Abstract
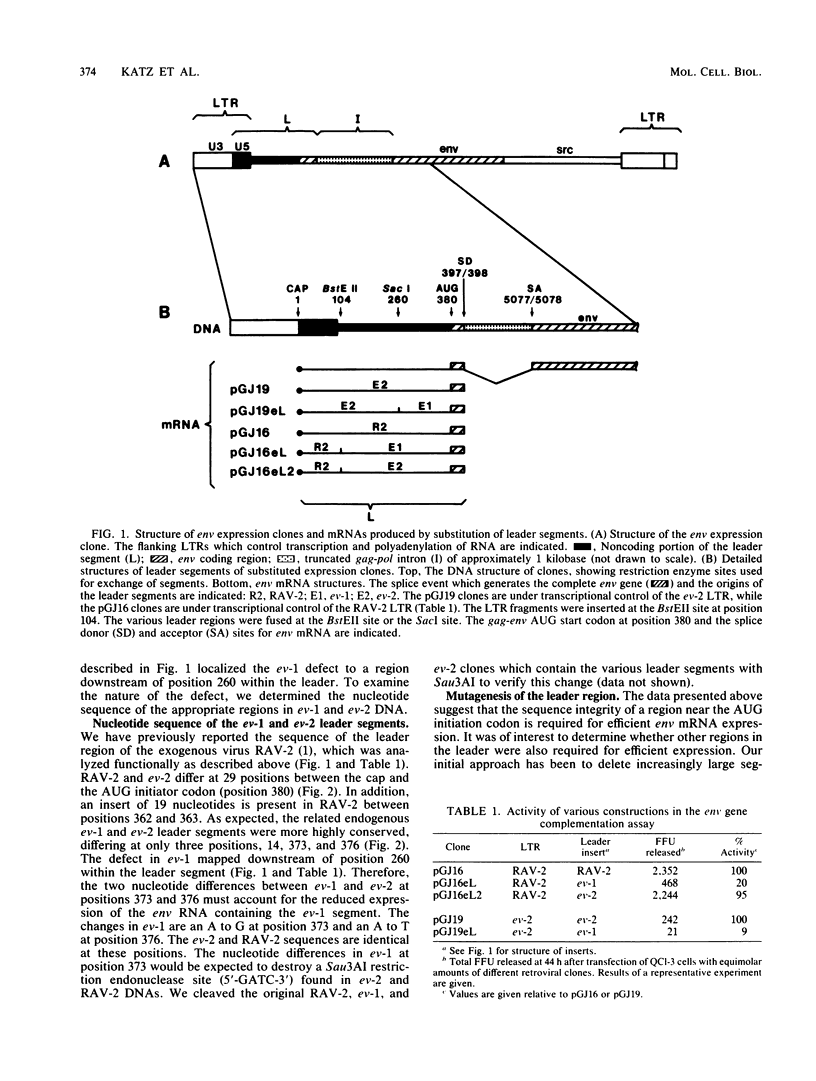
Avian retroviral mRNAs contain a long 5' untranslated leader of approximately 380 nucleotides. The leader includes sequences required for viral replication and three AUG codons which precede the AUG codon used for translational initiation of the gag and env genes. We have used sensitive, quantitative assays of viral gene transcription and translation to analyze the role of this mRNA leader in viral gene expression. By substituting segments from related viruses, we had previously shown that the endogenous avian provirus ev-1 contained a defective leader segment (B. R. Cullen, A. M. Skalka, and G. Ju, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:2946-2950, 1983). The sequence analysis presented here, followed by comparison with the nondefective ev-2 endogenous provirus segment, identified the critical changes at nucleotides 4 and 7 upstream of the initiator AUG. These differences do not alter the most conserved nucleotides within the consensus sequence which precedes eucaryotic initiation codons, but lie within a nine-nucleotide region that is otherwise highly conserved among avian retrovirus strains. Analysis of a series of deletion mutants indicated that other sequences within the leader are also required for efficient expression. Characterization of the altered transcripts demonstrated that the presence of the defective ev-1 segment or the deletion of a ca. 200-nucleotide leader segment did not affect the steady-state level or splicing efficiency of these mRNAs. Thus, we conclude that the reduced expression of these mRNAs is due to a translational deficiency. These results indicate that specific leader sequences, other than the previously identified consensus nucleotides which precede eucaryotic AUG initiator codons, can influence eucaryotic gene translation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bizub D., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence of noncoding regions in Rous-associated virus-2: comparisons delineate conserved regions important in replication and oncogenesis. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):557–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.557-565.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Functional analysis of the transcription control region located within the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):438–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Skalka A. M., Ju G. Endogenous avian retroviruses contain deficient promoter and leader sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Zuker M., Spahr P. F. Structure-function relationship of Rous sarcoma virus leader RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5183–5196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficht T. A., Chang L. J., Stoltzfus C. M. Avian sarcoma virus gag and env gene structural protein precursors contain a common amino-terminal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):362–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett P. B., Swanstrom R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The leader sequence of the subgenomic mRNA's of Rous sarcoma virus is approximately 390 nucleotides. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):527–534. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.527-534.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hishinuma F., DeBona P. J., Astrin S., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence of acceptor site and termini of integrated avian endogenous provirus ev1: integration creates a 6 bp repeat of host DNA. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H. Sequence of the long terminal repeat and adjacent segments of the endogenous avian virus Rous-associated virus 0. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):191–200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.191-200.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S., Mellstrom K., Kosik E., Tamanoi F., Brugge J. Mutation of a termination codon affects src initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1738–1746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen H., Schümperli D., Rosenberg M. Affecting gene expression by altering the length and sequence of the 5' leader. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7698–7702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama T., Harada F., Kawai S. Characterization of a Rous sarcoma virus mutant defective in packaging its own genomic RNA: biochemical properties of mutant TK15 and mutant-induced transformants. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):154–162. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.154-162.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influence of mRNA secondary structure on binding and migration of 40S ribosomal subunits. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Mechanism of mRNA recognition by eukaryotic ribosomes during initiation of protein synthesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:81–123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Selection of initiation sites by eucaryotic ribosomes: effect of inserting AUG triplets upstream from the coding sequence for preproinsulin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3873–3893. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner T. L., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the Bryan high-titer strain of Rous sarcoma virus: extent of env deletion and possible genealogical relationship with other viral strains. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):549–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.549-556.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Initiation of translation at internal AUG codons in mammalian cells. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):82–85. doi: 10.1038/309082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., McAndrew S. J. Eukaryotic ribosomes can recognize preproinsulin initiation codons irrespective of their position relative to the 5' end of mRNA. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):221–226. doi: 10.1038/299221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T. Use of recombinant DNA technology to program eukaryotic cells to synthesize rat proinsulin: a rapid expression assay for cloned genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5798–5802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Omata T., Toyoda H., Kuge S., Horie H., Kataoka Y., Genba Y., Nakano Y., Imura N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated poliovirus Sabin 1 strain genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5' noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen R. B., Hensel C. H., Hackett P. B. Identification of a ribosome-binding site for a leader peptide encoded by Rous sarcoma virus RNA. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):722–729. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.722-729.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholl D. R., Kahn S., Malavarca R., Astrin S., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence of the long terminal repeat and flanking cellular sequences of avian endogenous retrovirus ev-2: variation in Rous-associated virus-0 expression cannot be explained by differences in primary sequence. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):868–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.868-871.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Linial M. Avian oncovirus mutant (SE21Q1b) deficient in genomic RNA: characterization of a deletion in the provirus. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):450–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.450-456.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Allfrey V. G., Hanafusa H. Microinjection analysis of envelope-glycoprotein messenger activities of avian leukosis viral RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1614–1618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R. Site on the RNA of an avian sarcoma virus at which primer is bound. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):553–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.553-558.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thireos G., Penn M. D., Greer H. 5' untranslated sequences are required for the translational control of a yeast regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




