Abstract
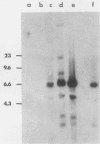
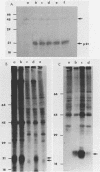
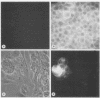
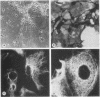
We transfected the human EJ bladder carcinoma oncogene (Ha-rasEJ-1) into multipotential embryonal carcinoma cell line P19. The transgenic P19(ras+) cells expressed high levels of both the mRNA and the p21EJ protein derived from the oncogene. When cultured in the presence of retinoic acid, P19(ras+) cells differentiated and developed into the same spectrum of differentiated cell types as the parental P19 cells (namely, neurons, astrocytes, and fibroblast-like cells). Thus, it seems unlikely that the Ha-ras-1 proto-oncogene product plays a role in initiation of differentiation or in the choice of differentiated cell lineage. Most of the P19(ras+)-derived differentiated cells contained relatively low levels of p21EJ and were nontransformed, whereas certain cells with fibroblast-like morphology continued to express the Ha-rasEJ-1 gene at high levels and were transformed (i.e., immortal and anchorage independent). Fibroblasts derived from P19 cells did not become transformed following transfection of the Ha-rasEJ-1 oncogene, suggesting that transformation of the fibroblast cells only occurred if the oncogene was present and expressed during the early stages of the developmental lineage.
Full text
PDF

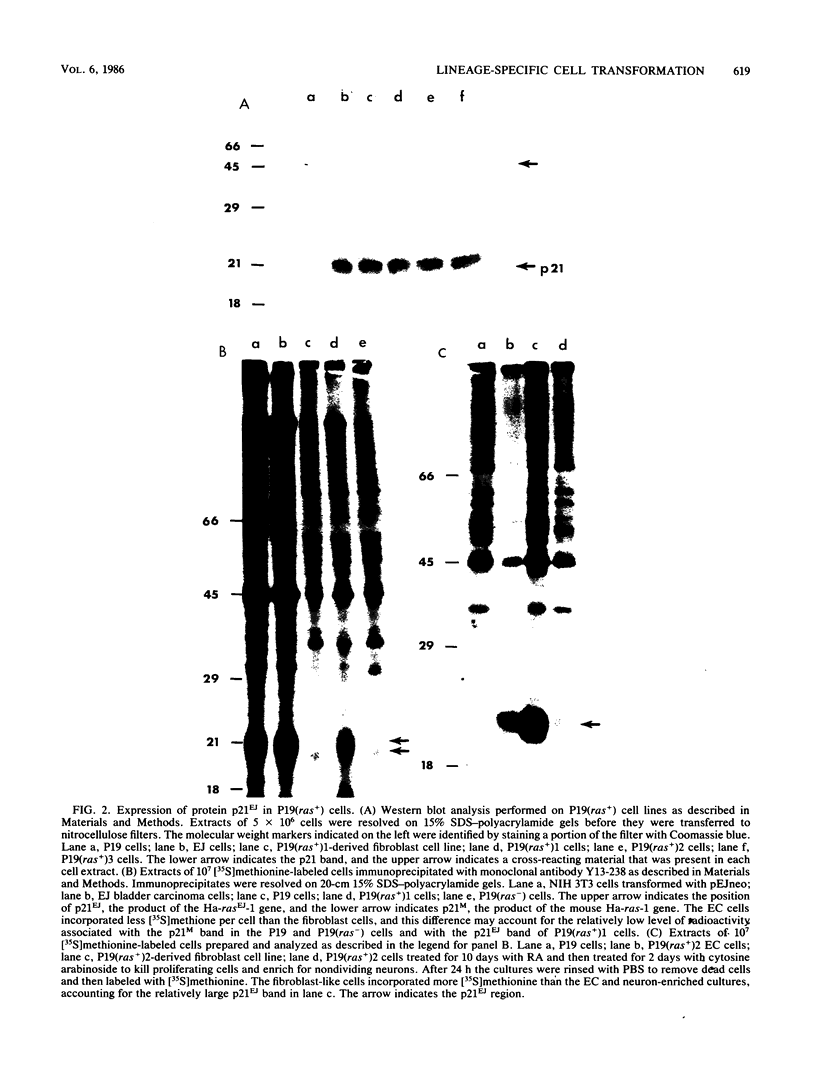
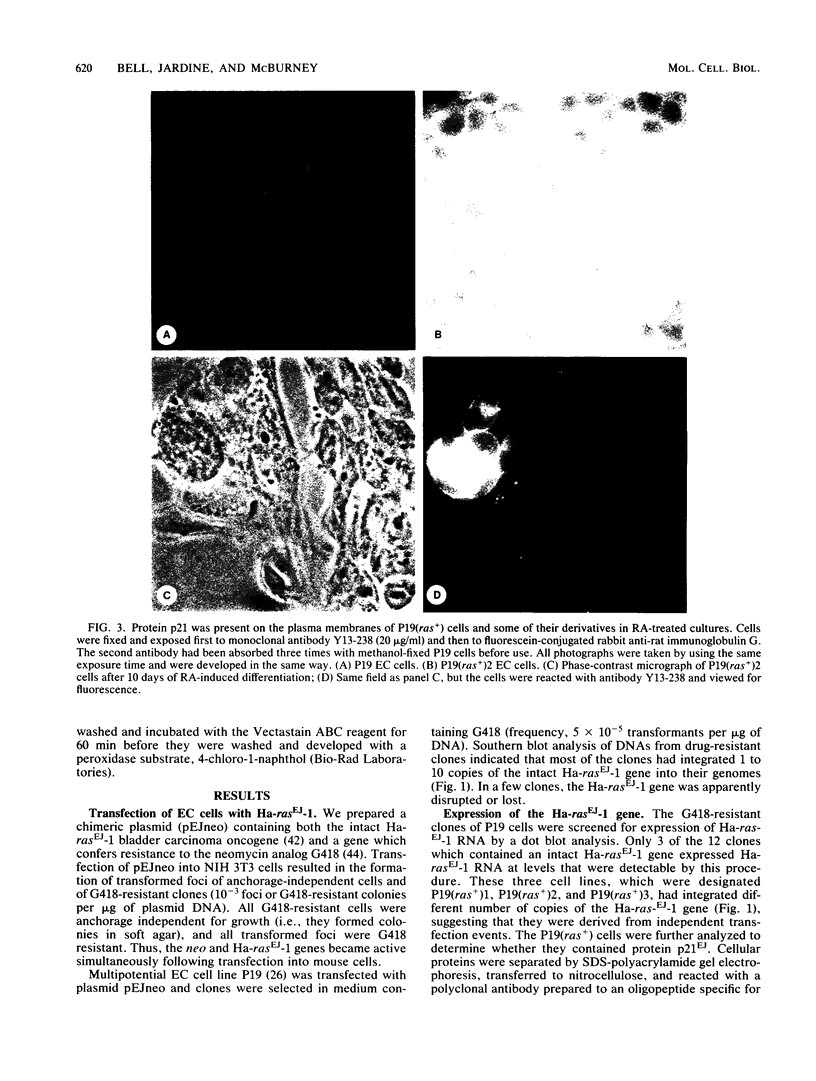
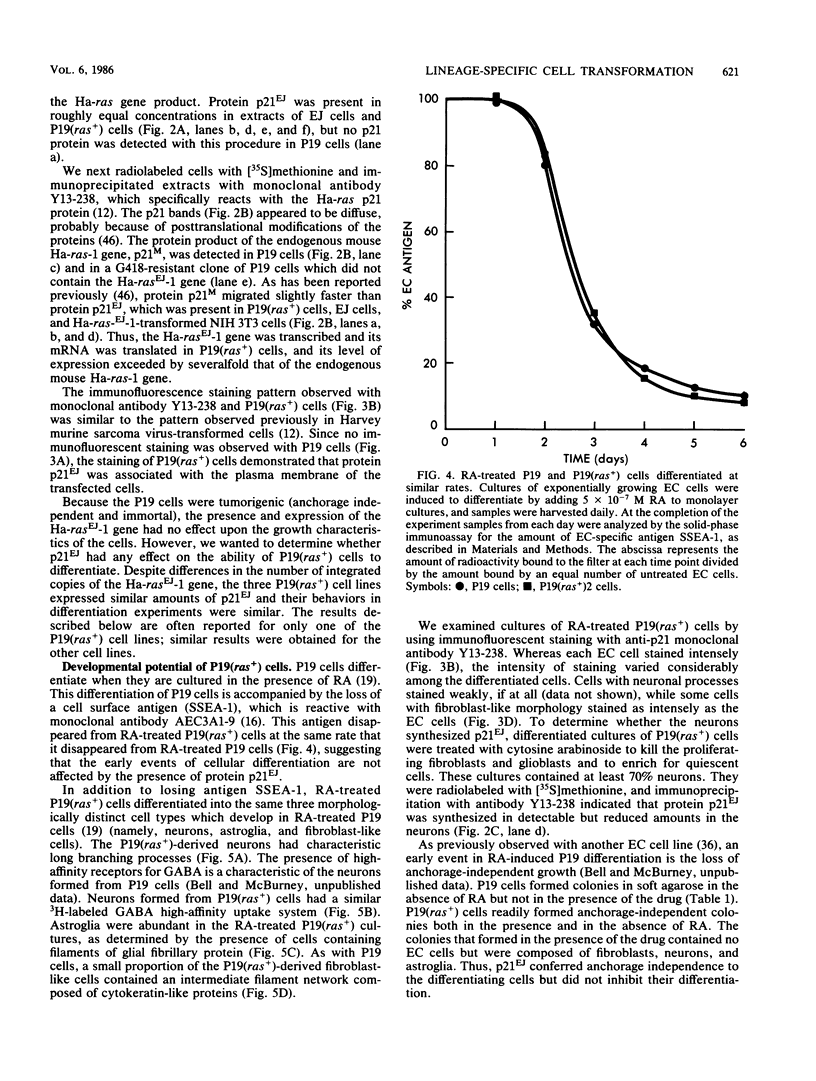
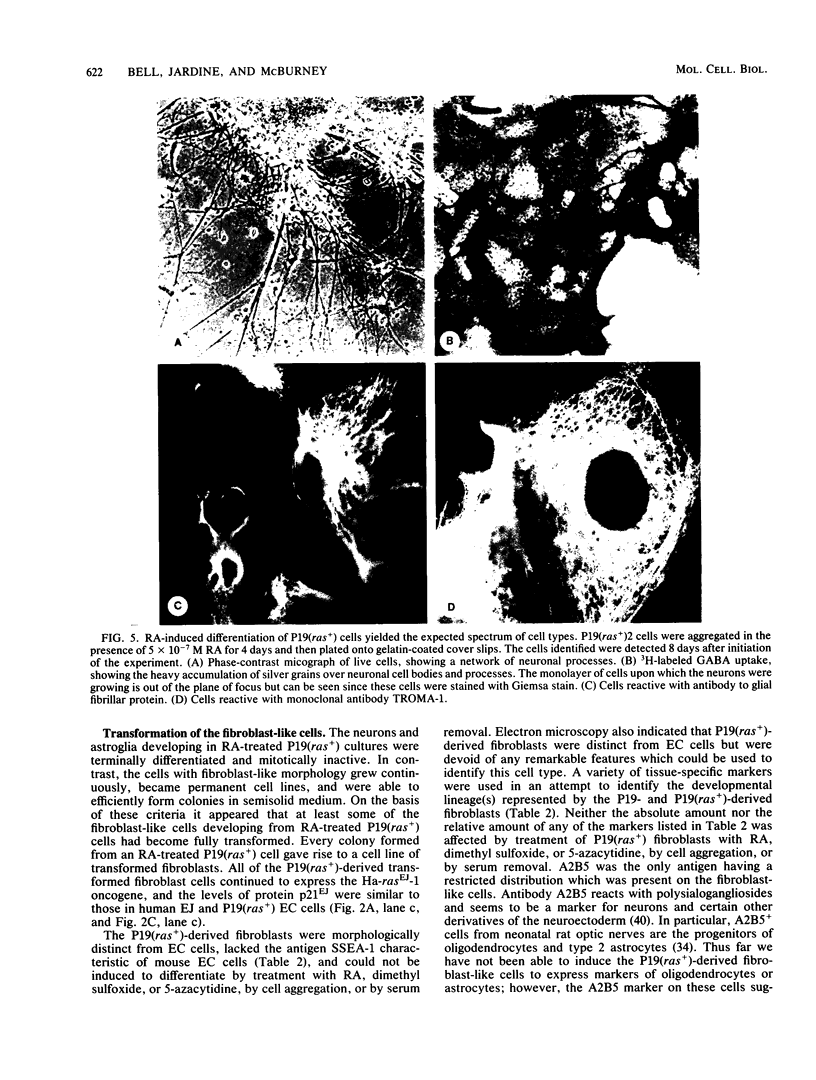



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemà S., Casalbore P., Agostini E., Tatò F. Differentiation of PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells induced by v-src oncogene. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):557–559. doi: 10.1038/316557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. C., Brown E. G., Takayesu D., Prevec L. Protein kinase activity associated with immunoprecipitates of the vesicular stomatitis virus phosphoprotein NS. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Leutz A., Kahn P., Graf T. Ts mutants of E26 leukemia virus allow transformed myeloblasts, but not erythroblasts or fibroblasts, to differentiate at the nonpermissive temperature. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90465-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresser J., Hubbell H. R., Gillespie D. Biological activity of mRNA immobilized on nitrocellulose in NaI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6523–6527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campione-Piccardo J., Craig J., Sun J. J., McBurney M. W. Commitment in a murine embryonal carcinoma cell line during differentiation induced by retinoic acid. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Feb;156(2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90561-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. M., Lane M. A. Cellular transforming genes and oncogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;738(1-2):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(84)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcone G., Tatò F., Alemà S. Distinctive effects of the viral oncogenes myc, erb, fps, and src on the differentiation program of quail myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):426–430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D. W., Towle A. C., Lauder J. M., Maness P. F. pp60c-src in the developing cerebellum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Vapnek D. A simple method of preparing large amounts of phiX174 RF 1 supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Metcalf D. Expression of myb, myc and fos proto-oncogenes during the differentiation of a murine myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):249–251. doi: 10.1038/310249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. F., Chin J., Jewett M. A., Kennedy M., Gorczynski R. M. Monoclonal antibodies against SSEA-1 antigen: binding properties and inhibition of human natural killer cell activity against target cells bearing SSEA-1 antigen. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2502–2509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Kao H. T., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Strickland S. Common control of the heat shock gene and early adenovirus genes: evidence for a cellular E1A-like activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Currie G. A. Cellular immortalization by a cDNA clone encoding the transformation-associated phosphoprotein p53. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):651–654. doi: 10.1038/312651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., McBurney M. W., Rogers K. A., Kalnins V. I. Retinoic acid induces embryonal carcinoma cells to differentiate into neurons and glial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):253–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., McGill