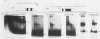Abstract
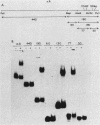
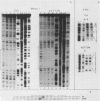
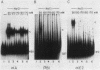
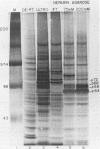
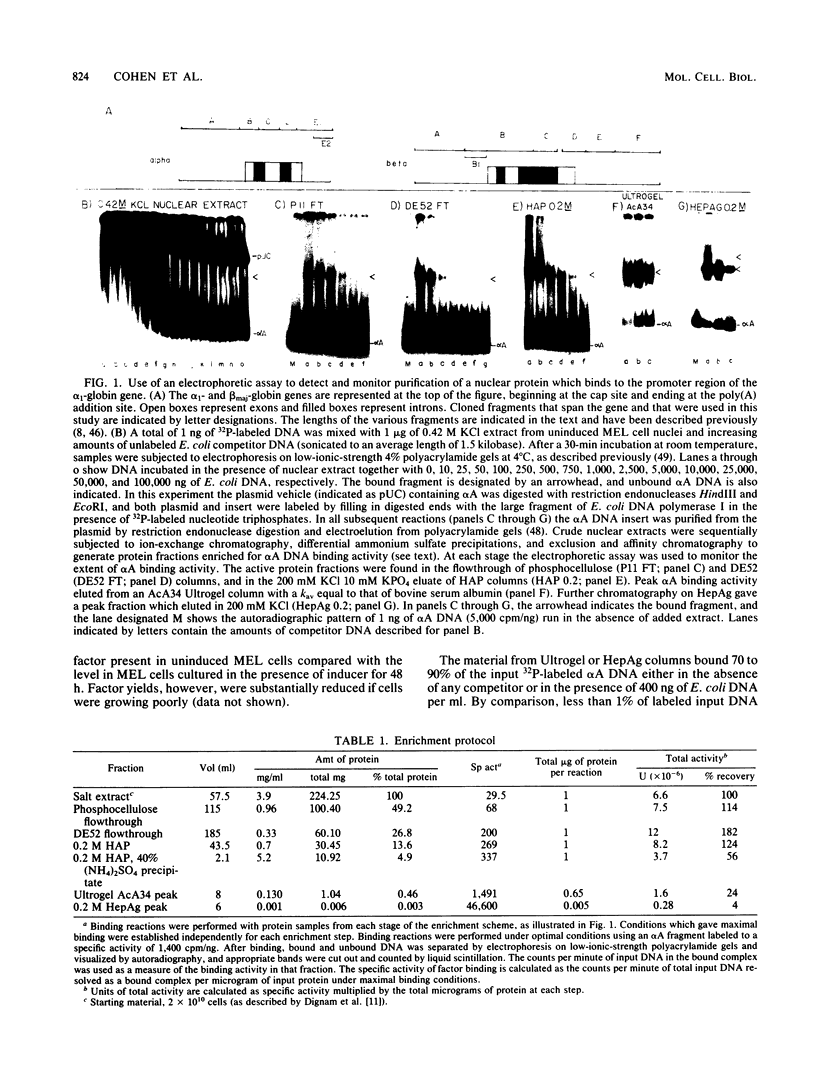
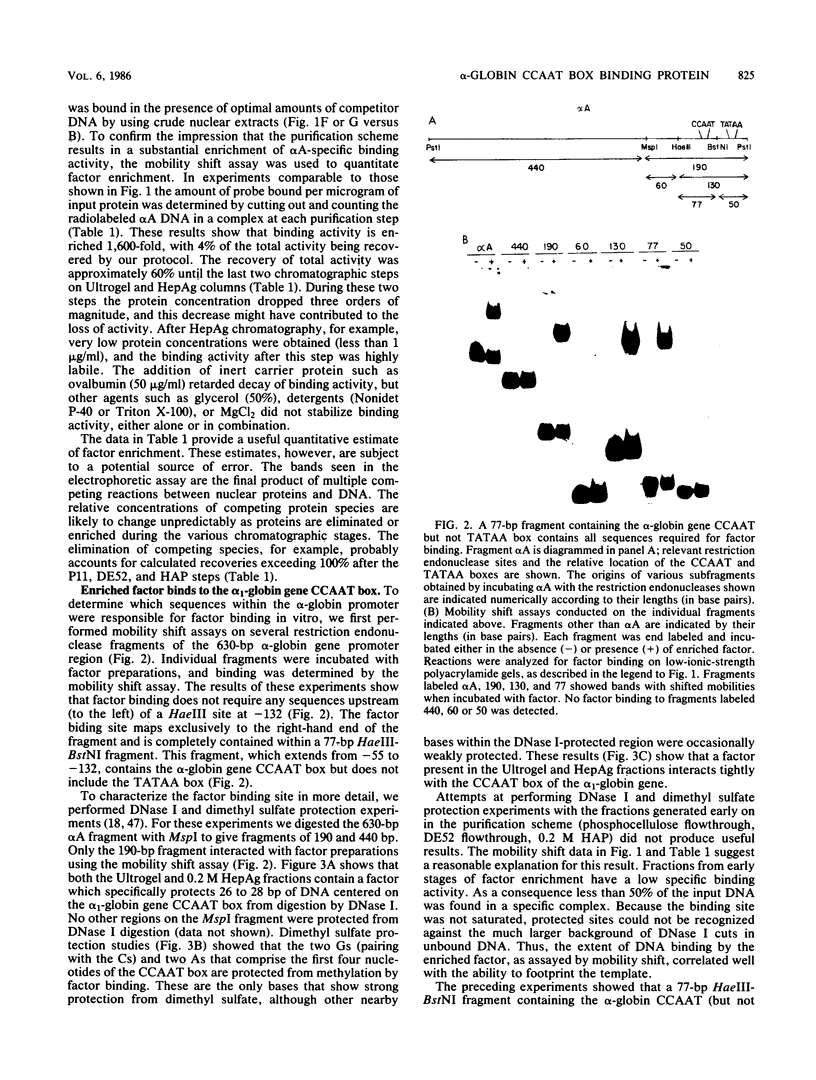
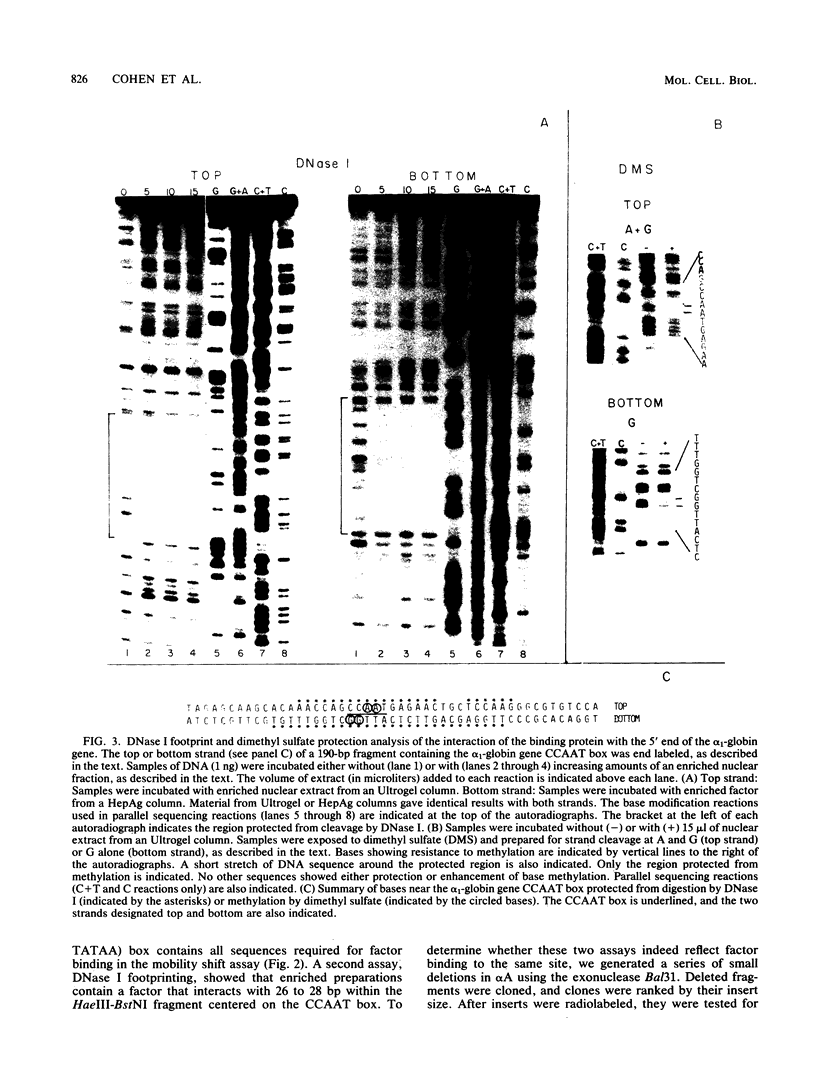
We enriched a fraction from nuclear extracts of murine erythroleukemia cells which contains a protein able to form stable complexes with the promoter region of the alpha 1-globin gene. Binding activity, which is present in mouse brain and a variety of cultured mouse and human cell lines, is not erythroid cell specific. Binding studies with alpha-globin gene promoter deletion mutants as well as DNase I footprinting and dimethyl sulfate protection studies showed that the factor bound specifically to the CCAAT box of the alpha 1 promoter. Enriched factor preparations exhibited weak binding to the promoter region of the beta maj-globin gene. This suggests that this protein could bind differentially to these two promoters in vivo. The enriched factor may be a ubiquitous nuclear protein involved in the differential regulation of the alpha 1- and beta maj-globin genes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V., Mellon P., Charnay P., Maniatis T., Axel R. The regulated expression of beta-globin genes introduced into mouse erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):483–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Treisman R., Mellon P., Chao M., Axel R., Maniatis T. Differences in human alpha- and beta-globin gene expression in mouse erythroleukemia cells: the role of intragenic sequences. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90547-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. B., Sheffery M. Nucleosome disruption precedes transcription and is largely limited to the transcribed domain of globin genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):109–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Metherall J. E., Yamakawa M., Pan J., Weissman S. M., Forget B. G. A point mutation in the A gamma-globin gene promoter in Greek hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):325–326. doi: 10.1038/313325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egly J. M., Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Chambon