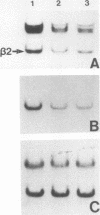
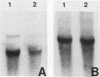
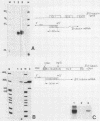
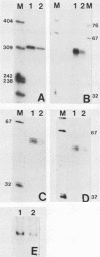
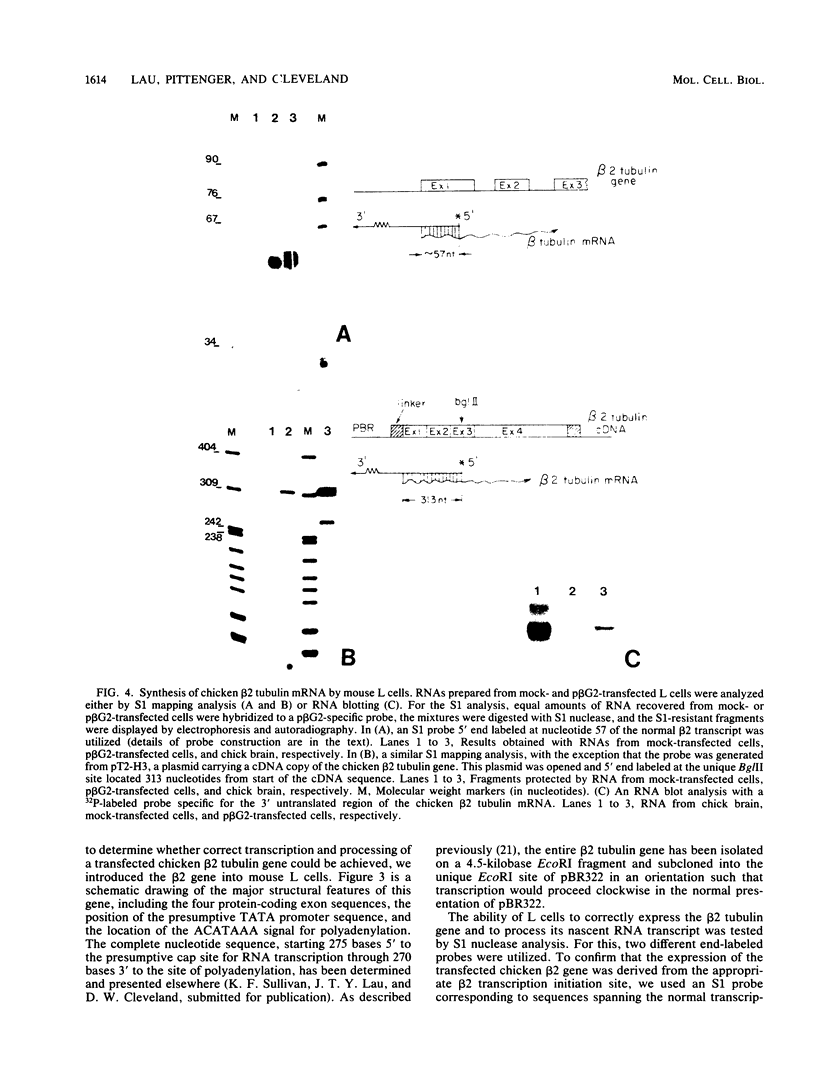
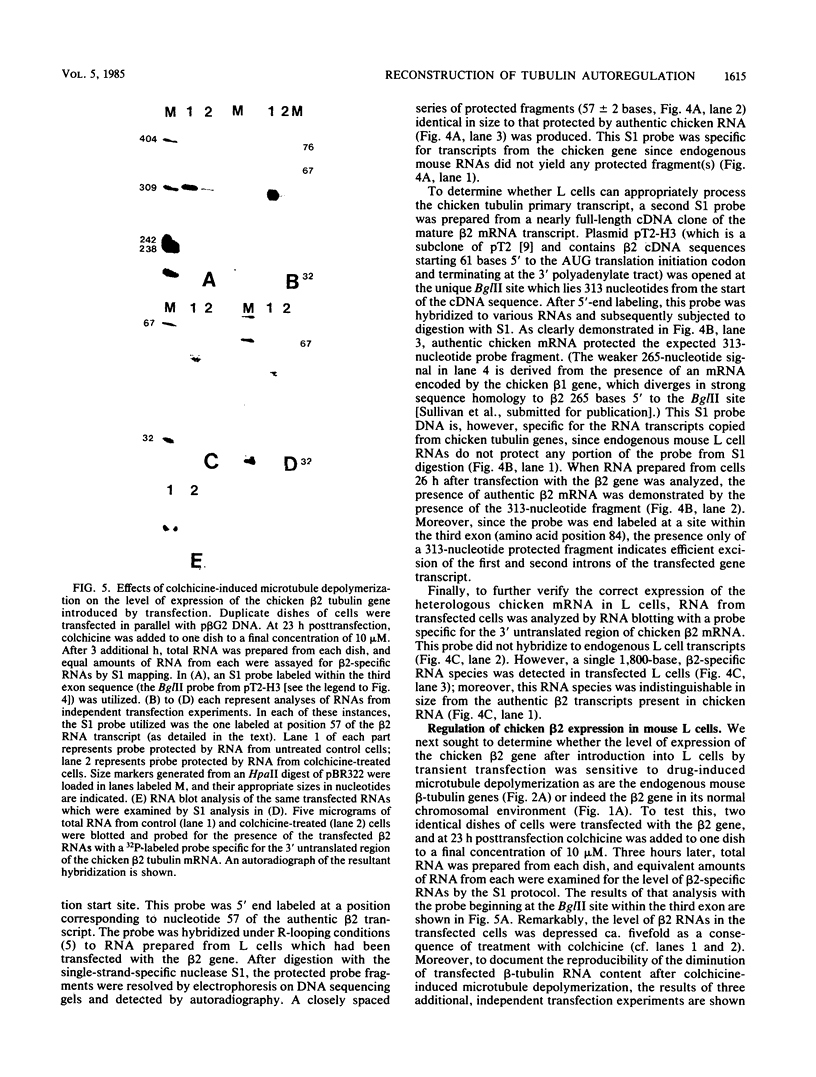
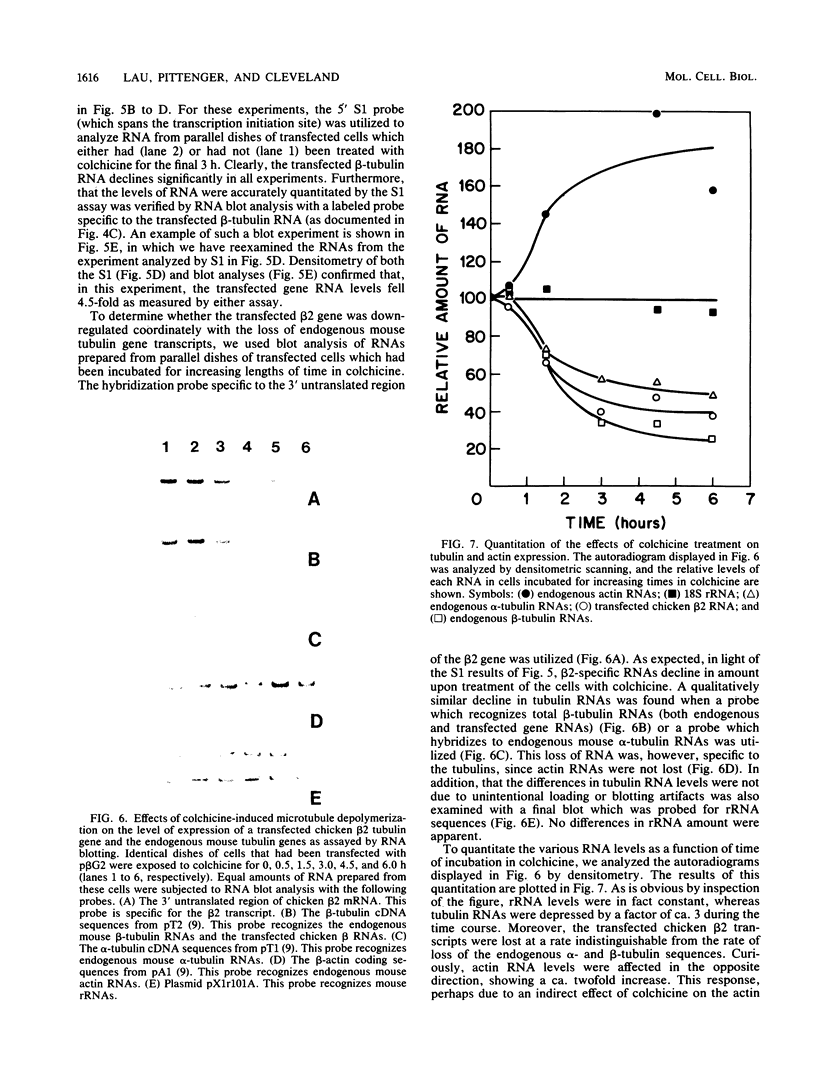
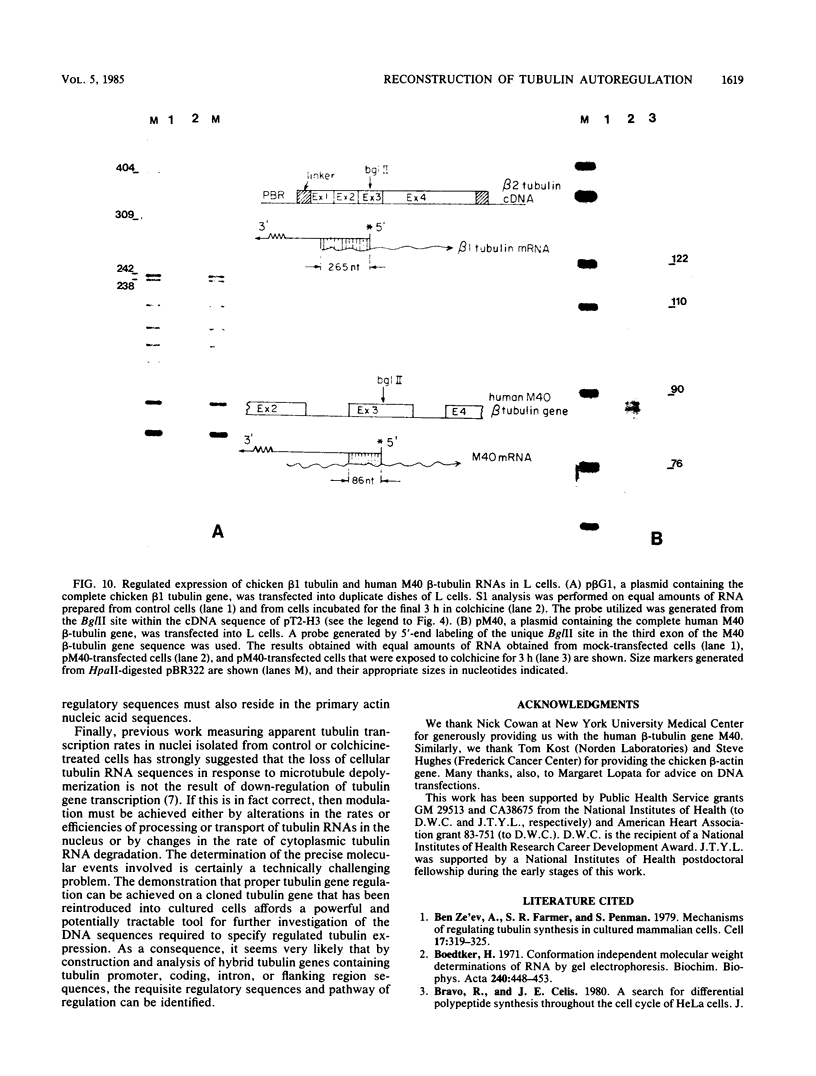
Abstract
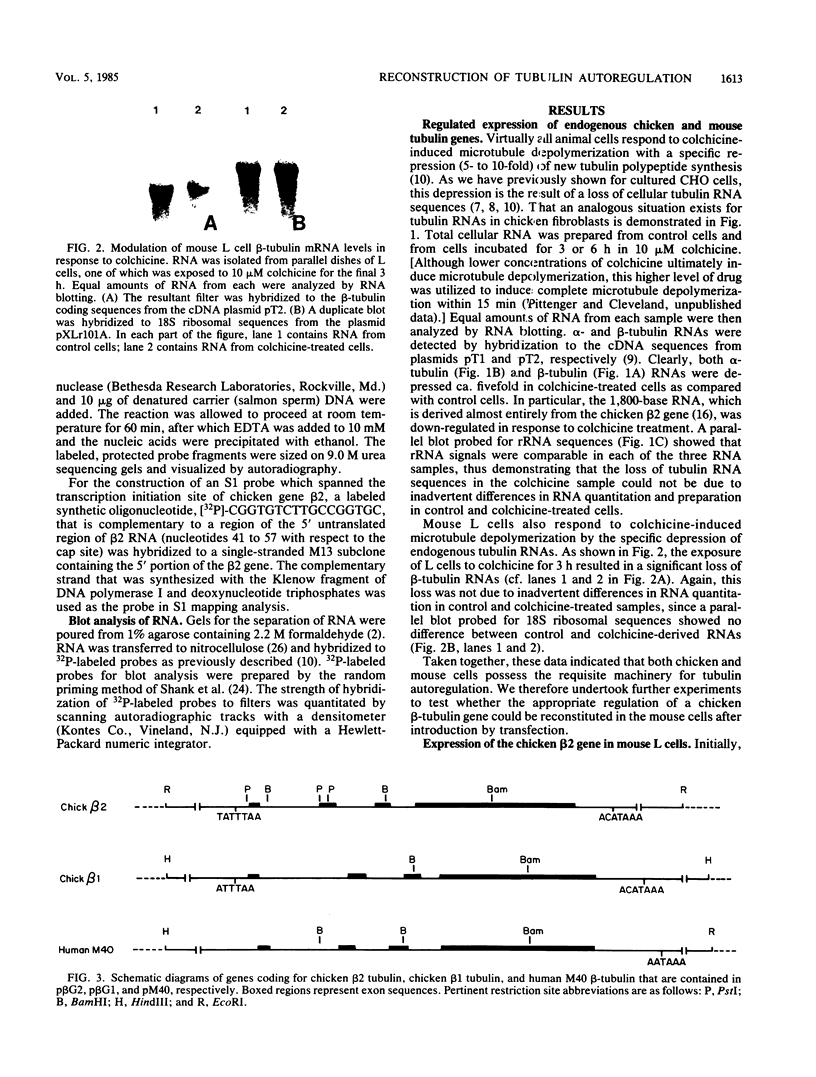
Most animal cells rapidly depress the synthesis of new alpha- and beta-tubulin polypeptides in response to microtubule inhibitors that increase the pool of depolymerized subunits. This apparent autoregulatory control of tubulin synthesis is achieved through the modulation of tubulin mRNA levels. To begin to analyze the molecular mechanism responsible for such regulation, we have introduced exogenous beta-tubulin gene sequences into cultured mouse cells by DEAE-dextran-mediated DNA transfection. We find that the heterologous tubulin genes are expressed and that their RNA transcripts are accurately processed to mature mRNAs. Moreover, after drug-induced microtubule depolymerization, the expression of unintegrated tubulin gene sequences is regulated coordinately with the endogenous mouse alpha- and beta-tubulin RNA transcripts. Such regulation appears to be specific for transfected tubulin genes, since similar down-regulation is not observed in a contransfected beta-actin gene. Curiously, in response to microtubule depolymerization, the amount of RNA transcripts from a transfected beta-actin gene increases twofold, which qualitatively and quantitatively parallels that seen by the RNAs encoded by the endogenous actin genes. Thus, the transient DNA transfection approach may permit the unambiguous elucidation of regulatory sequences involved in establishing the proper level of expression of these two important cytoskeletal gene families.