C., Fasano O., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genetic analysis of yeast RAS1 and RAS2 genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Skoultchi A. I. Expression of c-myc changes during differentiation of mouse erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):592–594. doi: 10.1038/310592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Viruses as probes for development and differentiation. Adv Virus Res. 1981;26:65–116. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60421-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Jones-Villeneuve E. M., Edwards M. K., Anderson P. J. Control of muscle and neuronal differentiation in a cultured embryonal carcinoma cell line. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):165–167. doi: 10.1038/299165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Rogers B. J. Isolation of male embryonal carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Zokas L., Schreiber R. D., Verma I. M. Rapid induction of the expression of proto-oncogene fos during human monocytic differentiation. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Wagner E. F. Differentiation of F9 teratocarcinoma stem cells after transfer of c-fos proto-oncogenes. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):438–442. doi: 10.1038/311438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Regulation of the cellular p53 tumor antigen in teratocarcinoma cells and their differentiated progeny. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):443–449. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Messing A., Brinster R. L. SV40 enhancer and large-T antigen are instrumental in development of choroid plexus tumours in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):457–460. doi: 10.1038/316457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Amiel T., Hinze E., Auersperg N., Neave N., Sobolewski A., Weeks G. Regulation of a ras-related protein during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):33–39. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Miller R. H., Noble M. A glial progenitor cell that develops in vitro into an astrocyte or an oligodendrocyte depending on culture medium. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):390–396. doi: 10.1038/303390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond C. D., Gomer R. H., Mehdy M. C., Firtel R. A. Developmental regulation of a Dictyostelium gene encoding a protein homologous to mammalian ras protein. