Abstract
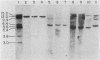
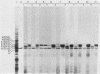
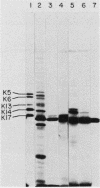
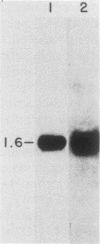
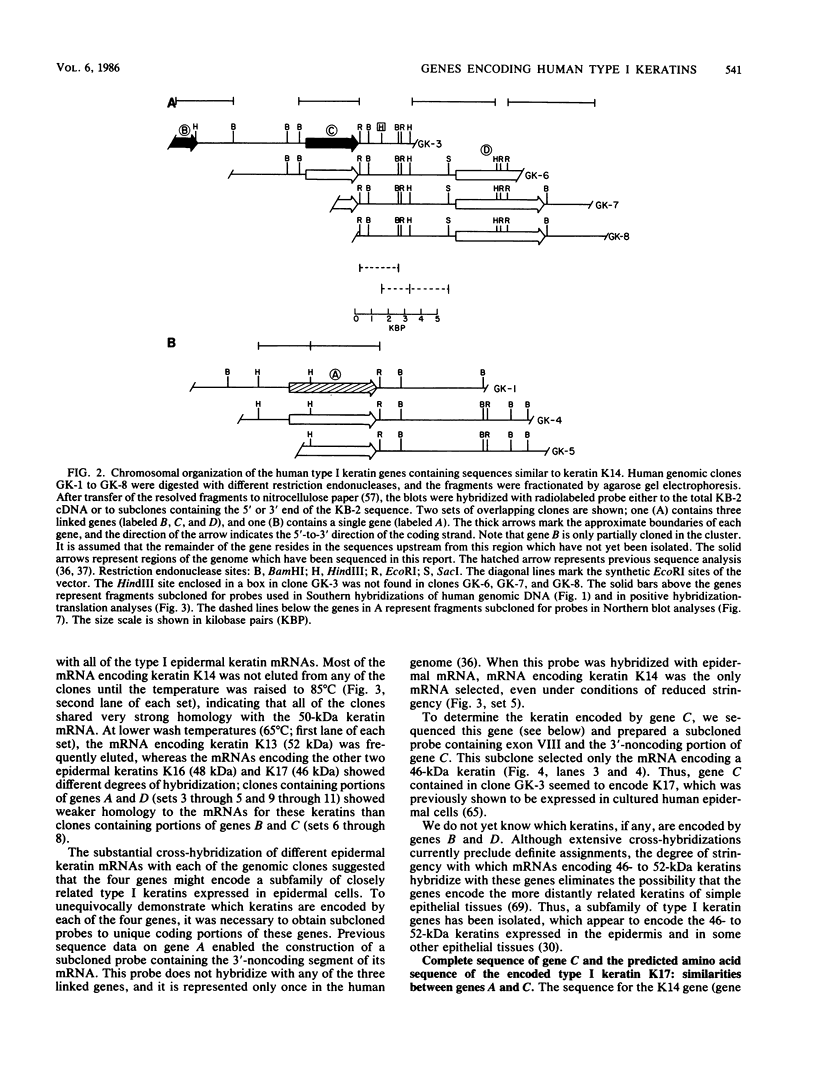
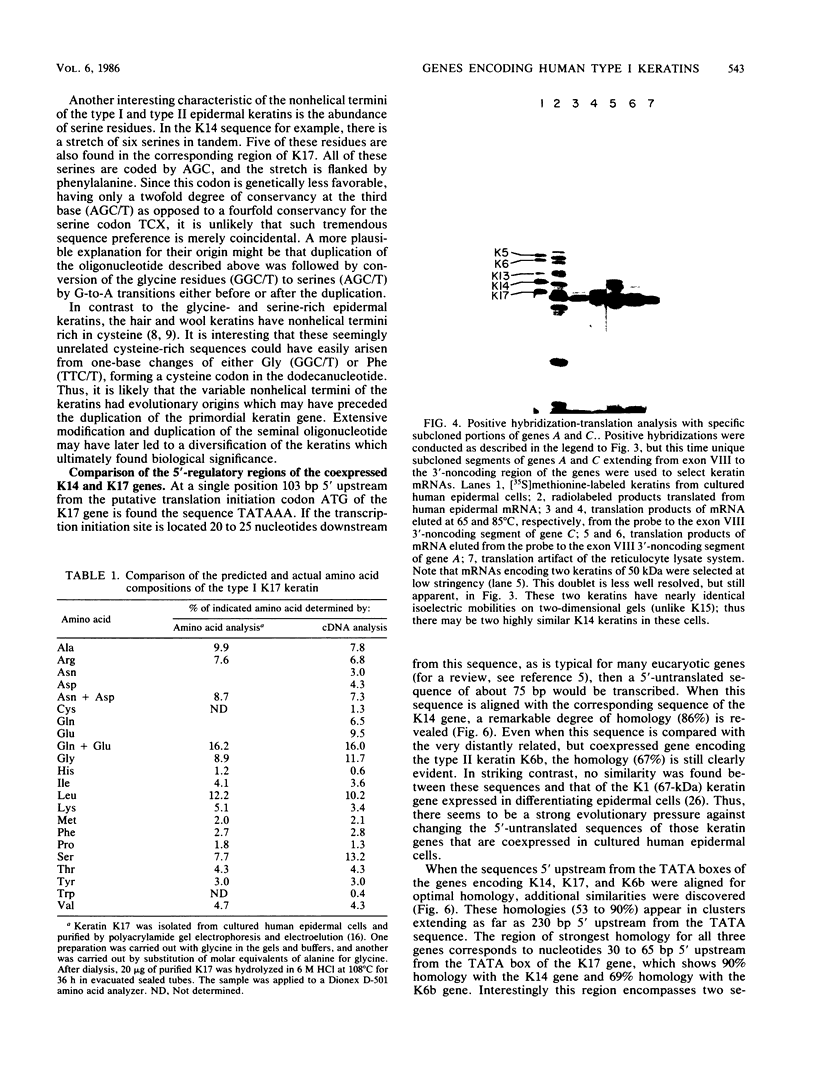
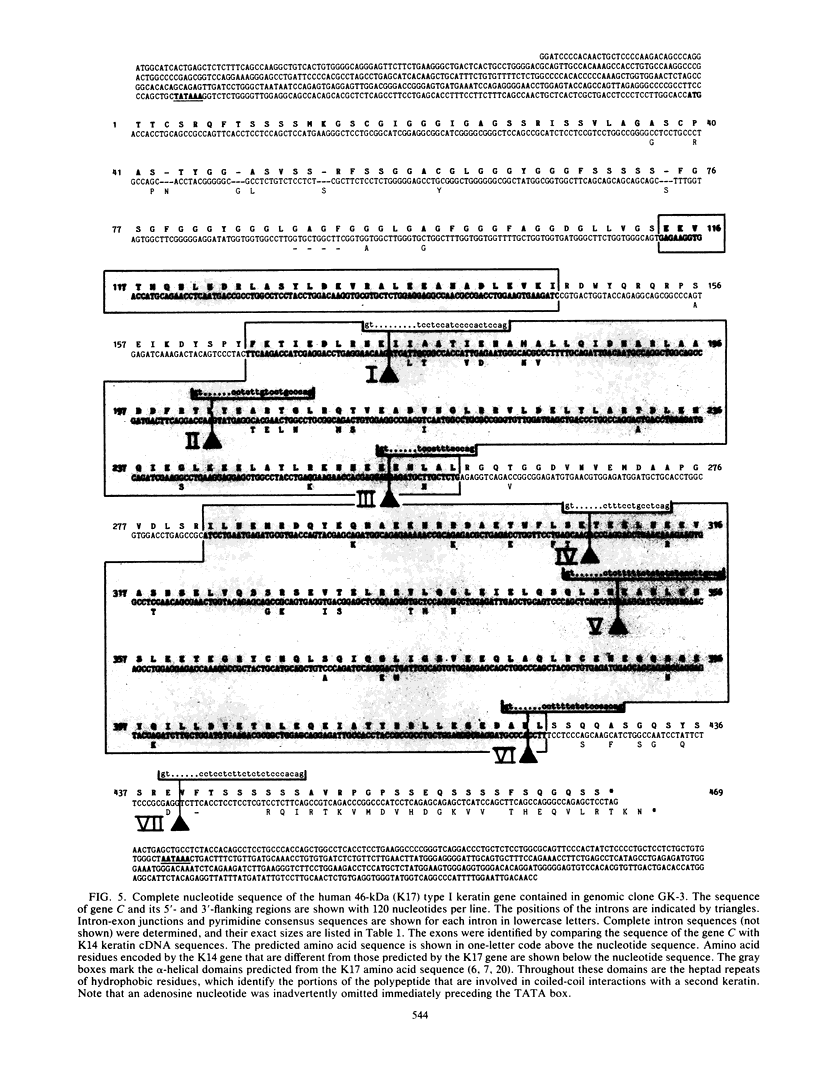
We have isolated and subcloned three separate segments of human DNA which share strong sequence homology with a previously sequenced gene encoding a type I keratin, K14 (50 kilodaltons). Restriction endonuclease mapping has demonstrated that these three genes are tightly linked chromosomally, whereas the K14 gene appears to be separate. As judged by positive hybridization-translation and Northern blot analyses, the central linked gene encodes a keratin, K17, which is expressed in abundance with K14 and two other type I keratins in cultured human epidermal cells. None of these other epidermal keratin mRNAs appears to be generated from the K17 gene through differential splicing of its transcript. The sequence of the K17 gene reveals striking homologies not only with the coding portions and intron positions of the K14 gene, but also with its 5'-noncoding and 5'-upstream sequences. These similarities may provide an important clue in elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying the coexpression of the two genes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. Shotgun DNA sequencing using cloned DNase I-generated fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3015–3027. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G. S., Boardman M., Storti R. V. Alternative splicing of a Drosophila tropomyosin gene generates muscle tropomyosin isoforms with different carboxy-terminal ends. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2828–2836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladon P. T., Bowden P. E., Cunliffe W. J., Wood E. J. Prekeratin biosynthesis in human scalp epidermis. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 15;208(1):179–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2080179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of beta-turns. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):367–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85259-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichner R., Bonitz P., Sun T. T. Classification of epidermal keratins according to their immunoreactivity, isoelectric point, and mode of expression. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1388–1396. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Hatzfeld M., Winter S. Protein complexes of intermediate-sized filaments: melting of cytokeratin complexes in urea reveals different polypeptide separation characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7113–7117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. V., Coppock S. M., Green H., Cleveland D. W. Two distinct classes of keratin genes and their evolutionary significance. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Changes in keratin gene expression during terminal differentiation of the keratinocyte. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Multiple keratins of cultured human epidermal cells are translated from different mRNA molecules. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. The expression of keratin genes in epidermis and cultured epidermal cells. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Hanukoglu I. Unraveling the structure of the intermediate filaments. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):332–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Antiparallel orientation of the two double-stranded coiled-coils in the tetrameric protofilament unit of intermediate filaments. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Proteinchemical characterization of three structurally distinct domains along the protofilament unit of desmin 10 nm filaments. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C., Kim K. H., Fuchs E. Sequence and expression of a human type II mesothelial keratin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2366–2373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a Type II cytoskeletal keratin reveals constant and variable structural domains among keratins. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a human epidermal keratin: divergence of sequence but conservation of structure among intermediate filament proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. D., Idler W. W., Zhou X. M., Roop D. R., Steinert P. M. Structure of a gene for the human epidermal 67-kDa keratin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1896–1900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorcano J. L., Franz J. K., Franke W. W. Amino acid sequence diversity between bovine epidermal cytokeratin polypeptides of the basic (type II) subfamily as determined from cDNA clones. Differentiation. 1984;28(2):155–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorcano J. L., Rieger M., Franz J. K., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Franke W. W. Identification of two types of keratin polypeptides within the acidic cytokeratin subfamily I. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 25;179(2):257–281. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Marchuk D., Fuchs E. Expression of unusually large keratins during terminal differentiation: balance of type I and type II keratins is not disrupted. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1872–1877. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Rheinwald J. G., Fuchs E. V. Tissue specificity of epithelial keratins: differential expression of mRNAs from two multigene families. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):495–502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg T. M., Schafer M. P., Cheng C. K., Filpula D., Flaherty P., Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Organization of a type I keratin gene. Evidence for evolution of intermediate filaments from a common ancestral gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5867–5870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehnert M. E., Jorcano J. L., Zentgraf H., Blessing M., Franz J. K., Franke W. W. Characterization of bovine keratin genes: similarities of exon patterns in genes coding for different keratins. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3279–3287. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., McCrohon S., Fuchs E. Complete sequence of a gene encoding a human type I keratin: sequences homologous to enhancer elements in the regulatory region of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., McCrohon S., Fuchs E. Remarkable conservation of structure among intermediate filament genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):491–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham B. E., Little J. W., Mount D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the lexA gene of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4149–4161. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry T. J., Lindquist S. The preferential translation of Drosophila hsp70 mRNA requires sequences in the untranslated leader. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):903–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Coiled coil formation and sequence regularities in the helical regions of alpha-keratin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M. Tropomyosin coiled-coil interactions: evidence for an unstaggered structure. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 25;98(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medford R. M., Nguyen H. T., Destree A. T., Summers E., Nadal-Ginard B. A novel mechanism of alternative RNA splicing for the developmentally regulated generation of troponin T isoforms from a single gene. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):409–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90496-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Sun T. T. The 50- and 58-kdalton keratin classes as molecular markers for stratified squamous epithelia: cell culture studies. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):244–251. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Hawley-Nelson P., Cheng C. K., Yuspa S. H. Keratin gene expression in mouse epidermis and cultured epidermal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):716–720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Davidson N. Drosophila has one myosin heavy-chain gene with three developmentally regulated transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerrow D., Skerrow C. J. Tonofilament differentiation in human epidermis, isolation and polypeptide chain composition of keratinocyte subpopulations. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jan;143(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W. The polypeptide composition of bovine epidermal alpha-keratin. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):603–614. doi: 10.1042/bj1510603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Zimmerman S. B. Self-assembly of bovine epidermal keratin filaments in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 15;108(3):547–567. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Parry D. A., Racoosin E. L., Idler W. W., Steven A. C., Trus B. L., Roop D. R. The complete cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of a type II mouse epidermal keratin of 60,000 Da: analysis of sequence differences between type I and type II keratins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5709–5713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rice R. H., Roop D. R., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Complete amino acid sequence of a mouse epidermal keratin subunit and implications for the structure of intermediate filaments. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):794–800. doi: 10.1038/302794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Steven A. C., Roop D. R. The molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M. Structure of the three-chain unit of the bovine epidermal keratin filament. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 25;123(1):49–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven A. C., Hainfeld J. F., Trus B. L., Wall J. S., Steinert P. M. Epidermal keratin filaments assembled in vitro have masses-per-unit-length that scale according to average subunit mass: structural basis for homologous packing of subunits in intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1939–1944. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Keratin filaments of cultured human epidermal cells. Formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds during terminal differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):2053–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyner A. L., Eichman M. J., Fuchs E. The sequence of a type II keratin gene expressed in human skin: conservation of structure among all intermediate filament genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4683–4687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Parker L. M., Binder N. E., Beckett M. A., Sinard J. H., Griffiths C. T., Rheinwald J. G. The mesothelial keratins: a new family of cytoskeletal proteins identified in cultured mesothelial cells and nonkeratinizing epithelia. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):693–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. W., Zweers A., Cohen L. H. Influence of single amino acid substitutions on electrophoretic mobility of sodium dodecyl sulfate-protein complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90907-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]