Abstract
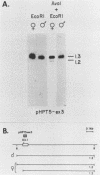
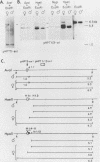
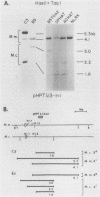
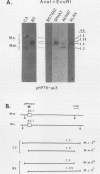
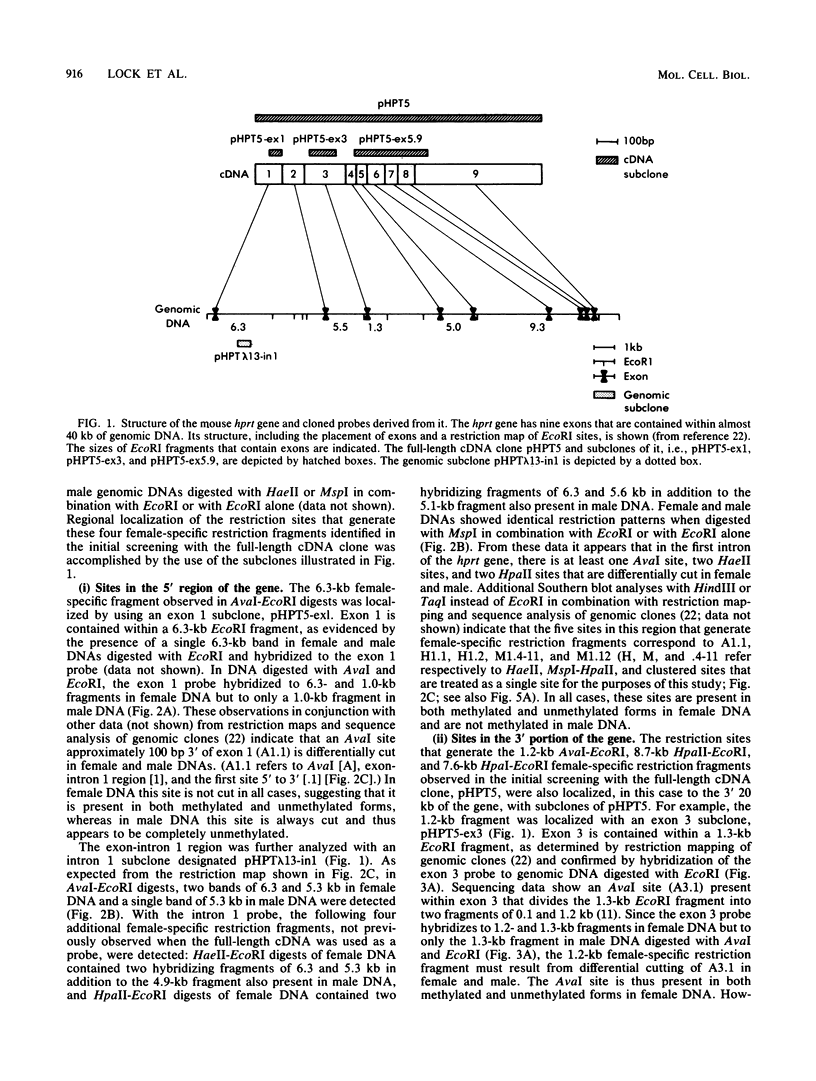
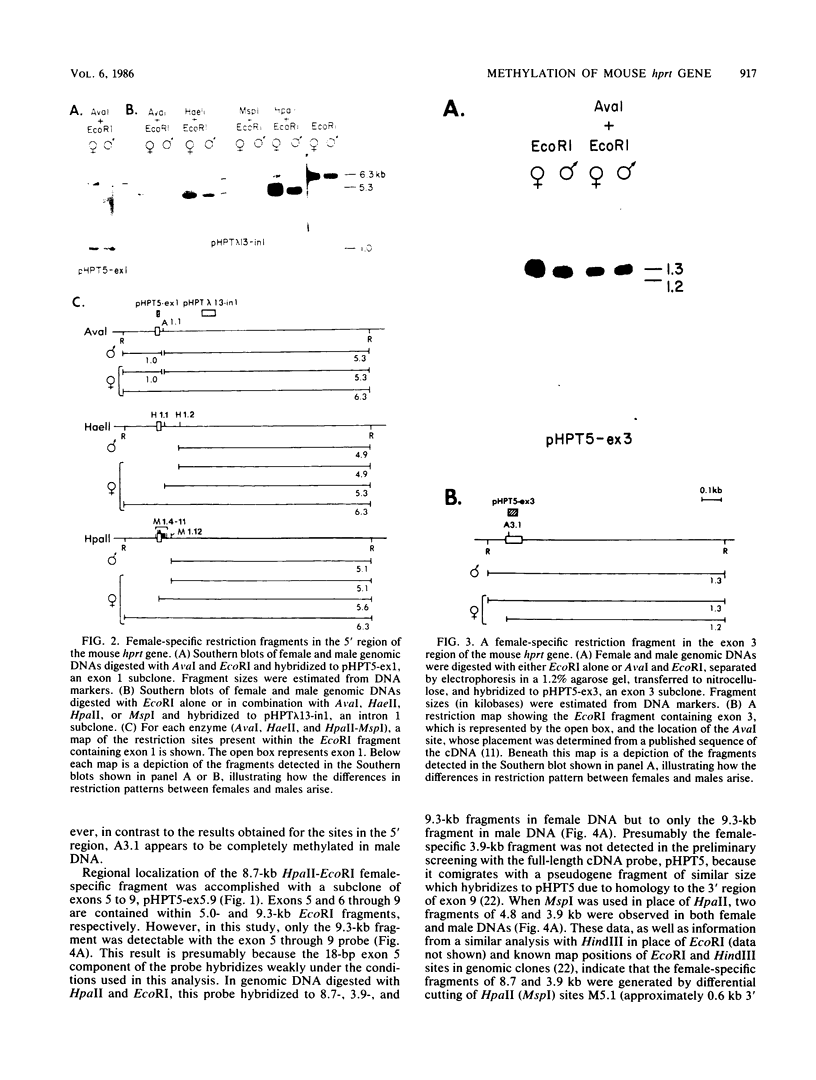
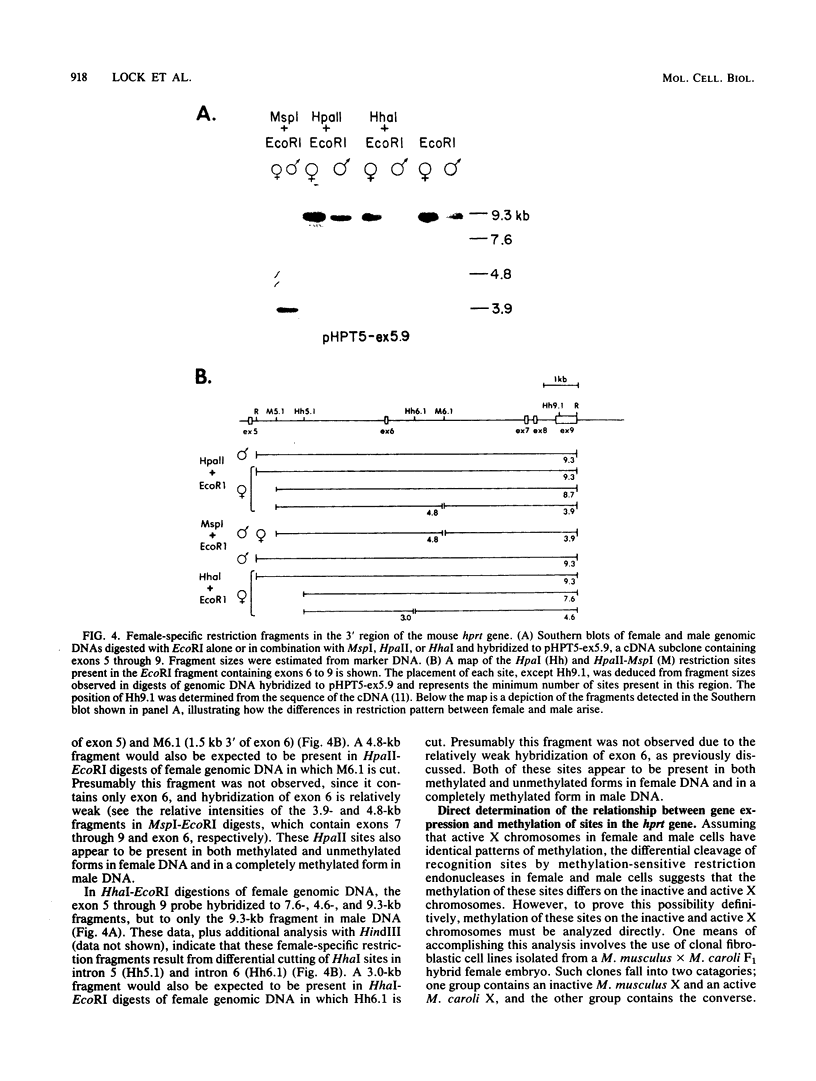
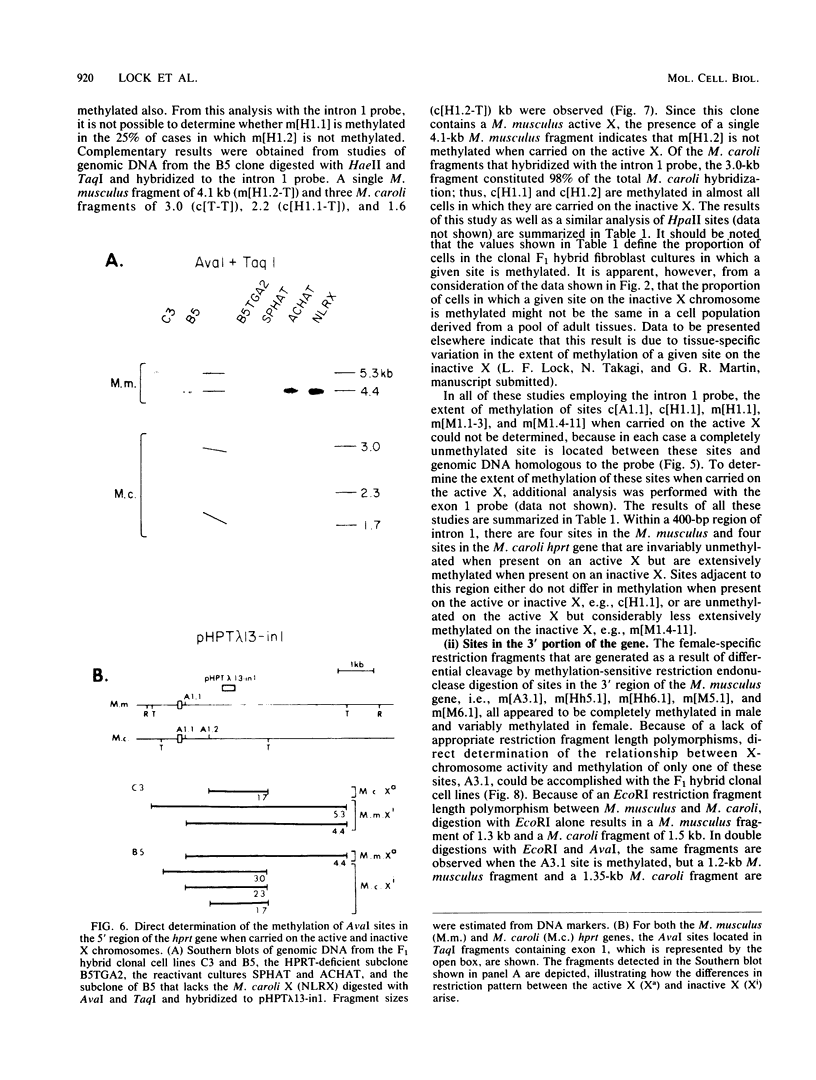
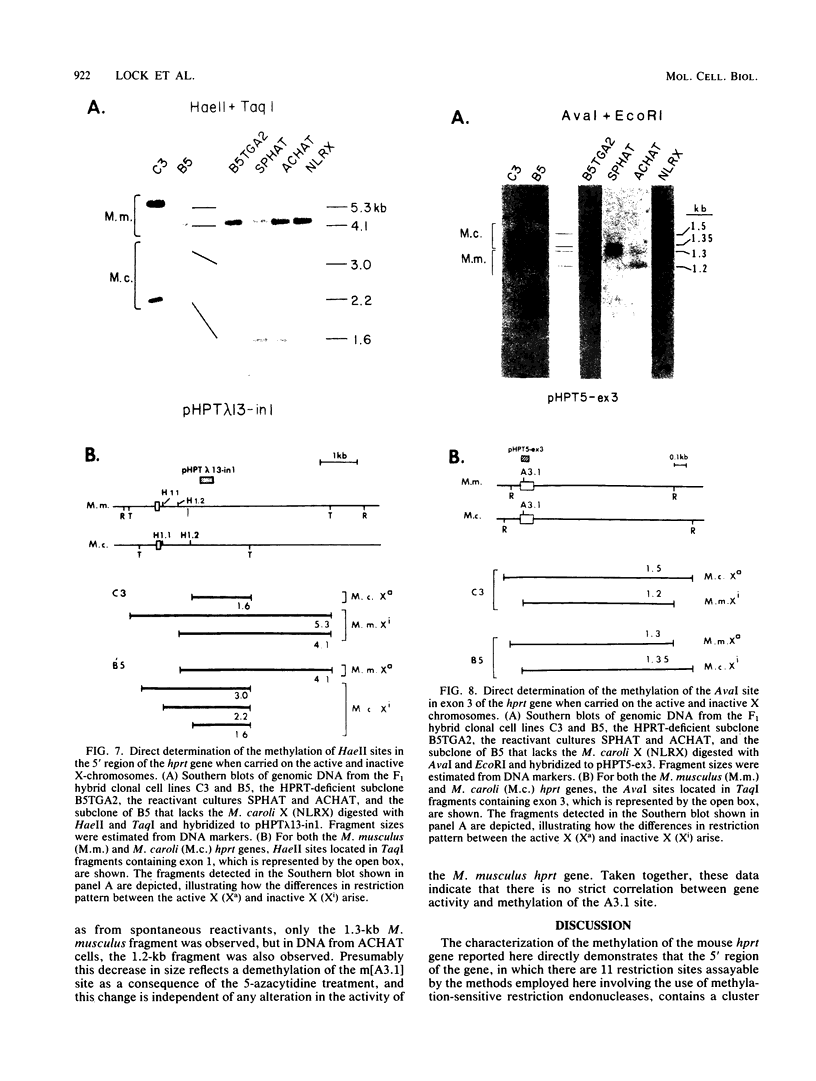
It has been proposed that DNA methylation is involved in the mechanism of X inactivation, the process by which equivalence of levels of X-linked gene products is achieved in female (XX) and male (XY) mammals. In this study, Southern blots of female and male DNA digested with methylation-sensitive restriction endonucleases and hybridized to various portions of the cloned mouse hprt gene were compared, and sites within the mouse hprt gene were identified that are differentially methylated in female and male cells. The extent to which these sites are methylated when carried on the active and inactive X chromosomes was directly determined in a similar analysis of DNA from clonal cell lines established from a female