Abstract
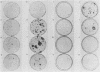
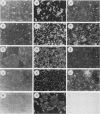
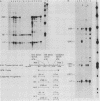
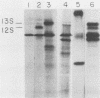
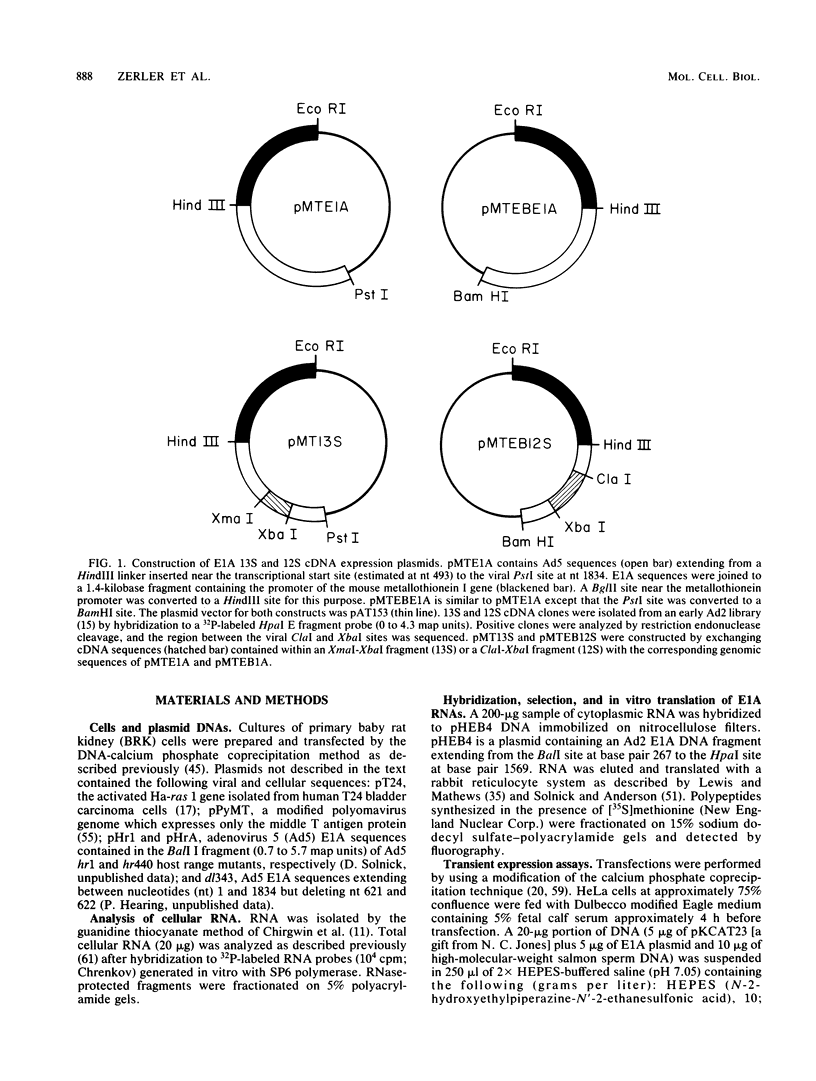
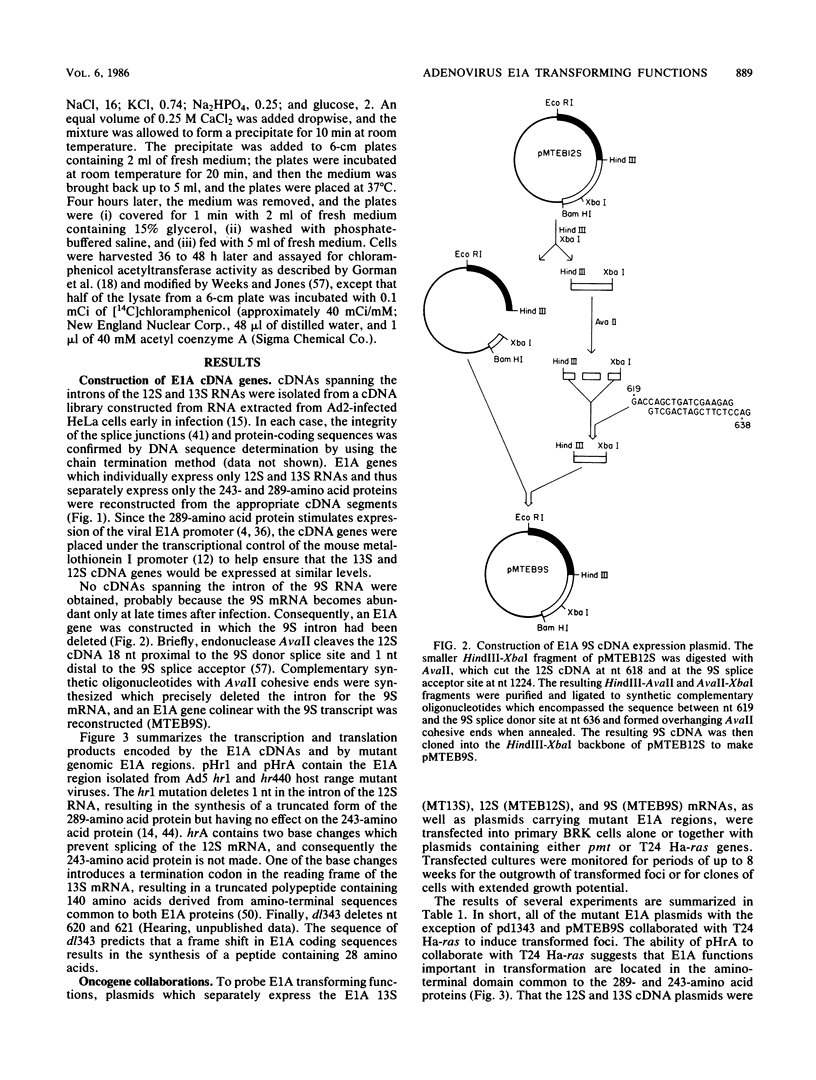
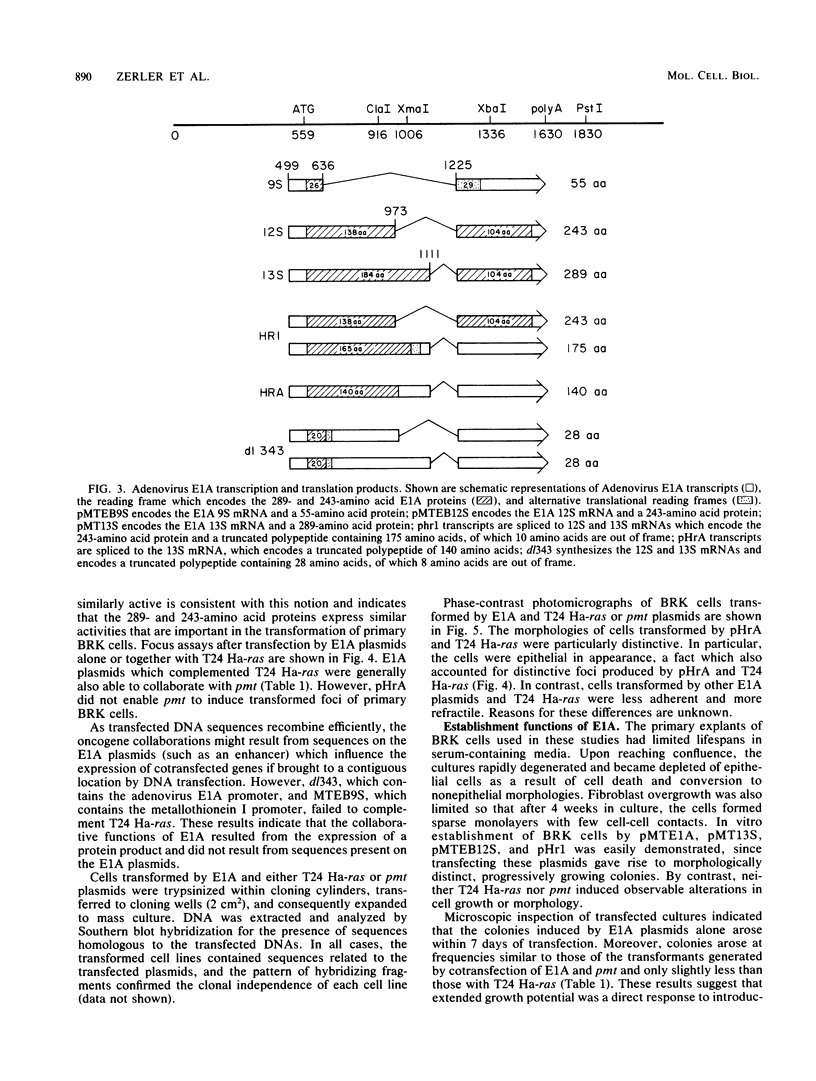
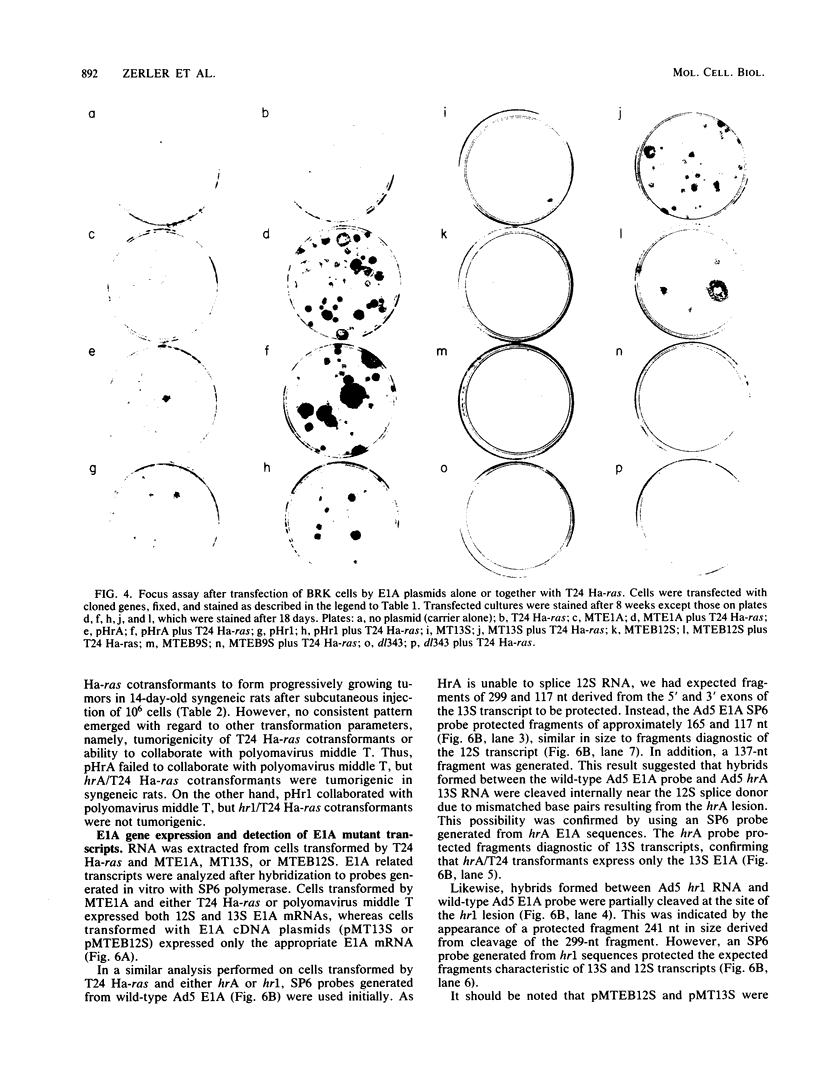
Plasmids expressing partial adenovirus early region 1A (E1A) coding sequences were tested for activities which facilitate in vitro establishment (immortalization) of primary baby rat kidney cells and which enable the T24 Harvey ras-related oncogene and the polyomavirus middle T antigen (pmt) gene to transform primary baby rat kidney cells. E1A cDNAs expressing the 289- and 243-amino acid proteins expressed both E1A transforming functions. Mutant hrA, which encodes a 140-amino acid protein derived from the amino-terminal domain shared by the 289- and 243-amino acid proteins, enabled ras (but not pmt) to transform and facilitated in vitro establishment to a low, but detectable, extent. These studies suggest that E1A functions which collaborate with ras oncogenes and those which facilitate establishment are linked. Furthermore, E1A transforming functions are not associated with activities of the 289-amino acid E1A proteins required for efficient transcriptional activation of viral early region promoters.