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues M., Balicki D., Newrock K. M., Mukherjee B. B. Lack of correlation between loss of anchorage-independent growth and levels of transformation-specific p53 protein in retinoic acid-treated F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jan;156(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Tanaka K., Lau C. C., Ebina Y., Anisowicz A. Resistance of human cells to tumorigenesis induced by cloned transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7601–7605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarut J., Gazzolo L. Target cells infected by avian erythroblastosis virus differentiate and become transformed. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):921–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J., Schachner M. Cell type specificity of a neural cell surface antigen recognized by the monoclonal antibody A2B5. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;224(3):625–636. doi: 10.1007/BF00213757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Human N-myc gene contributes to neoplastic transformation of mammalian cells in culture. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):160–162. doi: 10.1038/316160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukumar S., Notario V., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Induction of mammary carcinomas in rats by nitroso-methylurea involves malignant activation of H-ras-1 locus by single point mutations. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):658–661. doi: 10.1038/306658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Bradley S. M., Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A., Papageorge A. G., Scolnick E. M., Dhar R., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):143–149. doi: 10.1038/300143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Chaleff D. T., DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M. Requirement of either of a pair of ras-related genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for spore viability. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):523–527. doi: 10.1038/309523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Steinbusch H. W., Jessell T. M. Differentiated properties of identified serotonin neurons in dissociated cultures of embryonic rat brain stem. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):142–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]