Abstract
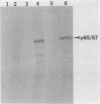
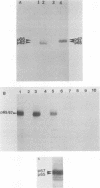
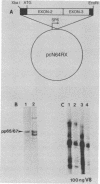
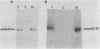
N-myc is a gene whose amplification has been implicated in the genesis of several malignant human tumors. We have identified two proteins with molecular weights of 65,000 and 67,000 encoded by N-myc. The abundance of these proteins in tumor cells was consonant with the extent of amplification of N-myc. The two proteins apparently arose from the same mRNA, were phosphorylated, were exceptionally unstable, were located in the nucleus of cells, and bound to both single- and double-stranded DNA. These properties suggest that the products of N-myc and of the related proto-oncogene c-myc may have similar biochemical functions and that N-myc may be a regulatory gene. Our findings sustain the view that inordinate expression of N-myc may contribute to the genesis of several different human tumors.
Full text
PDF


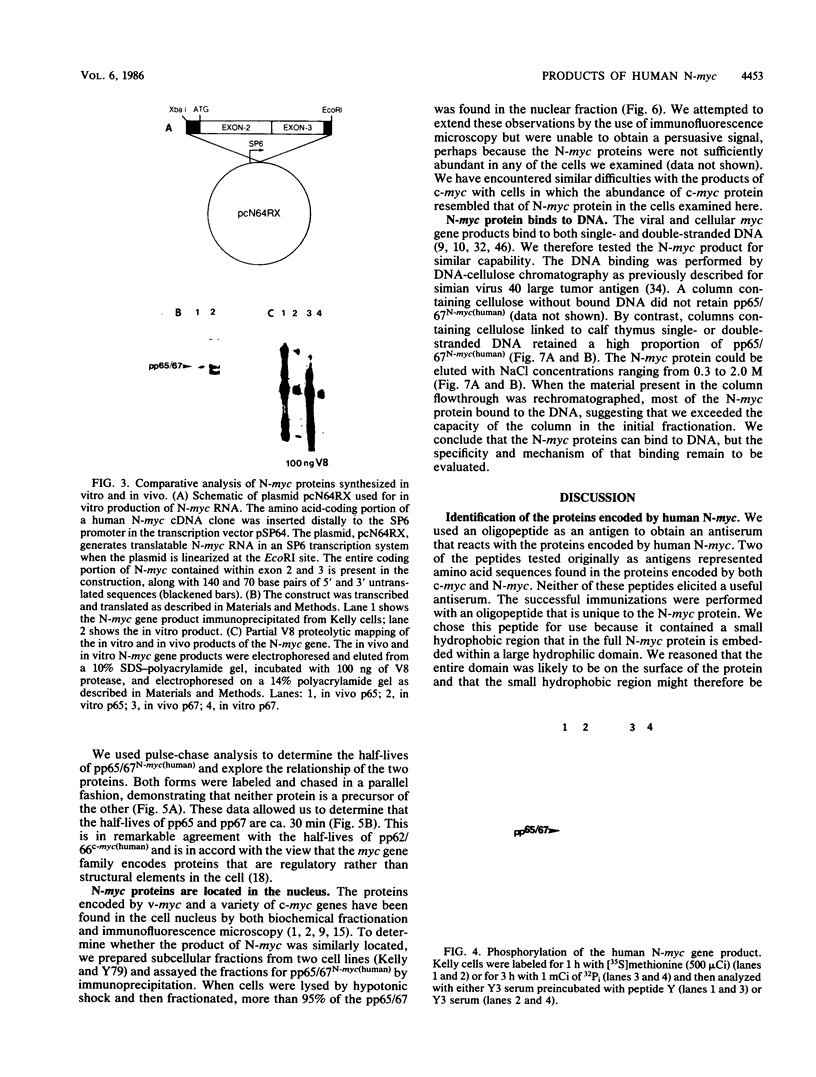
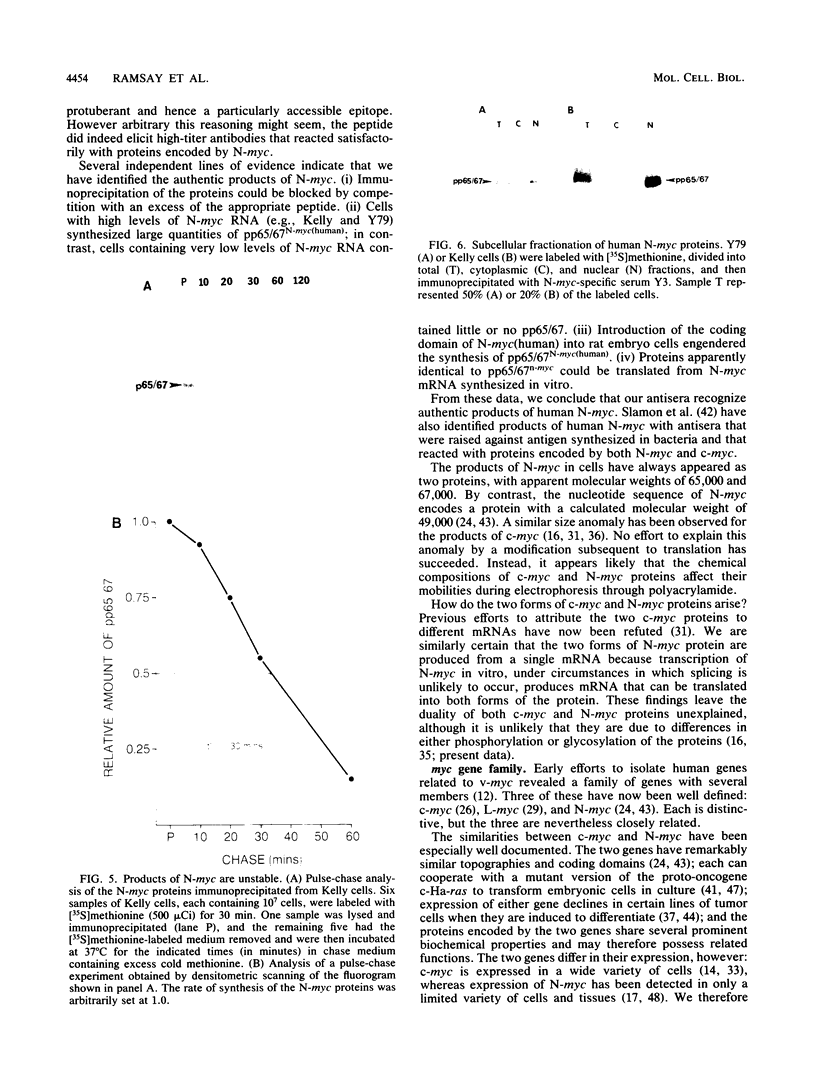
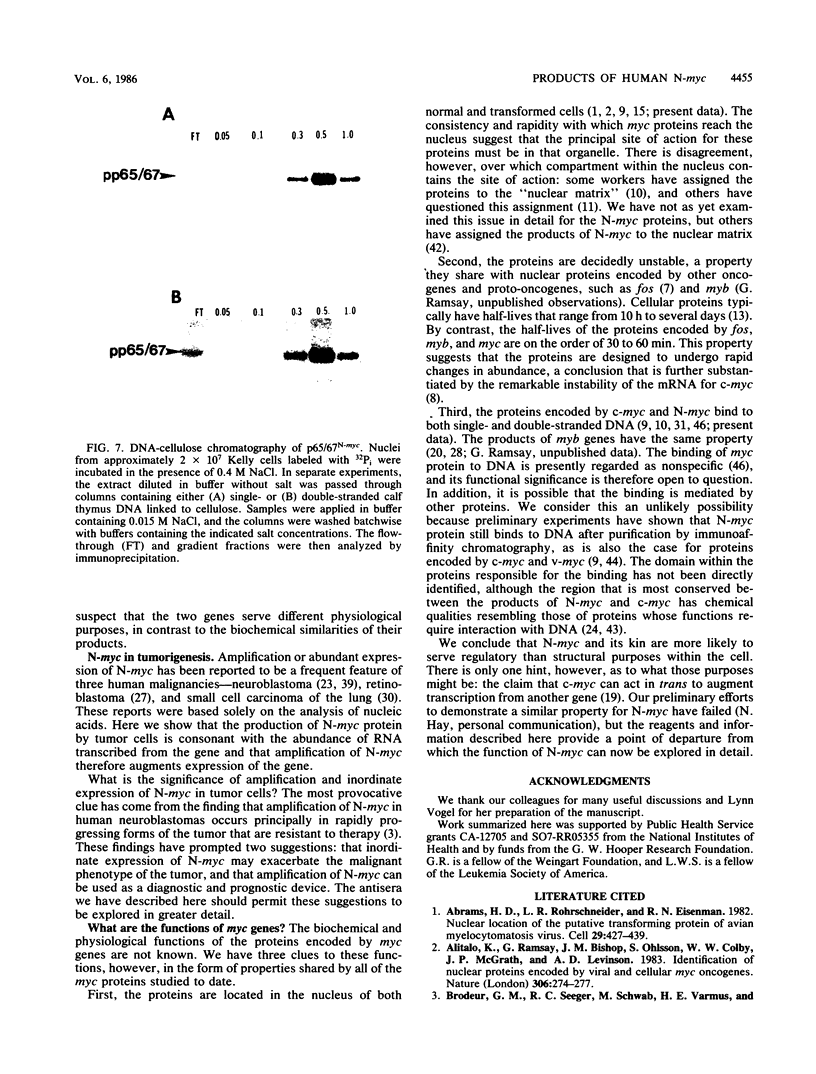


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Nuclear location of the putative transforming protein of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Pfeifer S. O., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Identification of nuclear proteins encoded by viral and cellular myc oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):274–277. doi: 10.1038/306274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur G. M., Seeger R. C., Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Amplification of N-myc in untreated human neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.6719137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Gelmann E. P., Martinotti S., Franchini G., Papas T. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Cloning and characterization of different human sequences related to the onc gene (v-myc) of avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6497–6501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner P., Greiser-Wilke I., Moelling K. Nuclear localization and DNA binding of the transforming gene product of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):262–269. doi: 10.1038/296262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Tachibana C. Y., Abrams H. D., Hann S. R. V-myc- and c-myc-encoded proteins are associated with the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Hancock D. C. Studies on the interaction of the human c-myc protein with cell nuclei: p62c-myc as a member of a discrete subset of nuclear proteins. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Sheiness D. K., Bishop J. M. Transcripts from the cellular homologs of retroviral oncogenes: distribution among chicken tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):617–624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by the human c-myc oncogene: differential expression in neoplastic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2486–2497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Schwab M., Bishop J. M., Martin G. R. Expression of N-myc in teratocarcinoma stem cells and mouse embryos. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):188–191. doi: 10.1038/318188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):280–282. doi: 10.1038/312280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Sippel A. E. Subnuclear localization of proteins encoded by the oncogene v-myb and its cellular homolog c-myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):62–69. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Symonds G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. Subcellular localization of proteins encoded by oncogenes of avian myeloblastosis virus and avian leukemia virus E26 and by chicken c-myb gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Gee C. E., Alt F. W. Activated expression of the N-myc gene in human neuroblastomas and related tumors. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1335–1337. doi: 10.1126/science.6505694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Kanda N., Schreck R. R., Bruns G., Latt S. A., Gilbert F., Alt F. W. Transposition and amplification of oncogene-related sequences in human neuroblastomas. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Legouy E., DePinho R. A., Nisen P. D., Smith R. K., Gee C. E., Alt F. W. Human N-myc is closely related in organization and nucleotide sequence to c-myc. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):73–77. doi: 10.1038/319073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
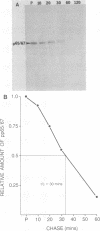
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Battey J., Lenoir G., Moulding C., Murphy W., Potter H., Stewart T., Taub R. Translocations among antibody genes in human cancer. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):765–771. doi: 10.1126/science.6356357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Murphree A. L., Benedict W. F. Expression and amplification of the N-myc gene in primary retinoblastoma. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):458–460. doi: 10.1038/309458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moelling K., Pfaff E., Beug H., Beimling P., Bunte T., Schaller H. E., Graf T. DNA-binding activity is associated with purified myb proteins from AMV and E26 viruses and is temperature-sensitive for E26 ts mutants. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):983–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90358-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau M. M., Brooks B. J., Battey J., Sausville E., Gazdar A. F., Kirsch I. R., McBride O. W., Bertness V., Hollis G. F., Minna J. D. L-myc, a new myc-related gene amplified and expressed in human small cell lung cancer. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):69–73. doi: 10.1038/318069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau M. M., Brooks B. J., Jr, Carney D. N., Gazdar A. F., Battey J. F., Sausville E. A., Minna J. D. Human small-cell lung cancers show amplification and expression of the N-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1092–1096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Hennighausen L., Taub R., DeGrado W., Leder P. Antibodies to human c-myc oncogene product: evidence of an evolutionarily conserved protein induced during cell proliferation. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):687–693. doi: 10.1126/science.6431612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Leder P. Nuclear localization and DNA binding properties of a protein expressed by human c-myc oncogene. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):718–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6463648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Goustin A. S., Rydnert J., Wahlström T., Bjersing L., Stehelin D., Ohlsson R. Spatial and temporal pattern of cellular myc oncogene expression in developing human placenta: implications for embryonic cell proliferation. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90513-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Barnet B., Scheller A., Khoury G., Jay G. Discrete regions of simian virus 40 large T antigen are required for nonspecific and viral origin-specific DNA binding. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):73–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.73-82.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the human proto-oncogene c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Hayman M. J., Bister K. Phosphorylation of specific sites in the gag-myc polyproteins encoded by MC29-type viruses correlates with their transforming ability. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1111–1116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Rothberg P. G., Astrin S. M., Trial J., Bar-Shavit Z., Hall A., Teitelbaum S. L., Kahn A. J. Regulation of myc gene expression in HL-60 leukaemia cells by a vitamin D metabolite. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):492–494. doi: 10.1038/306492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumour. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Ellison J., Busch M., Rosenau W., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Enhanced expression of the human gene N-myc consequent to amplification of DNA may contribute to malignant progression of neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4940–4944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Human N-myc gene contributes to neoplastic transformation of mammalian cells in culture. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):160–162. doi: 10.1038/316160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Boone T. C., Seeger R. C., Keith D. E., Chazin V., Lee H. C., Souza L. M. Identification and characterization of the protein encoded by the human N-myc oncogene. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):768–772. doi: 10.1126/science.3008339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Boone T. C., Seeger R. C., Keith D. E., Chazin V., Lee H. C., Souza L. M. Identification and characterization of the protein encoded by the human N-myc oncogene. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):768–772. doi: 10.1126/science.3008339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the human N-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1772–1776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele C. J., Reynolds C. P., Israel M. A. Decreased expression of N-myc precedes retinoic acid-induced morphological differentiation of human neuroblastoma. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):404–406. doi: 10.1038/313404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R. A., Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Expression and characterization of the human c-myc DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):448–456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Nisen P. D., Tesfaye A., Kohl N. E., Goldfarb M. P., Alt F. W. N-myc can cooperate with ras to transform normal cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Collum R. G., Smith R. K., Kohl N. E., Denis K. A., Nau M. M., Witte O. N., Toran-Allerand D., Gee C. E. Differential expression of myc family genes during murine development. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):780–783. doi: 10.1038/319780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]