Abstract
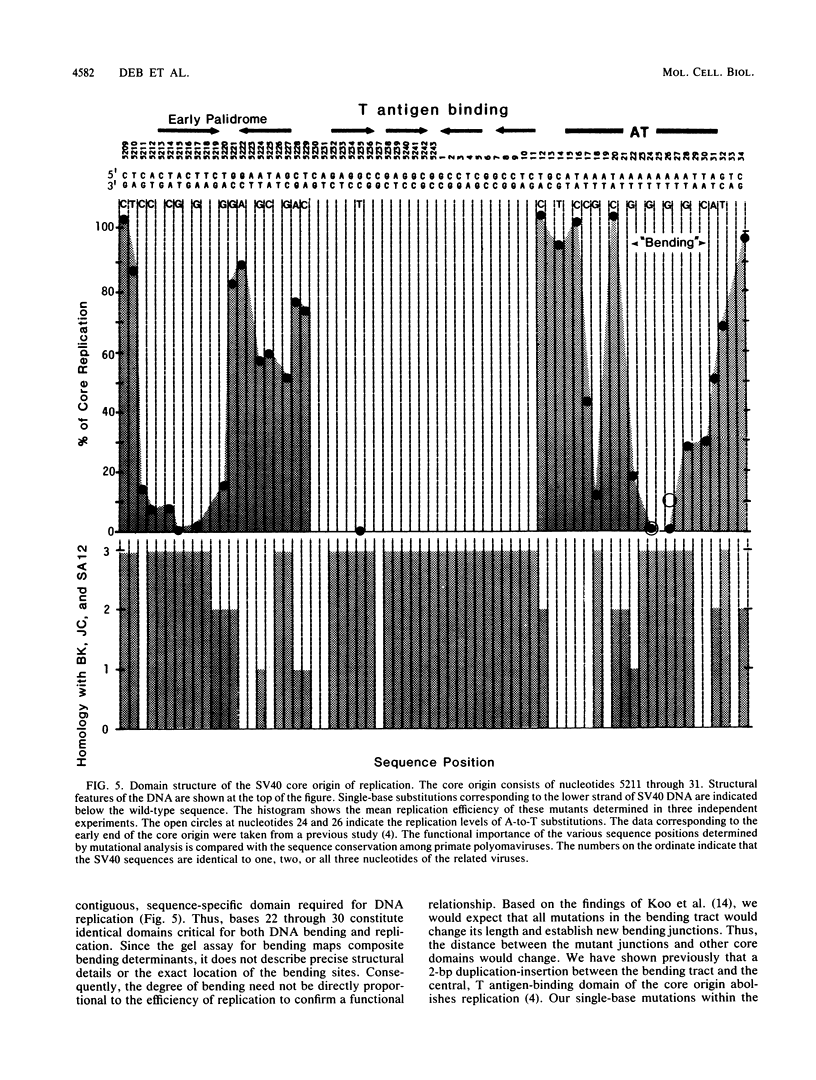
The simian virus 40 origin of replication contains a 20-base-pair adenine-thymine-rich segment with the sequence 5'-TGCATAAATAAAAAAAATTA-3'. The continuous tract of eight adenines is highly conserved among polyomaviruses. We used single-base substitutions to map structural and functional features of this DNA. Mutations in the AAA and AAAAAAAATT sequences significantly reduce DNA replication and thus identify two sequence-specific functional domains or a single domain with two parts. The AAAAAAAATT sequence also determines a DNA conformation that is characteristic of DNA bending. Single-base mutations in this domain change the degree of net bending, presumably by altering the length and location of the bending sequence. Thus, DNA bending in the correct conformation and location may be a structural signal for replication in polyomavirus origins and perhaps in other origins of replication with consecutive runs of adenines. The first five base pairs (TGCAT) of the 20-base-pair segment and the T between the AAA and AAAAAAAATT domains serve a sequence-independent function that may establish proper spacing within the core origin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake R. D., Lefoley S. G. Spectral analysis of high resolution direct-derivative melting curves of DNA for instantaneous and total base composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 27;518(2):233–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Smith D. M. Conformational change in the DNA associated with an unusual promoter mutation in a tRNA operon of Salmonella. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. P., Pipas J. M. Simian agent 12 is a BK virus-like papovavirus which replicates in monkey cells. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):483–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.483-492.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Deb S., Partin K., Tegtmeyer P. Functional interactions of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication with flanking regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.138-144.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Baur C. P., Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Domain structure of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1663–1670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Wang J. C. On the sequence determinants and flexibility of the kinetoplast DNA fragment with abnormal gel electrophoretic mobilities. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Bream G. L., Cannella M. T. Human polyomavirus JC virus genome. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):458–469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.458-469.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström T., Zenke W. M., Wintzerith M., Matthes H. W., Staub A., Chambon P. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis by microscale 'shot-gun' gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3305–3316. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication in vivo: location and structure of 5' ends of DNA synthesized in the ori region. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearsey S. Structural requirements for the function of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Regulation of initiation of DNA replication. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:355–391. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Peden K. W., Dixon R. A., Kelly T. Functional organization of the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1117–1128. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Silver S., DeLucia A. L., Fanning E., Tegtmeyer P. An altered DNA conformation in origin region I is a determinant for the binding of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90838-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A mammalian high mobility group protein recognizes any stretch of six A.T base pairs in duplex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B., Gerard R. D., Guggenheimer R. A., Gluzman Y. T antigen and template requirements for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2933–2939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamanoi F., Stillman B. W. The origin of adenovirus DNA replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;109:75–87. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69460-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Transcription from the SV40 early-early and late-early overlapping promoters in the absence of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., DePamphilis M. L. DNA binding site for a factor(s) required to initiate simian virus 40 DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1646–1650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Binding and bending of the lambda replication origin by the phage O protein. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3605–3616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Sequence-induced DNA curvature at the bacteriophage lambda origin of replication. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):451–453. doi: 10.1038/317451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