Full text
PDF

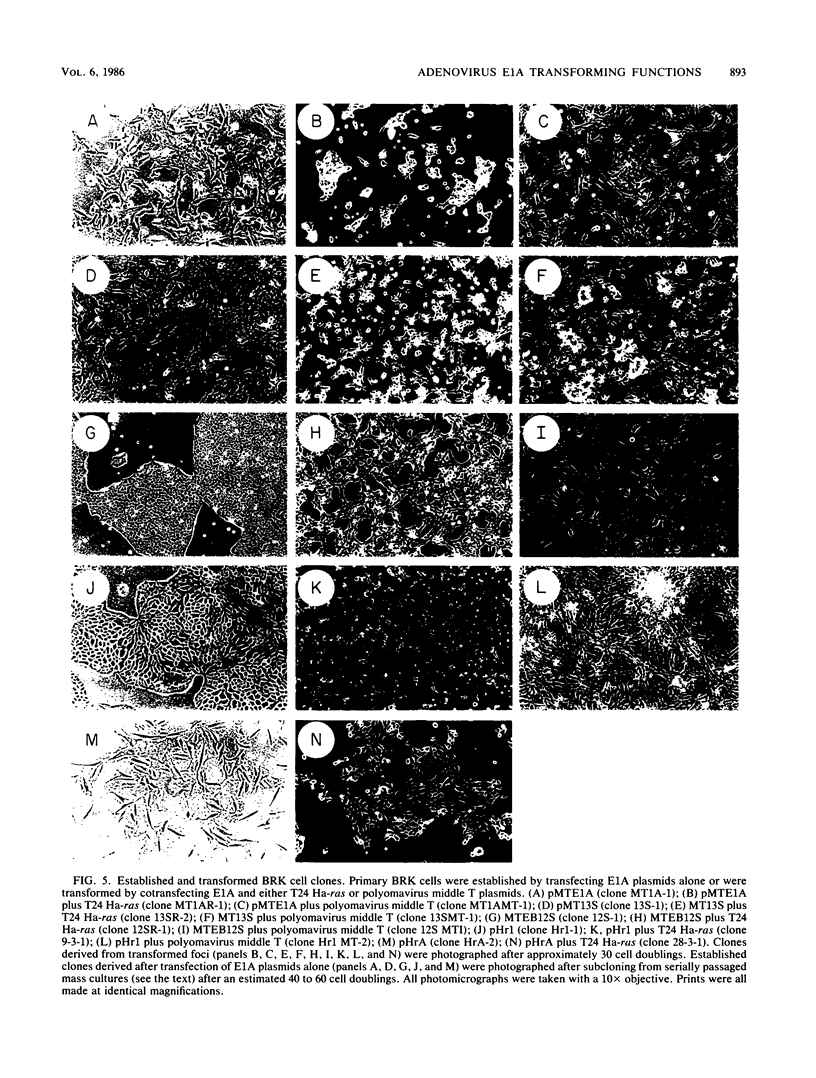

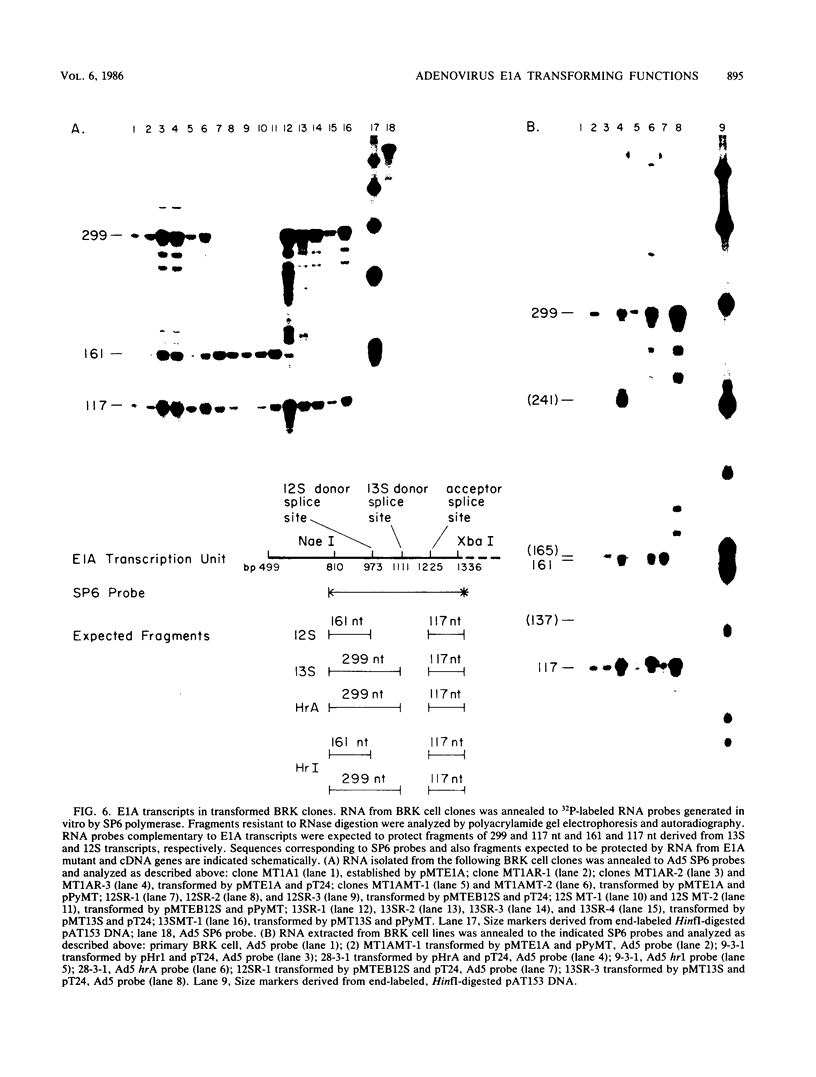
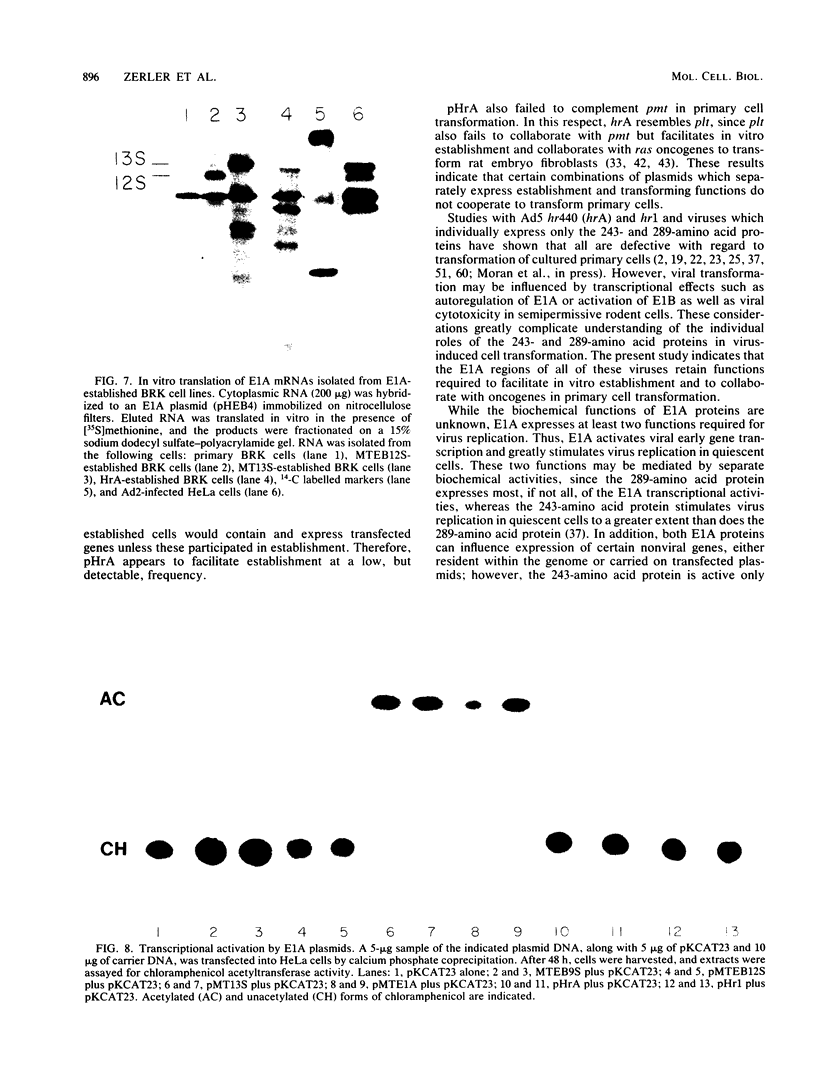



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan M., Zhu J. D., Montague P., Paul J. Differential response of multiple epsilon-globin cap sites to cis- and trans-acting controls. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90495-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Fisher P. B. Cold-sensitive expression of transformation by a host range mutant of type 5 adenovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1352–1356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellett A. J., Li P., David E. T., Mackey E. J., Braithwaite A. W., Cutt J. R. Control functions of adenovirus transformation region E1A gene products in rat and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1933–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Khoury G. trans Activation of the simian virus 40 late transcription unit by T-antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Jones N. C. Transformation-defective mutant of adenovirus type 5 containing a single altered E1a mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.657-664.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. H., Milovanovic Z. Z., Babiss L. E., Fisher P. B. Accelerated onset of viral transcription in adenovirus-infected HeLa cells treated with the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):563–566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Slamon D. J., Rosenblatt J. D., Shah N. P., Quan S. G., Wachsman W. The x gene is essential for HTLV replication. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):54–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2990037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Perrin F., Gannon F., Palmiter R. D. Isolation and characterization of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esche H., Mathews M. B., Lewis J. B. Proteins and messenger RNAs of the transforming region of wild-type and mutant adenoviruses. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):399–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyer G. A., Katoh Y., Roberts R. J. Characterization of the major mRNAs from adenovirus 2 early region 4 by cDNA cloning and sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3503–3519. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Berk A. J. Cis-acting induction of adenovirus transcription. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):683–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb M., Shimizu K., Perucho M., Wigler M. Isolation and preliminary characterization of a human transforming gene from T24 bladder carcinoma cells. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):404–409. doi: 10.1038/296404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Harrison T., Williams J. Defective transforming capacity of adenovirus type 5 host-range mutants. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley K. P., Overhauser J., Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Jones N. C. Transformation properties of type 5 adenovirus mutants that differentially express the E1A gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Galos R., Williams J. Isolation of type 5 adenovirus mutants with a cold-sensitive host range phenotype: genetic evidence of an adenovirus transformation maintenance function. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):109–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz D. R., Chinnadurai G. Evidence that a second tumor antigen coded by adenovirus early gene region E1a is required for efficient cell transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):163–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Kao H. T., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Strickland S. Common control of the heat shock gene and early adenovirus genes: evidence for a cellular E1A-like activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus 5 E2 transcription unit: an E1A-inducible promoter with an essential element that functions independently of position or orientation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):875–882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Currie G. A. Cellular immortalization by a cDNA clone encoding the transformation-associated phosphoprotein p53. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):651–654. doi: 10.1038/312651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Nevins J. R. Transcriptional activation and subsequent control of the human heat shock gene during adenovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2058–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):280–282. doi: 10.1038/312280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Elkaim R., Goding C. R., Jalinot P., Sassone-Corsi P., Perricaudet M., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Individual products of the adenovirus 12S and 13S EIa mRNAs stimulate viral EIIa and EIII expression at the transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Mathews M. B. Control of adenovirus early gene expression: a class of immediate early products. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold R. F., Overell R. W. Fibroblast immortality is a prerequisite for transformation by EJ c-Ha-ras oncogene. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):648–651. doi: 10.1038/304648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Cowie A., Carr A., Glaichenhaus N., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The roles of individual polyoma virus early proteins in oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):713–718. doi: 10.1038/300713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Naghashfar Z., Cowie A., Carr A., Grisoni M., Kamen R., Cuzin F. Expression of the large T protein of polyoma virus promotes the establishment in culture of "normal" rodent fibroblast cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4354–4358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Selective inhibition of adenovirus type 2 early region II and III transcription by an anisomycin block of protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):789–799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Rosen C., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A transcriptional activator protein encoded by the x-lor region of the human T-cell leukemia virus. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1430–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2990028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. An adenovirus mutant defective in splicing RNA from early region 1A. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):508–510. doi: 10.1038/291508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Anderson M. A. Transformation-deficient adenovirus mutant defective in expression of region 1A but not region 1B. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Eng C. Y., Berk A. J. An adenovirus early region 1A protein is required for maximal viral DNA replication in growth-arrested human cells. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):742–750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.742-750.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus 2 early region 1A stimulates expression of both viral and cellular genes. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):789–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Green M. R., Maniatis T. cis and trans activation of globin gene transcription in transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Novak U., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Transformation of rat cells by an altered polyoma virus genome expressing only the middle-T protein. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):595–600. doi: 10.1038/292595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen A., Pettersson U. The molecular structure of the 9S mRNA from early region 1A of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 15;165(3):496–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberg G., Shenk T. Dissection of overlapping functions within the adenovirus type 5 E1A gene. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1907–1912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]