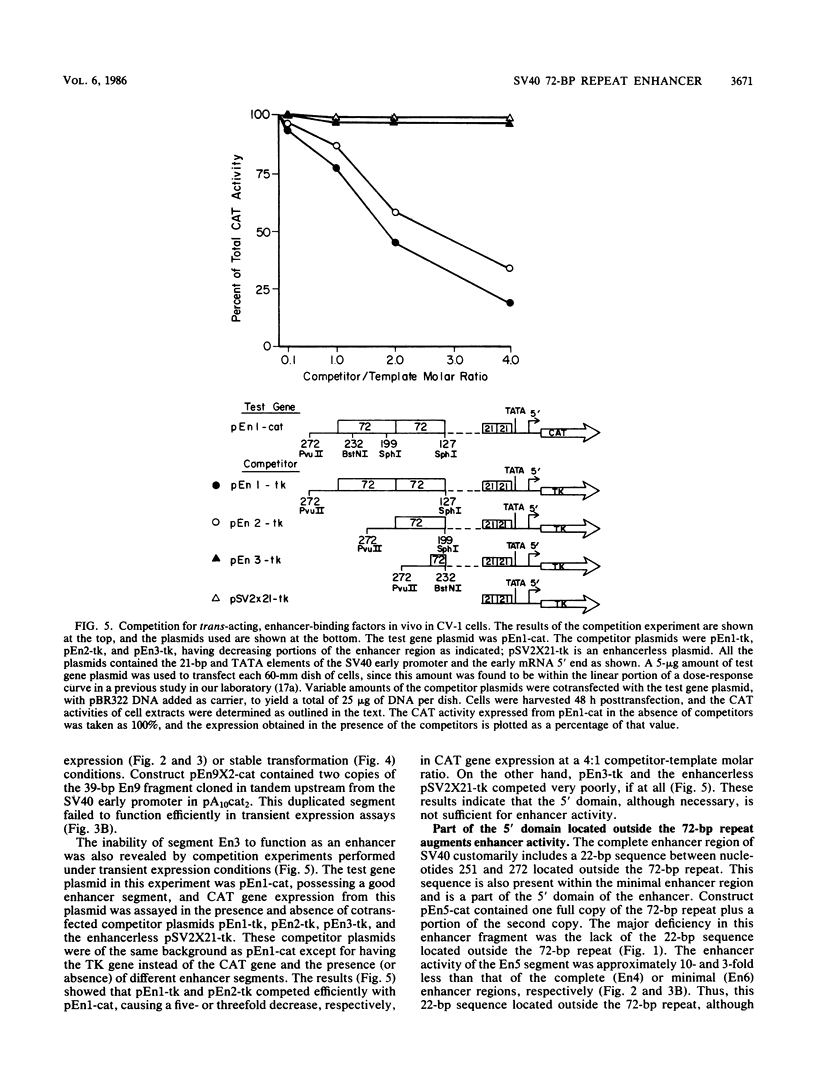
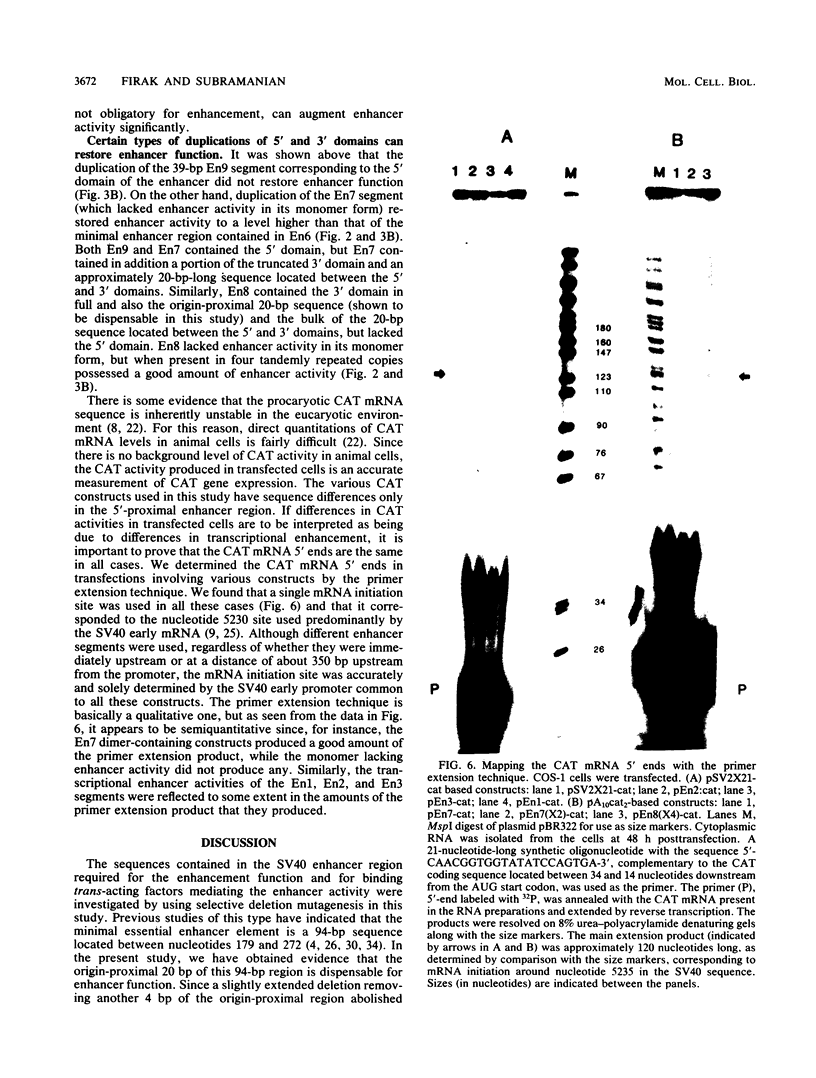
We have assayed the ability of segments of the simian virus 40 (SV40) 72-base-pair (bp) repeat enhancer region to activate gene expression under the control of the SV40 early promoter and to compete for trans-acting enhancer-binding factors of limited availability in vivo in monkey CV-1 or human HeLa cells. The bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase and the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase genes were used as reporters in these assays. A 94-bp sequence located between SV40 nucleotides 179 and 272, including one copy of the 72-bp repeat, has been termed the minimal enhancer in previous studies. In the present study, we found that the 20-bp origin-proximal region located between nucleotides 179 and 198 was dispensable, since its removal caused only a slight reduction in enhancer activity. However, the deletion of another 4 bp up to nucleotide 202 abolished the enhancer activity. We propose that the minimal enhancer is a 74-bp sequence located between nucleotides 199 and 272, including 52 bp of one copy of the 72-bp repeat and a 22-bp adjacent sequence up to the PvuII site at 272. The nonamer 5'-AAGT/CATGCA-3', which we term the K core, occurred as a tandem duplication around the SphI site at nucleotide 200, and we found that this duplication was essential for enhancement and factor-binding activities. A heterologous core element (which we term the C core), 5'-GTGGA/TA/TA/TG-3', identified earlier (G. Khoury and P. Gruss, Cell 33:313-314, 1983; Weiher et al., Science 219:626-631, 1983) also occurred in duplicate, with one of the copies located within the 22-bp sequence near nucleotide 272 present outside the 72-bp repeat. We provide direct evidence that this 22-bp sequence augments enhancer activity considerably. We also found that in addition to the heterologous interaction occurring normally between the K and C cores within the minimal enhancer, certain homologous interactions were also permitted provided there was proper spacing between the elements.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne B. J., Davis M. S., Yamaguchi J., Bergsma D. J., Subramanian K. N. Definition of the simian virus 40 early promoter region and demonstration of a host range bias in the enhancement effect of the simian virus 40 72-base-pair repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):721–725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen D., van de Voorde A., Contreras R., Vanderheyden J., Duerinck F., Fiers W. Simian virus 40 mutants carrying extensive deletions in the 72-base-pair repeat region. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's contain multiple 5' termini upstream and downstream from a Hogness-Goldberg sequence; a shift in 5' termini during the lytic cycle is mediated by large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):224–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.224-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell S. W., Byrne B. J., Subramanian K. N. The simian virus 40 minimal origin and the 72-base-pair repeat are required simultaneously for efficient induction of late gene expression with large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6335–6339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gluzman Y. Duplications of a mutated simian virus 40 enhancer restore its activity. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):711–714. doi: 10.1038/313711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Firak T. A., Schroll C. T., Subramanian K. N. Activation of gene expression is adversely affected at high multiplicities of linked simian virus 40 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3199–3203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Berg L., Weiher H., Botchan M. Bovine papilloma virus contains an activator of gene expression at the distal end of the early transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1108–1122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosthaf L., Pawlita M., Gruss P. A viral enhancer element specifically active in human haematopoietic cells. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):597–600. doi: 10.1038/315597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA contains Z-DNA segments within transcriptional enhancer sequences. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):674–679. doi: 10.1038/303674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Piatak M., Weissman S. M. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's. I. Genomic localization of 3' and 5' termini and two major splices in mRNA from transformed and lytically infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):279–296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.279-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swimmer C., Shenk T. A viable simian virus 40 variant that carries a newly generated sequence reiteration in place of the normal duplicated enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6652–6656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heuverswyn H., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the Hind-C fragment of simian virus 40 DNA. Comparison of the 5'-untranslated region of wild-type virus and of some deletion Mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Sassone-Corsi P., Grundström T., Zenke M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from the SV40 early promoter by the enhancer involves a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3129–3133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