P. Is actin a transcription initiation factor for RNA polymerase B? EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2363–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo G., Razvi F., Ruberti I., Mohr I., Worcel A. Chromatin-specific hypersensitive sites are assembled on a Xenopus histone gene injected into Xenopus oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 5;181(3):333–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo G., Worcel A. Analysis of the chromatin assembled in germinal vesicles of Xenopus oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 5;170(3):699–722. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelinas R., Endlich B., Pfeiffer C., Yagi M., Stamatoyannopoulos G. G to A substitution in the distal CCAAT box of the A gamma-globin gene in Greek hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):323–325. doi: 10.1038/313323a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., Shewmaker C. K., Jat P., Flavell R. A. Localization of DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison R. C. The nucleotide sequence of the rabbit embryonic globin gene beta 4. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8739–8744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer E., Hofer-Warbinek R., Darnell J. E., Jr Globin RNA transcription: a possible termination site and demonstration of transcriptional control correlated with altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):887–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. K., Ley T., Turner P., Moulton A. D., Nienhuis A. W. Differences in human alpha-, beta- and delta-globin gene expression in monkey kidney cells. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. A method for mapping intranuclear protein-DNA interactions and its application to a nuclease hypersensitive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2296–2300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Eiferman F., van de Rijn P., Gorin M. B., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. The evolution of alpha-fetoprotein and albumin. II. The structures of the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes in the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1960–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Zimmermann W., Oliff A., Friedrich R. Molecular analysis of the envelope gene and long terminal repeat of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: implications for the functions of these sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):828–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.828-840.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Goossens M. J., Kan Y. W. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of human 5'-alpha-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7054–7058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Protein synthesis: its control in erythropoiesis. Science. 1972 Mar 3;175(4025):955–961. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4025.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Gene expression in murine erythroleukemia cells. Transcriptional control and chromatin structure of the alpha 1-globin gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):417–436. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Hexamethylenebisacetamide-resistant murine erythroleukemia cells have altered patterns of inducer-mediated chromatin changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3349–3353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation: DNase I hypersensitivity and DNA methylation near the globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1180–1184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O. Recovery of DNA from gels. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):371–380. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington C. A., Leder P. Rescuing the in vitro function of a globin pseudogene promoter. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):192–195. doi: 10.1038/298192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Green M. R., Maniatis T. cis and trans activation of globin gene transcription in transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Rosenthal A., Flavell R., Grosveld F. DNA sequences required for regulated expression of beta-globin genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90548-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., deBoer E., Grosveld F. G., Flavell R. A. Regulated expression of the human beta-globin gene family in murine erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):333–336. doi: 10.1038/305333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]