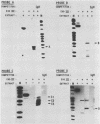
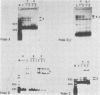
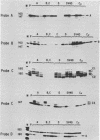
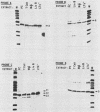
Abstract
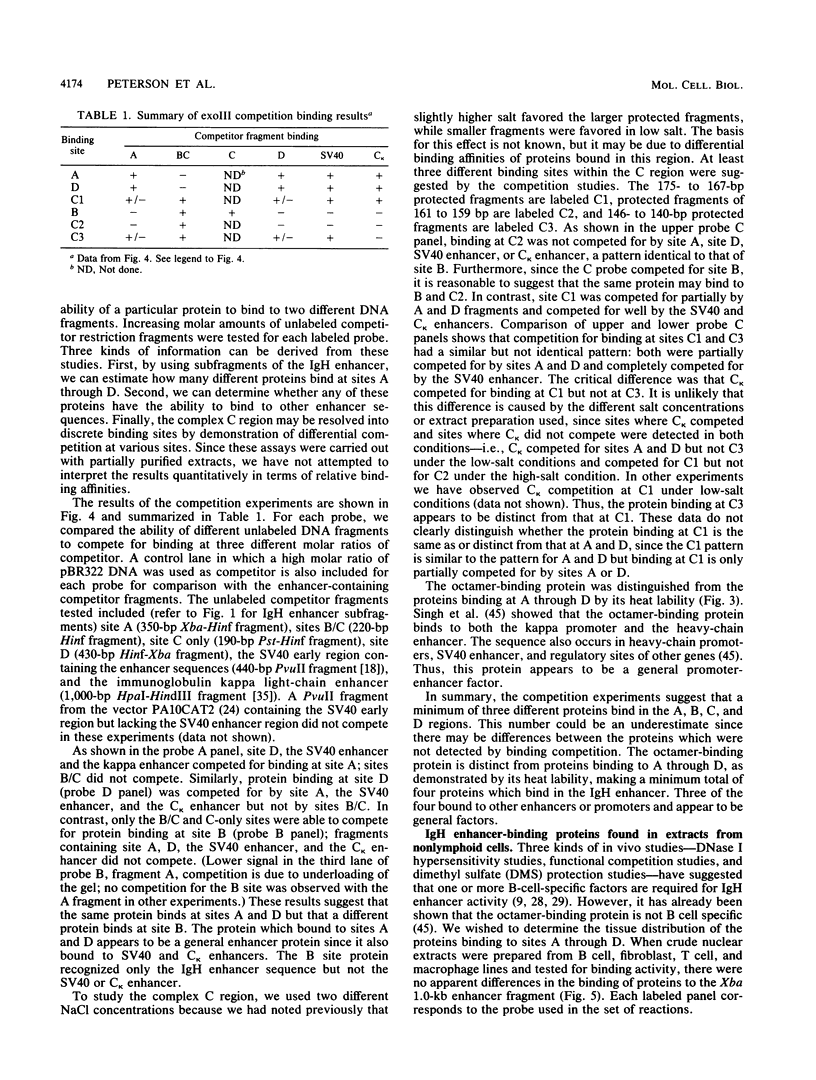
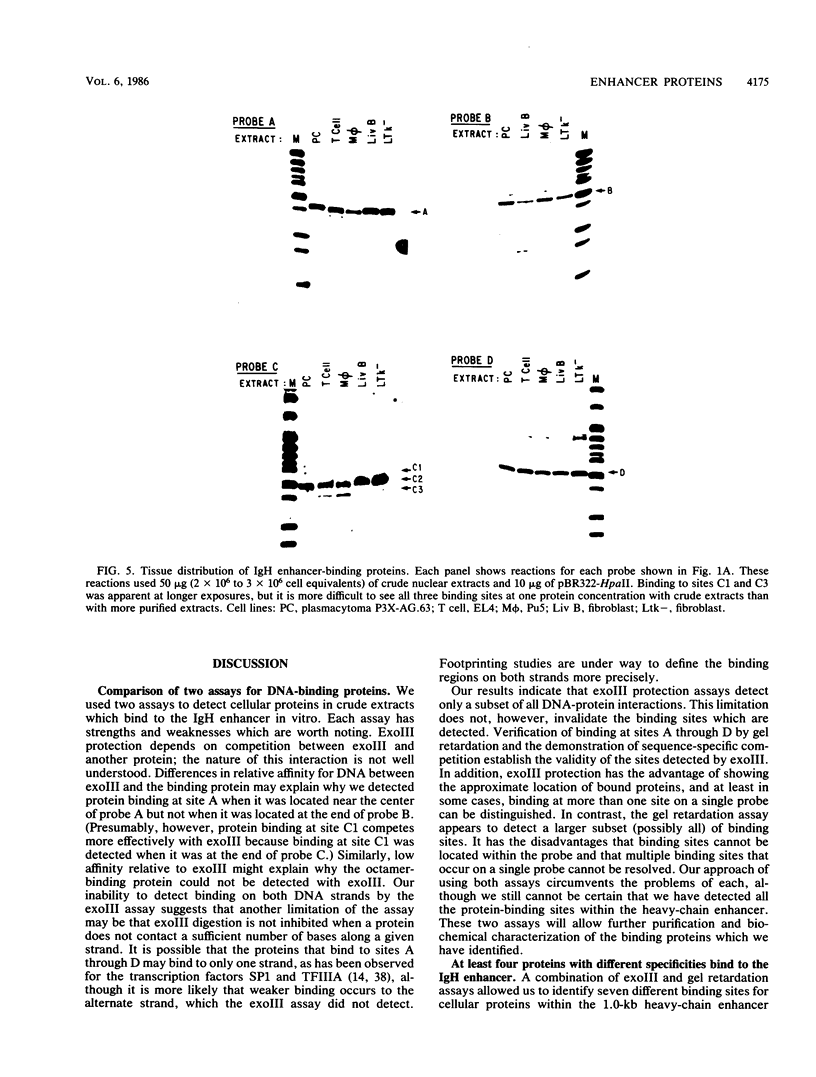
Seven protein-binding sites on the immunoglobulin heavy-chain (IgH) enhancer element have been identified by exonuclease III protection and gel retardation assays. It appears that the seven sites bind a minimum of four separate proteins. Three of these proteins also bind to other enhancers or promoters, but one protein seems to recognize exclusively IgH enhancer sequences. A complex of four binding sites, recognized by different proteins, is located within one 80-base-pair region of IgH enhancer DNA. Close juxtaposition of enhancer proteins may allow protein-protein interactions or be part of a mechanism for modulating enhancer protein activity. All IgH enhancer-binding proteins identified in this study were found in extracts from nonlymphoid as well as lymphoid cells. These data provide the first direct evidence that