Abstract
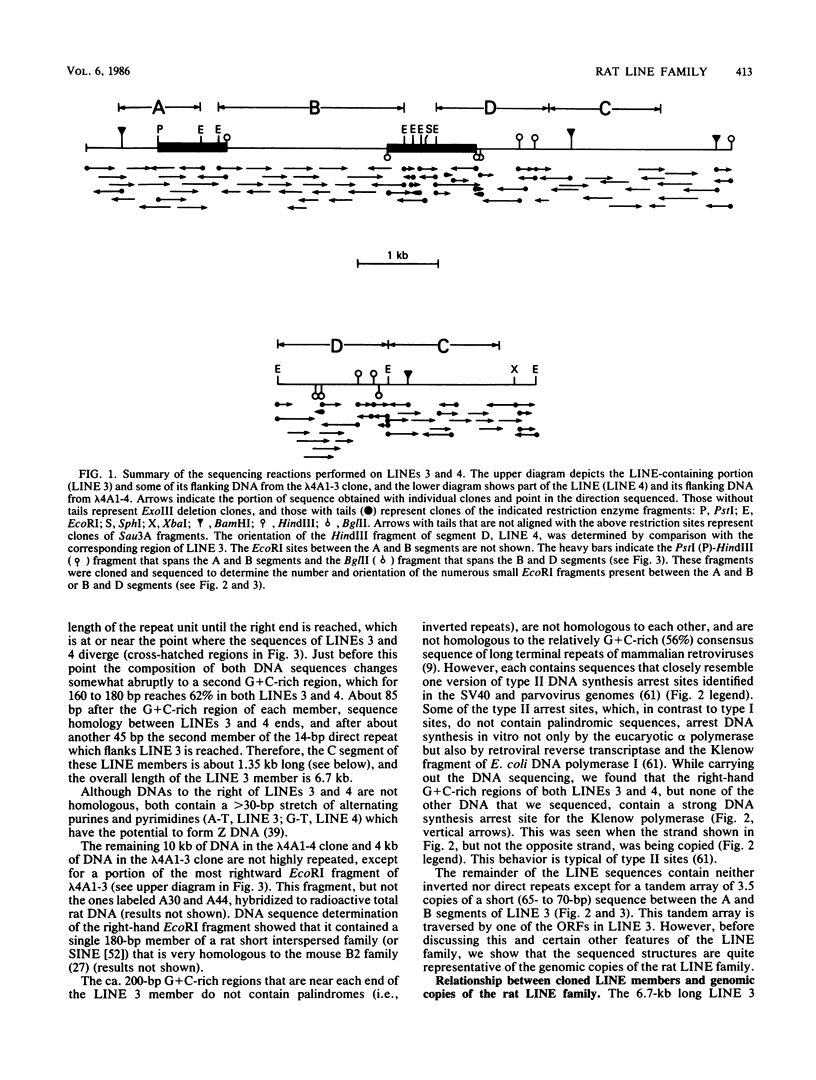
We present the DNA sequence of a 6.7-kilobase member of the rat long interspersed repeated DNA family (LINE or L1Rn). This member (LINE 3) is flanked by a perfect 14-base-pair (bp) direct repeat and is a full-length, or close-to-full-length, member of this family. LINE 3 contains an approximately 100-bp A-rich right end, a number of long (greater than 400-bp) open reading frames, and a ca. 200-bp G + C-rich (ca. 60%) cluster near each terminus. Comparison of the LINE 3 sequence with the sequence of about one-half of another member, which we also present, as well as restriction enzyme analysis of the genomic copies of this family, indicates that in length and overall structure LINE 3 is quite typical of the 40,000 or so other genomic members of this family which would account for as much as 10% of the rat genome. Therefore, the rat LINE family is relatively homogeneous, which contrasts with the heterogeneous LINE families in primates and mice. Transcripts corresponding to the entire LINE sequence are abundant in the nuclear RNA of rat liver. The characteristics of the rat LINE family are discussed with respect to the possible function and evolution of this family of DNA sequences.