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Farmer S. R., Penman S. Mechanisms of regulating tubulin synthesis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. Vinblastine and microtubules. I. Induction and isolation of crystals from sea urchin oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1971 May;66(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J., Davidson N. Rates of formation and thermal stabilities of RNA:DNA and DNA:DNA duplexes at high concentrations of formamide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1539–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Havercroft J. C. Is apparent autoregulatory control of tubulin synthesis nontranscriptionally regulated? J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):919–924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., Sherline P., Kirschner M. W. Unpolymerized tubulin modulates the level of tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Pittenger M. F., Feramisco J. R. Elevation of tubulin levels by microinjection suppresses new tubulin synthesis. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):738–740. doi: 10.1038/305738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Pittenger M. F., Lopata M. A. Autoregulatory control of expression of alpha and beta tubulin. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1983 Jan;15(1):353–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D., Kirschner M. Autoregulatory control of the expression of alpha- and beta-tubulins: implications for microtubule assembly. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):171–183. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Brabander M. J., Van de Veire R. M., Aerts F. E., Borgers M., Janssen P. A. The effects of methyl (5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl) carbamate, (R 17934; NSC 238159), a new synthetic antitumoral drug interfering with microtubules, on mammalian cells cultured in vitro. Cancer Res. 1976 Mar;36(3):905–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. II. Inhibition of protein synthesis at the level of initiation during mitosis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):655–670. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havercroft J. C., Cleveland D. W. Programmed expression of beta-tubulin genes during development and differentiation of the chicken. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1927–1935. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller G., Weber K. Radioimmunoassay for tubulin: a quantitative comparison of the tubulin content of different established tissue culture cells and tissues. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):795–804. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost T. A., Theodorakis N., Hughes S. H. The nucleotide sequence of the chick cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8287–8301. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Lewis S. A., Wilde C. D., Cowan N. J. Evolutionary history of a multigene family: an expressed human beta-tubulin gene and three processed pseudogenes. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90429-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Havercroft J. C., Chow L. T., Cleveland D. W. Four unique genes required for beta tubulin expression in vertebrates. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Fant J., Horwitz S. B. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):665–667. doi: 10.1038/277665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1561–1565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Hughes S. H., Kung H. J., Majors J. E., Quintrell N., Guntaka R. V., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Mapping unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: termini of linear DNA bear 300 nucleotides present once or twice in two species of circular DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1383–1395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Penningroth S. M., Kirschner M. W. Turnover of tubulin and the N site GTP in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):587–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W., Cleveland D. W. Nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequences encoded by alpha and beta tubulin mRNAs. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):650–655. doi: 10.1038/289650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pollack R., Bibring T. Antibody against tuberlin: the specific visualization of cytoplasmic microtubules in tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]