Abstract
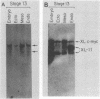
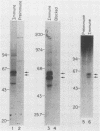
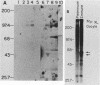
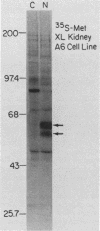
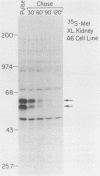
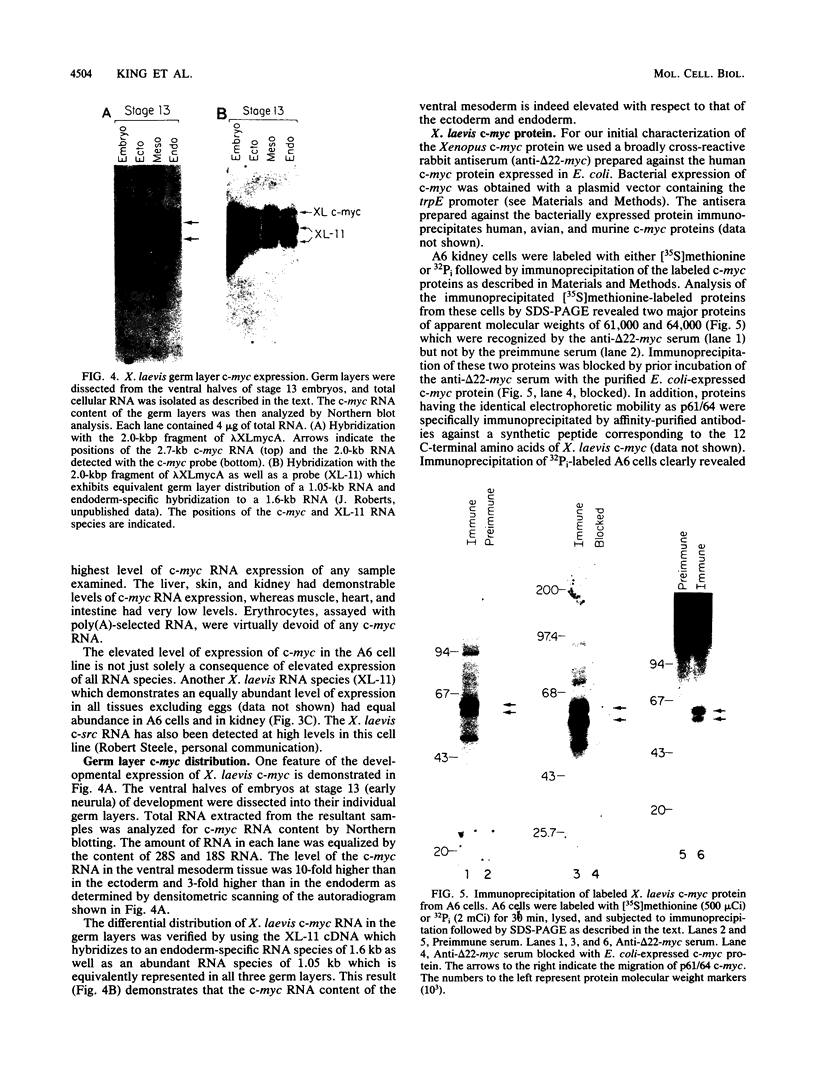
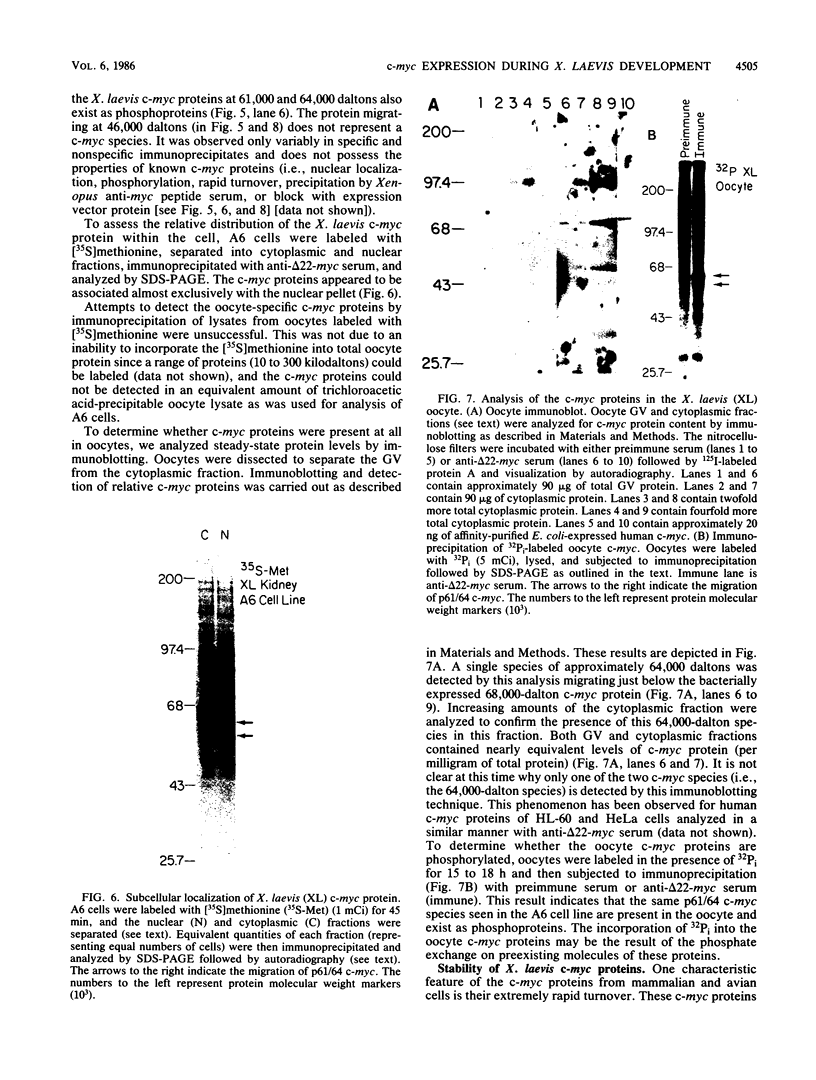
We isolated and characterized Xenopus laevis c-myc cDNAs from an oocyte-specific library. These cDNA clones encompass 2.35 kilobases of the X. laevis c-myc RNA and contain the entire coding domain of 1,257 nucleotides of the 419-amino acid-long X. laevis c-myc protein. The 2.7-kilobase X. laevis c-myc mRNA is expressed in the oocyte, maintained in the egg, and is present throughout the early cleavage stages of embryogenesis. At the time of transcriptional activation in the embryo the c-myc RNA levels show a significant decline and then reaccumulate continuously throughout the remainder of premorphogenic development. At the early neurula stage of embryogenesis the pattern of c-myc RNA expression is elevated in the mesoderm with respect to the endoderm and ectoderm. In the adult X. laevis the c-myc mRNA is expressed in some (e.g., skin, muscle) but not all differentiated tissues. The X. laevis c-myc protein migrates as a doublet of 61,000- and 64,000-dalton species. Both species are phosphorylated in oocytes and somatic cells, exhibit extremely short half-lives of less than 30 min, and are localized to the nuclear fraction of somatic cells. By contrast, the oocyte protein shows both cytoplasmic and germinal vesicle distribution and appears to be stable.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Nuclear location of the putative transforming protein of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Cory S., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Adams J. M. Sequence of the murine and human cellular myc oncogenes and two modes of myc transcription resulting from chromosome translocation in B lymphoid tumours. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2375–2383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., Dani C., Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Pouyssegur J., Jeanteur P. c-myc gene is transcribed at high rate in G0-arrested fibroblasts and is post-transcriptionally regulated in response to growth factors. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):443–445. doi: 10.1038/317443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Chen E. Y., Smith D. H., Levinson A. D. Identification and nucleotide sequence of a human locus homologous to the v-myc oncogene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):722–725. doi: 10.1038/301722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Graham M., Webb E., Corcoran L., Adams J. M. Variant (6;15) translocations in murine plasmacytomas involve a chromosome 15 locus at least 72 kb from the c-myc oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):675–681. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Bravo R., Müller R. Transient induction of c-fos and c-myc in an immediate consequence of growth factor stimulation. Cancer Surv. 1985;4(4):655–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic segregation of proteins and RNAs. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1021–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Sharnick S. V., Laskey R. A. A polypeptide domain that specifies migration of nucleoplasmin into the nucleus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dony C., Kessel M., Gruss P. Post-transcriptional control of myc and p53 expression during differentiation of the embryonal carcinoma cell line F9. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):636–639. doi: 10.1038/317636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Tachibana C. Y., Abrams H. D., Hann S. R. V-myc- and c-myc-encoded proteins are associated with the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Nadal-Ginard B. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of c-myc during myogenesis: its mRNA remains inducible in differentiated cells and does not suppress the differentiated phenotype. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1412–1421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J., Kirschner M. W., Newport J. W. Spontaneous formation of nucleus-like structures around bacteriophage DNA microinjected into Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Kozasa T., Kaziro Y., Takeda T., Yamamoto M. Role of a ras homolog in the life cycle of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J., Wu M., Kirschner M. Cell cycle dynamics of an M-phase-specific cytoplasmic factor in Xenopus laevis oocytes and eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Metcalf D. Expression of myb, myc and fos proto-oncogenes during the differentiation of a murine myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):249–251. doi: 10.1038/310249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Sheiness D. K., Bishop J. M. Transcripts from the cellular homologs of retroviral oncogenes: distribution among chicken tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):617–624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosso L. E., Pitot H. C. Transcriptional regulation of c-myc during chemically induced differentiation of HL-60 cultures. Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):847–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by the human c-myc oncogene: differential expression in neoplastic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2486–2497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Thompson C. B., Eisenman R. N. c-myc oncogene protein synthesis is independent of the cell cycle in human and avian cells. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):366–369. doi: 10.1038/314366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Weintraub H., McKnight S. L. Transcription of DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is influenced by template topology. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):38–43. doi: 10.1038/302038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Masui Y. Formation in vitro of sperm pronuclei and mitotic chromosomes induced by amphibian ooplasmic components. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):719–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6601299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake-Lye R., Kirschner M. W. Induction of early mitotic events in a cell-free system. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Lucocq J. M., Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. Assembly in vitro of nuclei active in nuclear protein transport: ATP is required for nucleoplasmin accumulation. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):501–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: II. Control of the onset of transcription. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):687–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Weeks D. L., Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Identification and cloning of localized maternal RNAs from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Wasserman W. J., Smith L. D. The mechanism for increased protein synthesis during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. 1982 Jan;89(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Drees B., Kornberg T., Bishop J. M. The nucleotide sequence and the tissue-specific expression of Drosophila c-src. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. E. Two divergent cellular src genes are expressed in Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1747–1761. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Levels of c-myc oncogene mRNA are invariant throughout the cell cycle. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):363–366. doi: 10.1038/314363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman W. J., Richter J. D., Smith L. D. Protein synthesis during maturation promoting factor- and progesterone-induced maturation in Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1982 Jan;89(1):152–158. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R., Stanton L. W., Marcu K. B., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M., Rovera G. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA of human c-myc oncogene. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):725–728. doi: 10.1038/303725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Collum R. G., Smith R. K., Kohl N. E., Denis K. A., Nau M. M., Witte O. N., Toran-Allerand D., Gee C. E. Differential expression of myc family genes during murine development. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):780–783. doi: 10.1038/319780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]