Abstract
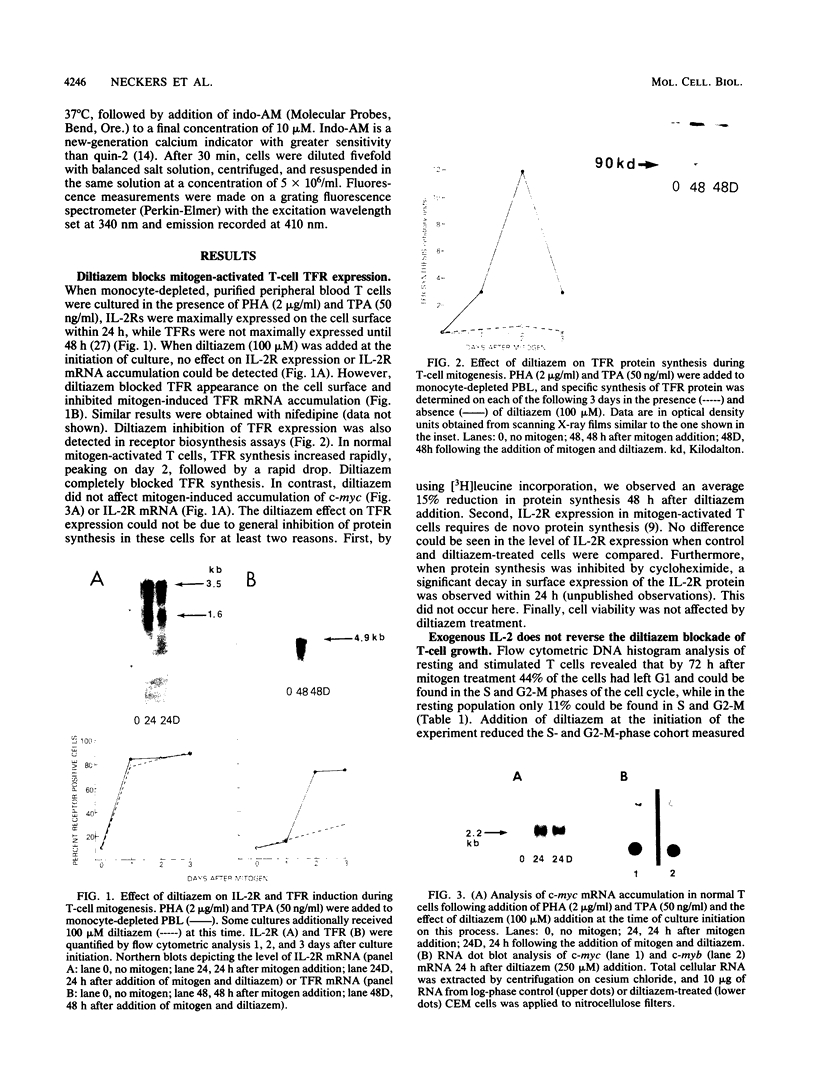
Transferrin receptor expression is essential for the proliferation of both normal and malignant T cells. While transferrin receptor expression in normal T cells is tightly coupled to interleukin-2 receptor expression, transferrin receptor expression in malignant cells is usually constitutive and is released from this constraint. Temporally, the appearance of these membrane receptors is preceded by changes in the expression of the proto-oncogenes c-myc and c-myb. In addition, although an increase in the level of intracellular free calcium occurs early in the sequence of T-cell activation, the activation events dependent on this calcium flux have not been resolved. In the present study we report that diltiazem, an ion channel-blocking agent that inhibits calcium influx, arrested the growth in vitro of both normal and malignant human T cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. However, diltiazem did not inhibit the expression of c-myc or interleukin-2 receptor mRNA and protein in normal mitogen-activated T cells or the constitutive expression of c-myc and c-myb mRNA in malignant T cells (T acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells). In contrast, diltiazem prevented the induction of transferrin receptor (mRNA and protein) in normal T cells and caused a progressive loss of transferrin receptor (mRNA and protein) in malignant T cells. These data demonstrate that diltiazem can dissociate several growth-related processes normally occurring in G1 and thereby disrupt the biochemical cascade leading to cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birx D. L., Berger M., Fleisher T. A. The interference of T cell activation by calcium channel blocking agents. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2904–2909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braylan R. C., Benson N. A., Nourse V., Kruth H. S. Correlated analysis of cellular DNA, membrane antigens and light scatter of human lymphoid cells. Cytometry. 1982 Mar;2(5):337–343. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990020511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Gupta S. A voltage-gated potassium channel in human T lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:197–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Cahalan M. D., Gupta S. Electroimmunology: the physiologic role of ion channels in the immune system. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2 Suppl):787s–791s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Cahalan M. D., McLaughlin C., Gupta S. Voltage-gated potassium channels are required for human T lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):369–385. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCoursey T. E., Chandy K. G., Gupta S., Cahalan M. D. Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: a role in mitogenesis? Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):465–468. doi: 10.1038/307465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Noguchi P. D., Cunningham R. E., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Regulation of interleukin 2 receptor expression: effects of phorbol diester, phospholipase C, and reexposure to lectin or antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3054–3061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., De Young M. B. Intracellular Ca2+ mobilization activated by extracellular ATP in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10653–10661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Wong-Staal F., Baluda M. A., Lengel C., Tronick S. R. Structural organization and expression of human DNA sequences related to the transforming gene of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7385–7389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Harford J., van Renswoude J. Rapid internalization of the transferrin receptor in K562 cells is triggered by ligand binding or treatment with a phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Daniele R. P., Greene W. C., Nowell P. C. Evidence for an interleukin-independent pathway for human lymphocyte activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3444–3447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Sequential expression of genes involved in human T lymphocyte growth and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of calcium channel blockade by verapamil, D600, diltiazem and nitrendipine in single dialysed heart cells. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):790–794. doi: 10.1038/302790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Peffer N. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 receptor gene expression in normal human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6281–6285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman A. H., Segel G. B., Lichtman M. A. The role of calcium in lymphocyte proliferation. (An interpretive review). Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):413–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattia E., Rao K., Shapiro D. S., Sussman H. H., Klausner R. D. Biosynthetic regulation of the human transferrin receptor by desferrioxamine in K562 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):2689–2692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Association of phorbol ester-induced hyperphosphorylation and reversible regulation of transferrin membrane receptors in HL60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckers L. M., Cossman J. Transferrin receptor induction in mitogen-stimulated human T lymphocytes is required for DNA synthesis and cell division and is regulated by interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3494–3498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckers L. M. Transferrin receptors regulate proliferation of normal and malignant B cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;113:62–68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69860-6_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckers L. M., Yenokida G., James S. P. The role of the transferrin receptor in human B lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2437–2441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckers L. M., Yenokida G., Trepel J. B., Lipford E., James S. Transferrin receptor induction is required for human B-lymphocyte activation but not for immunoglobulin secretion. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(4):377–389. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada S. A simple graphic method of computing the parameters of the life cycle of cultured mammalian cells in the exponential growth phase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Sep;34(3):915–916. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Grimm E. A., McGrogan M., Doyle M., Kawasaki E., Koths K., Mark D. F. Biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-2 produced in Escherichia coli. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6367046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Domingo D. L. Anti-transferrin receptor monoclonal antibody and toxin-antibody conjugates affect growth of human tumour cells. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):171–173. doi: 10.1038/294171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Lopez F. Monoclonal antibody to transferrin receptor blocks transferrin binding and inhibits human tumor cell growth in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1175–1179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