multiple proteins bind to enhancer elements and that while some of these proteins recognize common elements of many enhancers, others have more limited specificities.
Full text
PDF

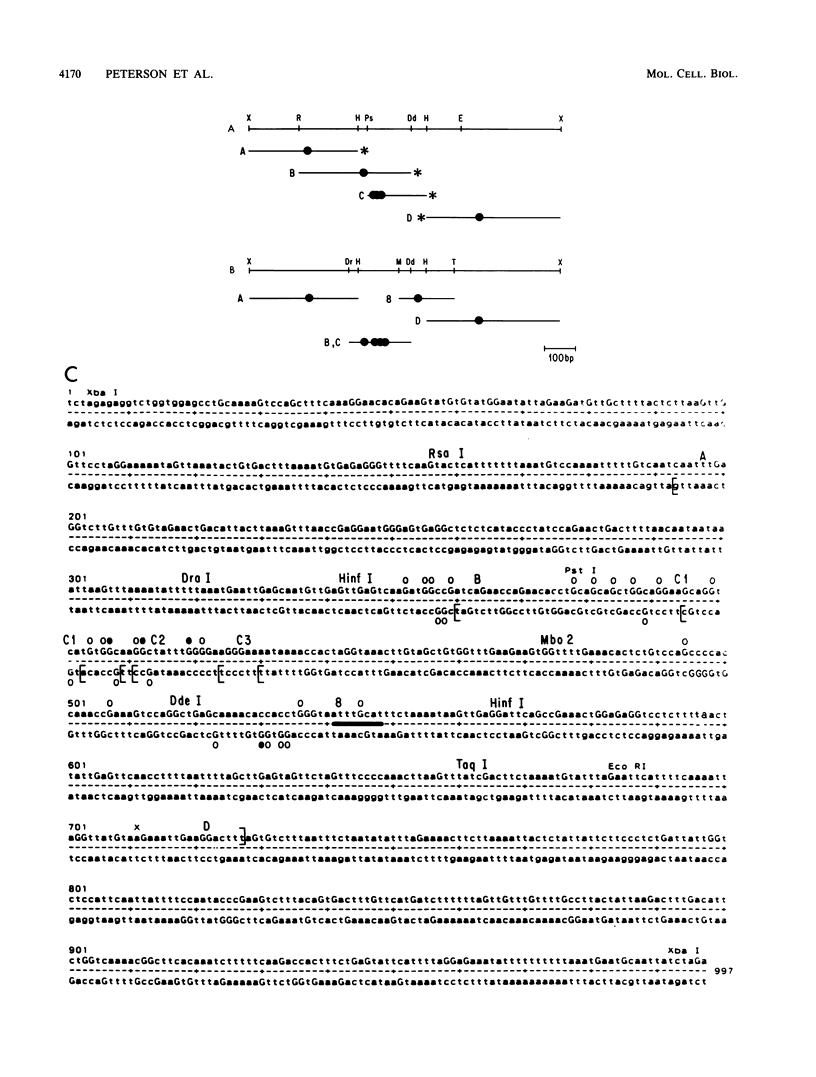
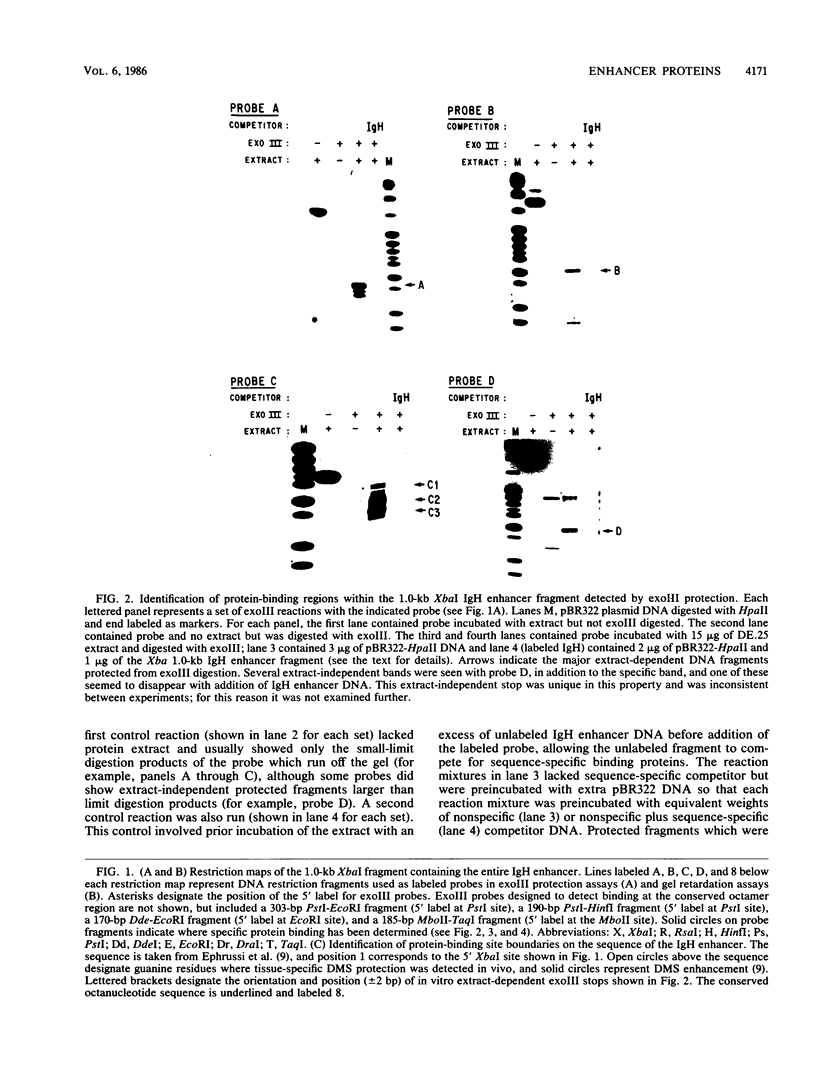
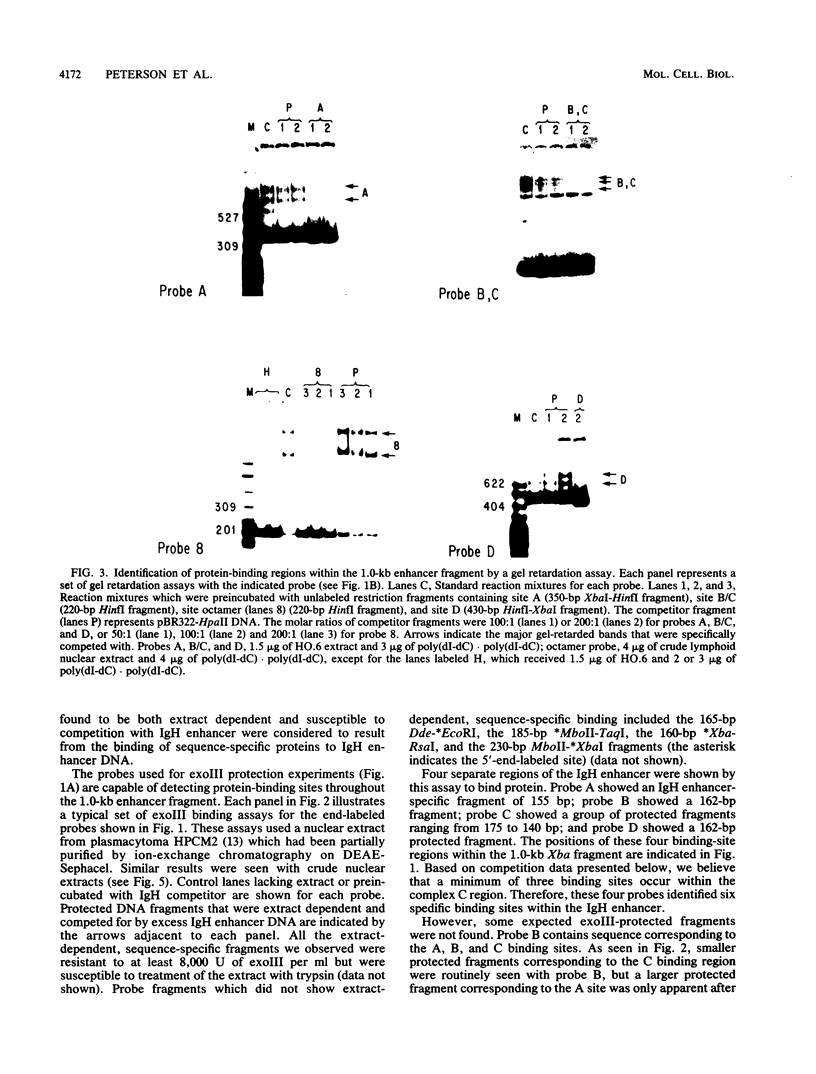
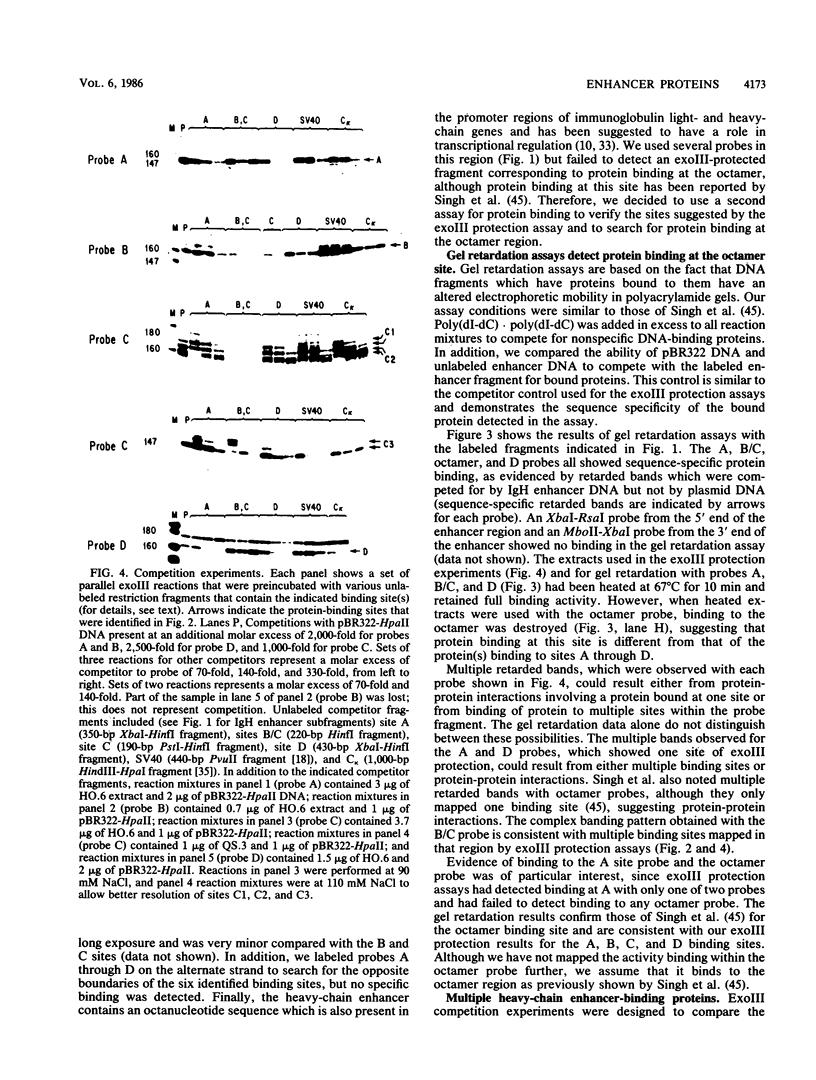



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Schlissel M. S. A positive transcription factor controls the differential expression of two 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Buttgereit D., Grummt I. A purified transcription factor (TIF-IB) binds to essential sequences of the mouse rDNA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):604–608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K. Nuclear activity from F9 embryonal carcinoma cells binding specifically to the enhancers of wild-type polyoma virus and PyEC mutant DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2845–2861. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J., Johnson N. D., Douglas R., Hood L. IgG antibodies to phosphorylcholine exhibit more diversity than their IgM counterparts. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):29–34. doi: 10.1038/291029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Wang X. F., Olsen J., Calame K. Transcriptional enhancer elements in the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.6306772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Fisher L. M., Kuroda R., Ford A. M., Gould H. J. DNase I hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of human mu immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):809–812. doi: 10.1038/306809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S. Expression and regulation of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene transfected into lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1373–1378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Leon M. A. Three IgA myeloma immunoglobulins from the BALB/ mouse: precipitation with pneumococcal C polysaccharide. Science. 1968 Oct 18;162(3851):369–371. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3851.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. G., Weiss B. Exonuclease III of Escherichia coli K-12, an AP endonuclease. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):201–211. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryals J., Dierks P., Ragg H., Weissmann C. A 46-nucleotide promoter segment from an IFN-alpha gene renders an unrelated promoter inducible by virus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):497–507. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholer H., Haslinger A., Heguy A., Holtgreve H., Karin M. In vivo competition between a metallothionein regulatory element and the SV40 enhancer. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3006253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Cell type-specific transcriptional enhancement in vitro requires the presence of trans-acting factors. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Binding of Drosophila heat-shock gene transcription factor to the hsp 70 promoter. Evidence for symmetric and dynamic interactions. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7934–7940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Wilson R., Selsing E., Walfield A. Rearranged and germline immunoglobulin kappa genes: different states of DNase I sensitivity of constant kappa genes in immunocompetent and nonimmune cells. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):990–996. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Maniatis T. Simian virus 40 enhancer increases number of RNA polymerase II molecules on linked DNA. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):73–75. doi: 10.1038/315072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., Schaffner W. Simian virus 40 enhancer increases RNA polymerase density within the linked gene. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):75–77. doi: 10.1038/315075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W. A small segment of polyoma virus DNA enhances the expression of a cloned beta-globin gene over a distance of 1400 base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6251–6264. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]