Abstract
The regulation of mRNA production for the yeast positive activator ADR1, a gene required for the expression of the glucose-repressible alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH II), was studied. ADR1 mRNA levels did not vary when yeasts were switched from glucose- to ethanol-containing medium, while ADH II expression increased 100-fold. The mRNA for the ADR1-5c allele, which augments ADH II expression 60-fold during glucose repression, was not present in greater abundance than ADR1 mRNA. Additionally, the ccr1-1 allele, which blocks ADH2 mRNA formation and partially suppresses the ADR1-5c phenotype, did not alter the levels of ADR1 mRNA. These results indicate that ADR1 is not transcriptionally controlled. To determine the character of the ADR1-5c mutation, the region containing the mutation was identified and sequenced. At base pair +683 a G-to-A transition was detected in the ADR1 coding sequence which would result in the substitution of a lysine residue for an arginine at amino acid 228. The location of the ADR1-5c mutation in the interior of the ADR1 coding sequences suggests that it enhances the activity of an extant but inactive ADR1 protein rather than increases the abundance of ADR1 by altered translation of its mRNA. The ADR1-5c mutation occurs in a region of the polypeptide corresponding to a cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation recognition sequence. The potential role of reversible phosphorylation in the posttranslational regulation of ADR1 is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke R. L., Tekamp-Olson P., Najarian R. The isolation, characterization, and sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2193–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. A yeast gene that is essential for release from glucose repression encodes a protein kinase. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1175–1180. doi: 10.1126/science.3526554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. Structure and expression of the SNF1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):54–60. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriacy M. Genetics of alcohol dehydrogenase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Two loci controlling synthesis of the glucose-repressible ADH II. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;138(2):157–164. doi: 10.1007/BF02428119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriacy M. Isolation and characterization of further cis- and trans-acting regulatory elements involved in the synthesis of glucose-repressible alcohol dehydrogenase (ADHII) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Nov;176(3):427–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00333107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriacy M. Isolation and characterization of yeast mutants defective in intermediary carbon metabolism and in carbon catabolite derepression. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jul 20;154(2):213–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00330840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
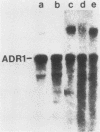
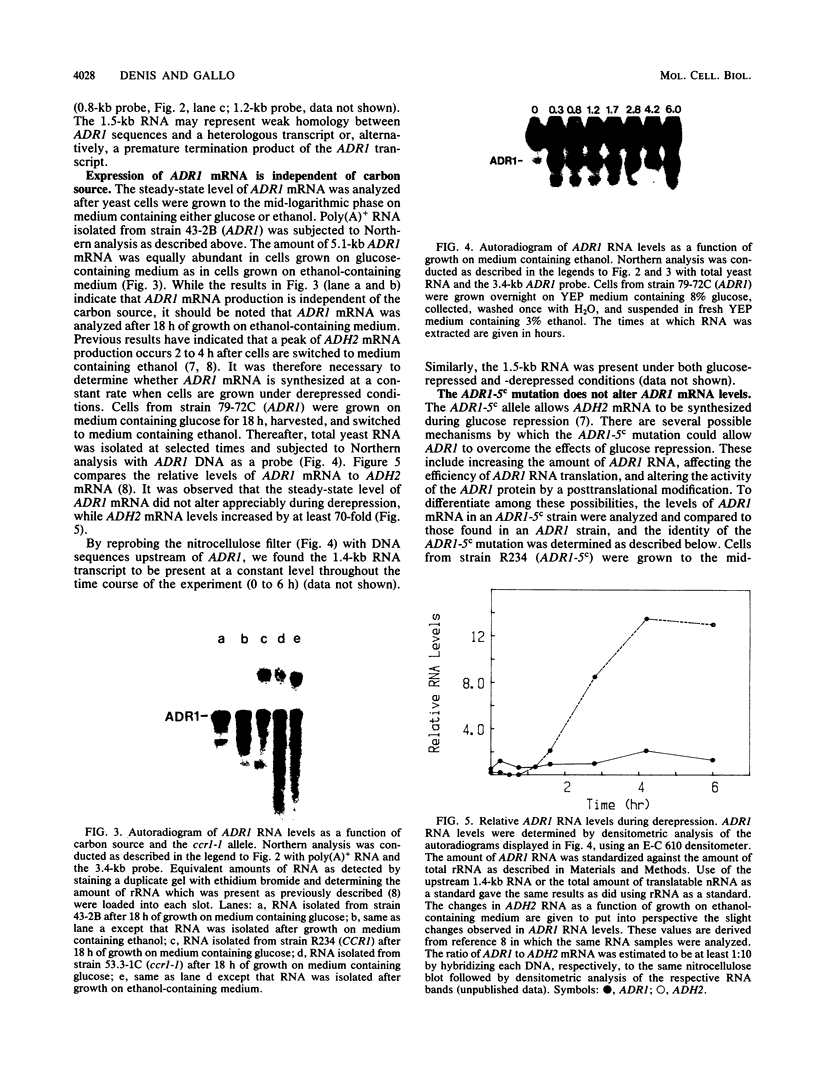
- Denis C. L., Ciriacy M., Young E. T. A positive regulatory gene is required for accumulation of the functional messenger RNA for the glucose-repressible alcohol dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):355–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis C. L., Ferguson J., Young E. T. mRNA levels for the fermentative alcohol dehydrogenase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae decrease upon growth on a nonfermentable carbon source. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1165–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis C. L. Identification of new genes involved in the regulation of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase II. Genetics. 1984 Dec;108(4):833–844. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis C. L., Young E. T. Isolation and characterization of the positive regulatory gene ADR1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):360–370. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne T. A., Blumberg H., Young E. T. Sequence homology of the yeast regulatory protein ADR1 with Xenopus transcription factor TFIIIA. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):283–287. doi: 10.1038/320283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Broek D., Wigler M. DNA sequence and characterization of the S. cerevisiae gene encoding adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse C., Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Phosphorylation of the yeast equivalent of ribosomal protein S6 is not essential for growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7515–7519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse J., Harrsch P. B., Kim J. N., Marcus F. Amino acid sequence of the phosphorylation site of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):3939–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson V. M., Young E. T., Ciriacy M. Transposable elements associated with constitutive expression of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase II. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]