Abstract
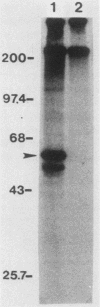
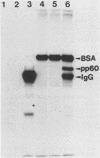
We constructed a mutant, called RSV-SF2, at the ATP-binding site of pp60v-src. In this mutant, lysine-295 is replaced with methionine. SF2 pp60v-src was found to have a half-life similar to that of wild-type pp60v-src and was localized in the membranous fraction of the cell. Rat cells expressing SF2 pp60v-src were morphologically untransformed and do not form tumors. The SF2 pp60v-src isolated from these cells lacked kinase activity with either specific immunoglobulin or other substrates, and expression of SF2 pp60v-src failed to cause an increase of total phosphotyrosine in the proteins of infected cells. Wild-type pp60v-src was phosphorylated on serine and tyrosine in infected cells, and the analogous phosphorylations could also be carried out in vitro. Phosphorylation of serine was catalyzed by a cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, and phosphorylation of tyrosine was perhaps catalyzed by pp60v-src itself. By contrast, SF2 pp60v-src could not be phosphorylated on serine or tyrosine either in infected cells or in vitro. These findings strengthen the belief that the phosphotransferase activity of pp60v-src is required for neoplastic transformation by the protein and suggest that the binding of ATP to pp60v-src elicits an allosteric change required for phosphorylation of serine in the protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker W. C., Dayhoff M. O. Viral src gene products are related to the catalytic chain of mammalian cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Hunter T. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus src gene products synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):551–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.551-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Pessac B. Growth stimulation of chicl embryo neuroretinal cells infected with Rous sarcoma virus: relationship to viral replication and morphological transformation. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):336–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Belzer S. K., Purchio A. F. Structurally and functionally modified forms of pp60v-src in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cell lysates. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1213–1220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Structural analysis of the avian sarcoma virus transforming protein: sites of phosphorylation. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):770–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.770-781.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson E., Purchio A. F., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. A normal cell protein similar in structure and function to the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3159–3163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Wells S. K., Purchio A. F. Physical modification of purified Rous sarcoma virus pp60v-src protein after incubation with ATP/Mg2+. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Esch F. S., Taylor S. S., Hunter T. Phosphorylation sites in enolase and lactate dehydrogenase utilized by tyrosine protein kinases in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7835–7841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J., Nakamura K. D., Hunter T., Weber M. J. Phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and expression of transformation parameters in cells infected with partial transformation mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):15–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.15-28.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus (pp60src) and a homologous protein in normal cells (pp60proto-src) are associated with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3783–3787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Local mutagenesis of Rous sarcoma virus: the major sites of tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of pp60src are dispensable for transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V. Structural aspects of the catalytic and regulatory function of glycogen phosphorylase. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(2):125–139. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L., Collett M. S., Erikson E., Purchio A. F. Evidence that the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product is a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6260–6264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. Transformation of rat cells by DNA of human adenovirus 5. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):536–539. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J. Surface and inside volumes in globular proteins. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):491–492. doi: 10.1038/277491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Taylor S. S., Sefton B. M. Direct evidence that oncogenic tyrosine kinases and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase have homologous ATP-binding sites. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):589–592. doi: 10.1038/310589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Evidence that the src gene product of Rous sarcoma virus is membrane associated. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):25–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The purified product of the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11973–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Kawai S. Two cellular proteins that immunoprecipitate with the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):736–751. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Levintow L., Bishop J. M. Uninfected vertebrate cells contain a protein that is closely related to the product of the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene (src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E. The structure and protein kinase activity of proteins encoded by nonconditional mutants and back mutants in the sec gene of avian sarcoma virus. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):47–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90526-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Esch F. S., Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M. Analysis of the sequence of amino acids surrounding sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):973–977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power and the environment. Nature. 1970 Aug 22;227(5260):777–777. doi: 10.1038/227777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a polypeptide encoded by the avian sarcoma virus src gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1567–1571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Wells S. K., Collett M. S. Increase in the phosphotransferase specific activity of purified Rous sarcoma virus pp60v-src protein after incubation with ATP plus Mg2+. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1589–1597. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Colby W. W., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Biological properties of human c-Ha-ras1 genes mutated at codon 12. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):71–75. doi: 10.1038/312071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K. Product of in vitro translation of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene has protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):311–318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.311-318.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K. Temperature-sensitive transformation by Rous sarcoma virus and temperature-sensitive protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):220–229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.220-229.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Patschinsky T., Berdot C., Hunter T., Elliott T. Phosphorylation and metabolism of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):813–820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.813-820.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Analysis of processing and polyadenylation signals of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene by using simian virus 40-hepatitis B virus chimeric plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2250–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Oppermann H., Czernilofsky A. P., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L., Bishop J. M. Characterization of sites for tyrosine phosphorylation in the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus (pp60v-src) and its normal cellular homologue (pp60c-src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M. A mutation at the major phosphotyrosine in pp60v-src alters oncogenic potential. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Phosphorylation of tyrosine-416 is not required for the transforming properties and kinase activity of pp60v-src. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Enrietto P. J., Wyke J. A. Functional domains of the pp60v-src protein as revealed by analysis of temperature-sensitive Rous sarcoma virus mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1508–1514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Cell-free translation of purified avian sarcoma virus src mRNA. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):476–478. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Jay G., Pastan I. Localization of the ASV src gene product to the plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]