Abstract
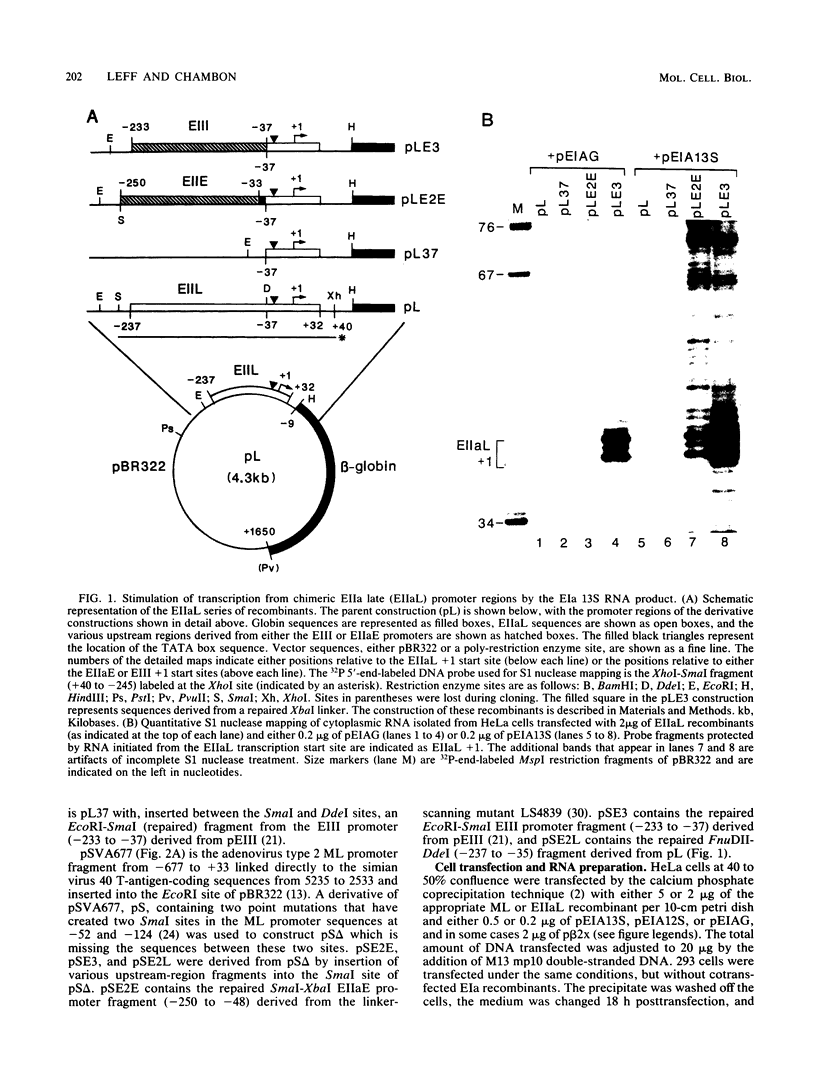
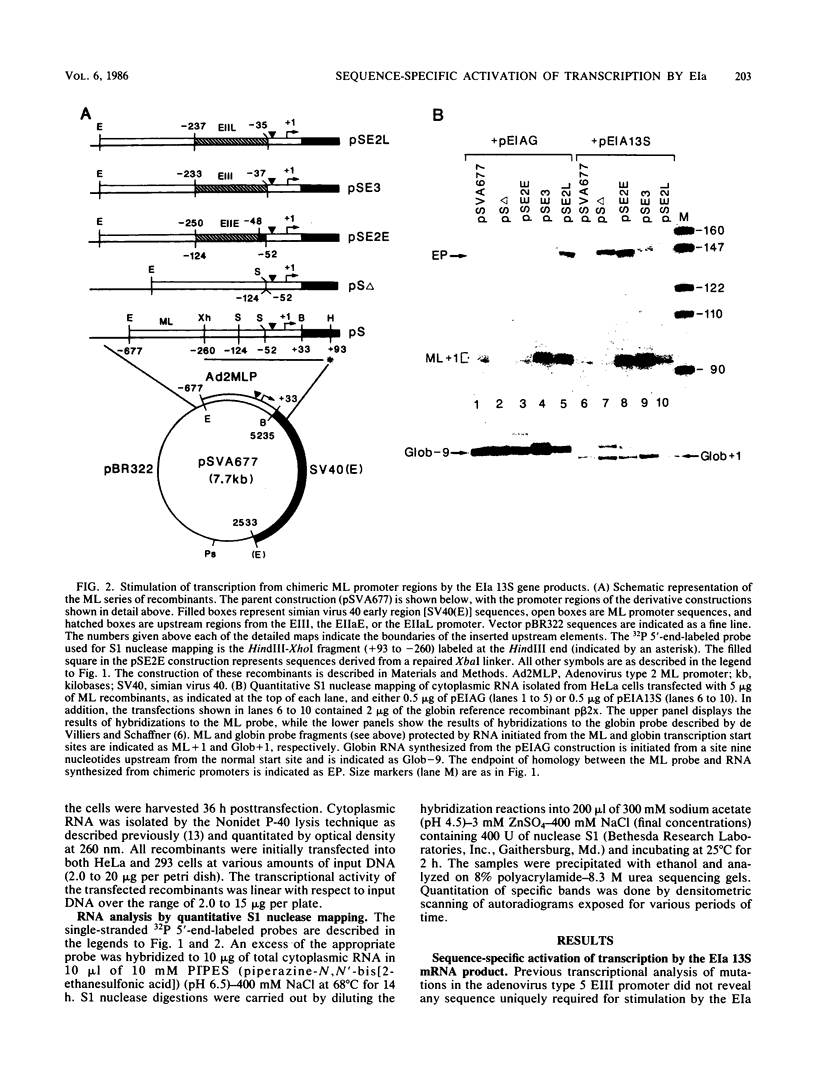
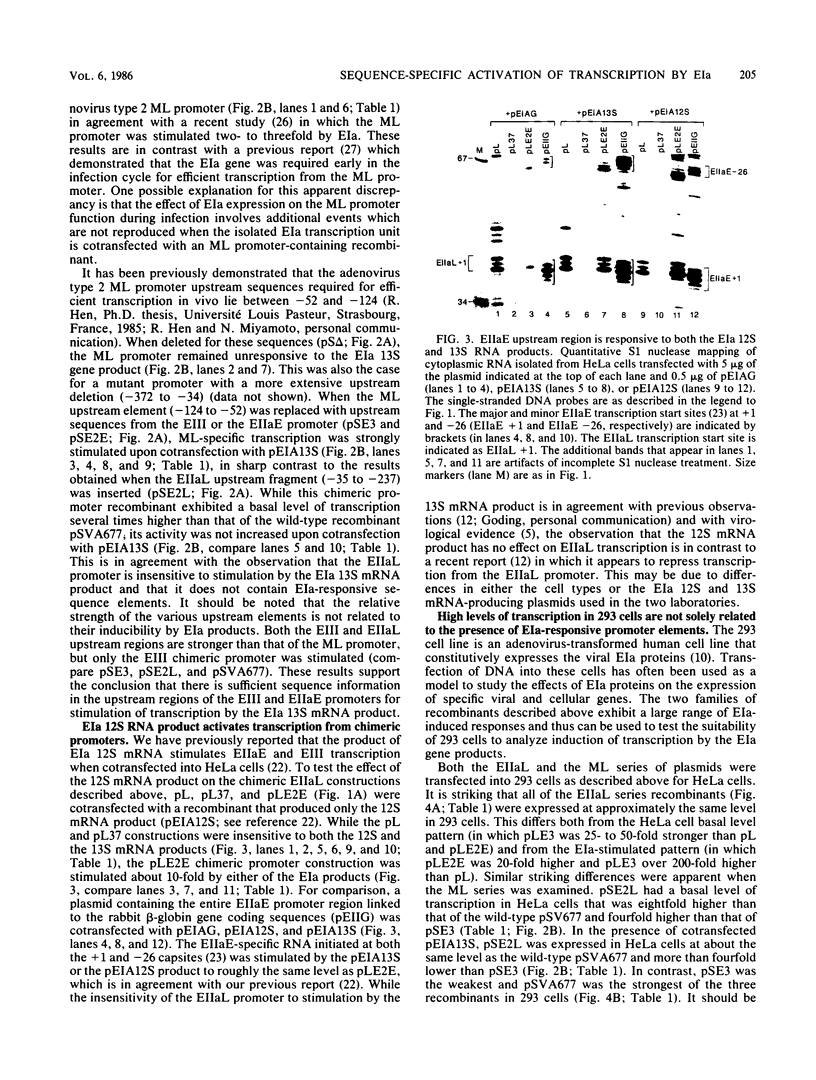
The adenovirus EIa gene products activate transcription from the viral EIII and EIIaE promoters. We studied the mechanism of this stimulation by constructing a series of chimeric promoter recombinants containing the upstream regions of the EIII and EIIaE promoters linked to the TATA box-start-site regions of the viral major late and EIIa late promoters. By introducing these recombinants into HeLa cells together with recombinants producing the EIa gene products, we demonstrated that the induction of EIII and EIIaE transcription by EIa 13S and 12S mRNA products is dependent on sequences located in the upstream region (approximately -40 to -250) of these promoters. In addition, we showed that the major late and EIIa late upstream promoter regions do not contain such EIa-responsive sequence elements. In contrast, after transfection of these chimeric promoter recombinants into 293 cells (which constitutively express the EIa proteins), we found that their relative levels of transcription are similar and markedly different from those observed when they are cotransfected into HeLa cells with EIa protein-producing recombinants. We conclude that the efficiency of transcription from a given promoter in 293 cells is not necessarily related to the presence of a specific EIa-responsive element.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C. Transient gene expression control: effects of transfected DNA stability and trans-activation by viral early proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1034–1042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Activation of early adenovirus transcription by the herpesvirus immediate early gene: evidence for a common cellular control factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4952–4956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Hillman D., Berk A. J. Adenovirus early region 1A protein activates transcription of a nonviral gene introduced into mammalian cells by infection or transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1193–1197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi P., Perricaudet M. The E4 transcriptional unit of Ad2: far upstream sequences are required for its transactivation by E1A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7877–7888. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle R. A., Osheroff W. P., Rossini M. Two functions encoded by adenovirus early region 1A are responsible for the activation and repression of the DNA-binding protein gene. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):707–713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Hart R. P., Nevins J. R. An enhancer-like element in the adenovirus E2 promoter contains sequences essential for uninduced and E1A-induced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Kao H. T., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Strickland S. Common control of the heat shock gene and early adenovirus genes: evidence for a cellular E1A-like activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus 5 E2 transcription unit: an E1A-inducible promoter with an essential element that functions independently of position or orientation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):875–882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Regulation of transcription of the adenovirus EII promoter by EIa gene products: absence of sequence specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1970–1977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Corden J., Elkaim R., Sassone-Corsi P. Transcriptional analysis of the adenovirus-5 EIII promoter: absence of sequence specificity for stimulation by EIa gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1209–1221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Elkaim R., Goding C. R., Jalinot P., Sassone-Corsi P., Perricaudet M., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Individual products of the adenovirus 12S and 13S EIa mRNAs stimulate viral EIIa and EIII expression at the transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Elkaim R., Kédinger C., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. Specific in vitro initiation of transcription on the adenovirus type 2 early and late EII transcription units. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7383–7387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Wintzerith M., Hen R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription by the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter involves a specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8779–8799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S. C., Bhat G. P., Thimmappaya B. Adenovirus EIIA early promoter: transcriptional control elements and induction by the viral pre-early EIA gene, which appears to be sequence independent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2230–2234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan V., Salzman N. P. Cis and trans activation of adenovirus IVa2 gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4067–4083. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajchowski D. A., Boeuf H., Kédinger C. The adenovirus-2 early EIIa transcription unit possesses two overlapping promoters with different sequence requirements for EIa-dependent stimulation. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1293–1300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]