Full text
PDF



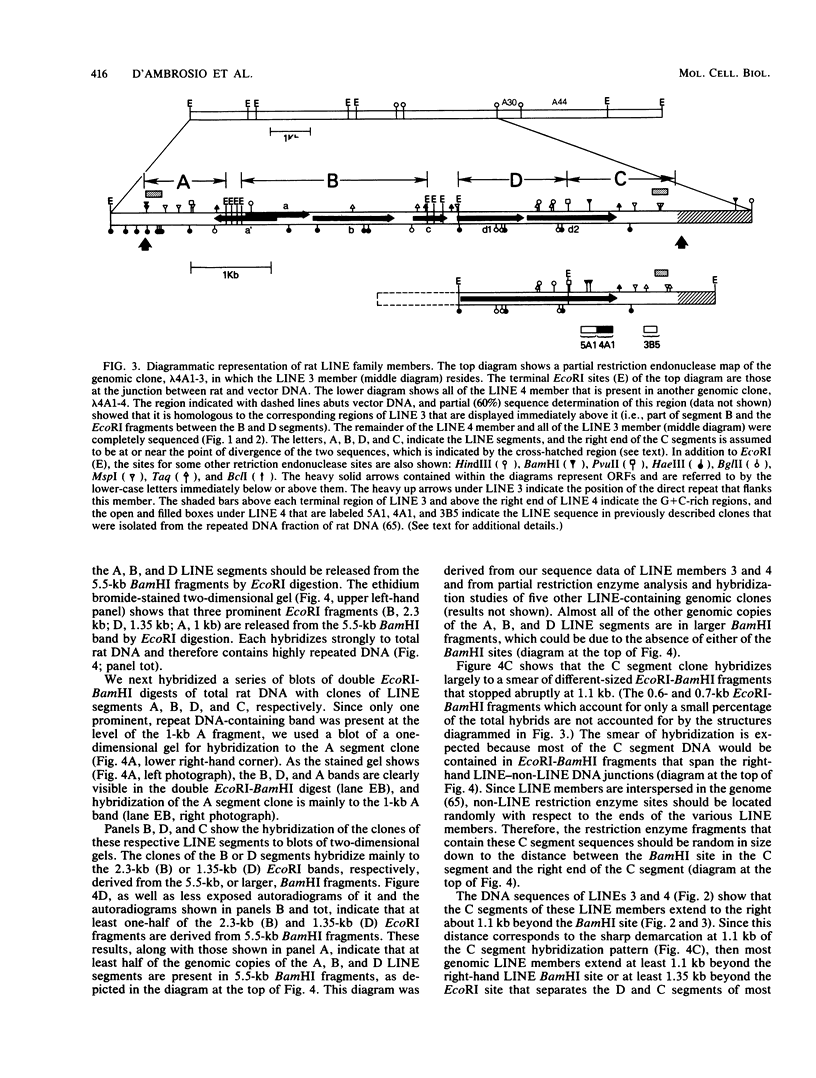

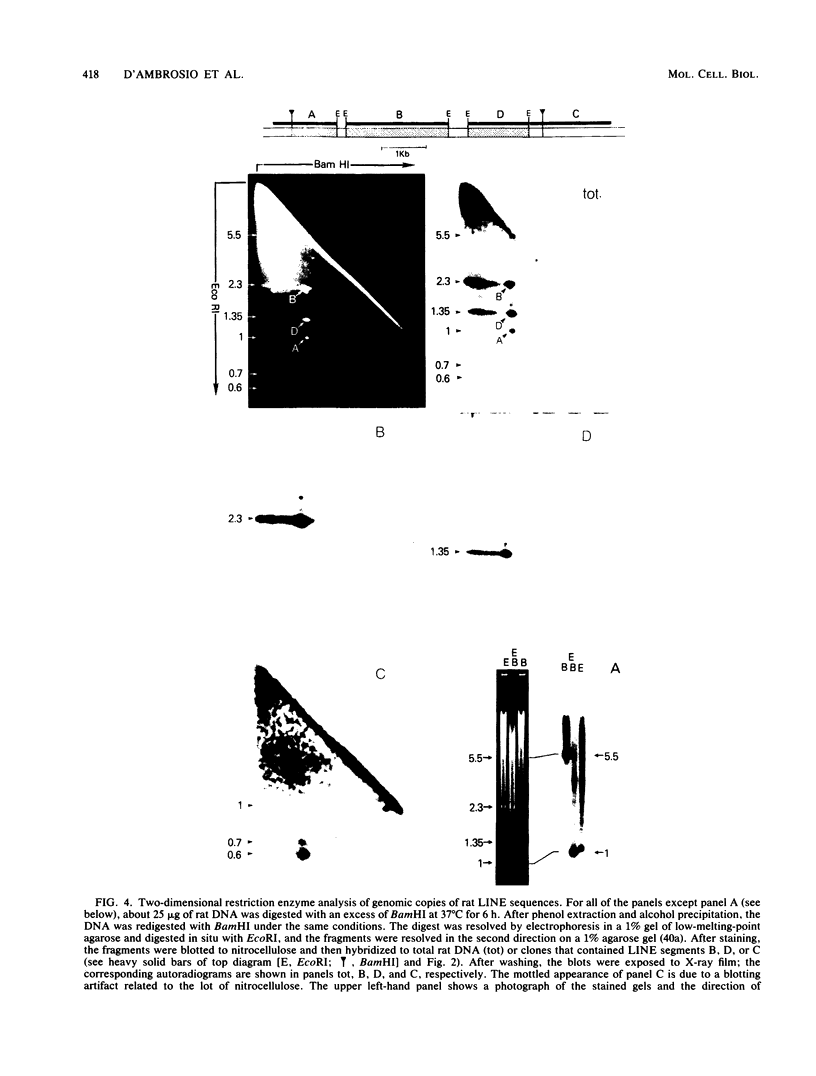






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. W., Kaufman R. E., Kretschmer P. J., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6113–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baran N., Neer A., Manor H. "Onion skin" replication of integrated polyoma virus DNA and flanking sequences in polyoma-transformed rat cells: termination within a specific cellular DNA segment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):105–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. Studies on simian virus 40 excision from cellular chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):709–719. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Dover G. Organization and evolutionary progress of a dispersed repetitive family of sequences in widely separated rodent genomes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):441–466. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L., Clayton J., Friedland P., Kedes L. H. SEQ: a nucleotide sequence analysis and recombination system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):279–294. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. R., Barker W. C. Nucleotide sequences of the retroviral long terminal repeats and their adjacent regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1767–1778. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. M., Schildkraut C. L. A family of moderately repetitive sequences in mouse DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4075–4090. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dush M. K., Sikela J. M., Khan S. A., Tischfield J. A., Stambrook P. J. Nucleotide sequence and organization of the mouse adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene: presence of a coding region common to animal and bacterial phosphoribosyltransferases that has a variable intron/exon arrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2731–2735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou-Pachnis A., Lohse M. A., Furano A. V., Tsichlis P. N. Insertion of long interspersed repeated elements at the Igh (immunoglobulin heavy chain) and Mlvi-2 (Moloney leukemia virus integration 2) loci of rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2857–2861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein D. A., Witney F. R., Furano A. V. The spread of sequence variants in Rattus satellite DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):973–988. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Size and structure of the highly repetitive BAM HI element in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5073–5091. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fickett J. W. Recognition of protein coding regions in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5303–5318. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Ansorge W. Improvements of DNA sequencing gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Jacobzone M., Mercier R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r43–r74. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. Members of the KpnI family of long interspersed repeated sequences join and interrupt alpha-satellite in the monkey genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):321–338. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Defining the beginning and end of KpnI family segments. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1753–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller D., Jackson M., Leinwand L. Organization and expression of non-Alu family interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 15;173(4):419–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90389-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M., Heller D., Leinwand L. Transcriptional measurements of mouse repeated DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3389–3403. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jukes T. H. Silent nucleotide substitutions and the molecular evolutionary clock. Science. 1980 Nov 28;210(4473):973–978. doi: 10.1126/science.7434017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole L. B., Haynes S. R., Jelinek W. R. Discrete and heterogeneous high molecular weight RNAs complementary to a long dispersed repeat family (a possible transposon) of human DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):257–286. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Markusheva T. V., Kramerov D. A., Ryskov A. P., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. Ubiquitous transposon-like repeats B1 and B2 of the mouse genome: B2 sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7461–7475. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmikumaran M. S., D'Ambrosio E., Laimins L. A., Lin D. T., Furano A. V. Long interspersed repeated DNA (LINE) causes polymorphism at the rat insulin 1 locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2197–2203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman M. I., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Kpn I family of long interspersed repeated DNA sequences in primates: polymorphism of family members and evidence for transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Mosig G. Regulation of a new bacteriophage T4 gene, 69, that spans an origin of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2863–2871. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Novel classes of mouse repeated DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3247–3258. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Nucleotide sequence definition of a major human repeated DNA, the Hind III 1.9 kb family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3211–3219. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Burton F. H., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd A large interspersed repeat found in mouse DNA contains a long open reading frame that evolves as if it encodes a protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2308–2312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Ivarie R. Asymmetrical distribution of CpG in an 'average' mammalian gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7865–7877. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Rotival M., Bernardi G. The Bam repeats of the mouse genome belong in several superfamilies the longest of which is over 9 kb in size. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1593–1608. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Rotival M., Soriano P., Cuny G., Strauss F., Bernardi G. Sequence organization and genomic distribution of the major family of interspersed repeats of mouse DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):355–359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miklos G. L., Willcocks D. A., Baverstock P. R. Restriction endonuclease and molecular analyses of three rat genomes with special reference to chromosome rearrangement and speciation problems. Chromosoma. 1980;76(3):339–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00327271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Lafer E. M., Peck L. J., Wang J. C., Stollar B. D., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled plasmids contain left-handed Z-DNA segments as detected by specific antibody binding. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Bunting S. L., Cole S. P., Seidman M. Two-dimensional electrophoretic display of restriction fragments from genomic DNA. Anal Biochem. 1985 Aug 15;149(1):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90492-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Igo-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Nucleotide sequence of a highly repetitive component of rat DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):417–432. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpulla R. C. Association of a truncated cytochrome c processed pseudogene with a similarly truncated member from a long interspersed repeat family of rat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):763–775. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Scott A. F., Smith K. D. Transcripts homologous to a long repeated DNA element in the human genome. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1218–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Jelinek W. R. The Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1065–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6281889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Brown F. L., Maio J. J., Adams J. W. KpnI families of long, interspersed repetitive DNAs associated with the human beta-globin gene cluster. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Brown F. L., Zavodny P. J., Maio J. J. Transcription of the KpnI families of long interspersed DNAs in human cells. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):277–280. doi: 10.1038/304277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F., Thayer R. E., Grimaldi G., Lerman M. I., Fanning T. G. Homology between the KpnI primate and BamH1 (M1F-1) rodent families of long interspersed repeated sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5739–5745. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Expression of a cytoplasmic LINE-1 transcript is regulated in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6050–6054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L., Paulson K. E., Schmid C. W., Kadyk L., Leinwand L. Non-Alu family interspersed repeats in human DNA and their transcriptional activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2669–2690. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Renz M. Simple sequences are ubiquitous repetitive components of eukaryotic genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4127–4138. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontano A., Scarlato V., Barni N., Cipollaro M., Franzè A., Macchiato M. F., Cascino A. Statistical evaluation of the coding capacity of complementary DNA strands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5049–5059. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voliva C. F., Jahn C. L., Comer M. B., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. The L1Md long interspersed repeat family in the mouse: almost all examples are truncated at one end. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8847–8859. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voliva C. F., Martin S. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Dispersal process associated with the L1 family of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):795–813. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90312-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. T., DePamphilis M. L. The role of palindromic and non-palindromic sequences in arresting DNA synthesis in vitro and in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):961–986. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witney F. R., Furano A. V. Highly repeated DNA families in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10481–10492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witney F. R., Furano A. V. The independent evolution of two closely related satellite DNA elements in rats (Rattus). Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):291–304. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. K., Masters J. N., Attardi G. Human dihydrofolate reductase gene organization. Extensive conservation of the G + C-rich 5' non-coding sequence and strong intron size divergence from homologous mammalian genes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 25;176(2):169–187. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis-Hadjopoulos M., Persico M., Martin R. G. The remarkable instability of replication loops provides a general method for the isolation of origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]