embryo derived from a mating of two species of mouse, Mus musculus and Mus caroli. The results revealed two regions of differential methylation in the mouse hprt gene. One region, in the first intron of the gene, includes four sites that are completely unmethylated when carried on the active X and extensively methylated when carried on the inactive X. These same sites are extensively demethylated in hprt genes reactivated either spontaneously or after 5-azacytidine treatment. The second region includes several sites in the 3' 20kilobases of the gene extending from exon 3 to exon 9 that show the converse pattern; i.e., they are completely methylated when carried on the active X and completely unmethylated when carried on the inactive X. At least one of these sites does not become methylated after reactivation of the gene. The results of this study, together with the results of previous studies by others of the human hprt gene, indicate that these regions of differential methylation on the active and inactive X are conserved between mammalian species. Furthermore, the data described here are consistent with the idea that at least the sites in the 5' region of the gene play a role in the X inactivation phenomenon and regulation of expression of the mouse hprt gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bücher T., Bender W., Fundele R., Hofner H., Linke I. Quantitative evaluation of electrophoretic allo-and isozyme patterns. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 30;115(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V. M., Kratzer P. G., Siracusa L. D., Quarantillo B. A., Evans R., Liskay R. M. Evidence for DNA modification in the maintenance of X-chromosome inactivation of adult mouse tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5357–5361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Andina R., Gant N. Ontogeny of X-chromosome inactivation in the female germ line. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Mar 15;91(2):454–457. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Riggs A. D. Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. A. 5-azacytidine-induced re-expression of alleles on the inactive X chromosome in a hybrid mouse cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R., Pugh J. E. DNA modification mechanisms and gene activity during development. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSSE J., KAISER A. D., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. VIII. Frequencies of nearest neighbor base sequences in deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:864–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. G. X chromosome activity in female germ cells of mice heterozygous for Searle's translocation T(X;16)16H. Genet Res. 1981 Jun;37(3):317–322. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Okayama H., Berg P., Esty A. C., Filpula D., Bohlen P., Johnson G. G., Shively J. E., Hunkapillar T., Friedmann T. Isolation and characterization of a full-length expressible cDNA for human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):477–481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Fuscoe J. C., Caskey C. T., Chinault A. C. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase genes of mouse and Chinese hamster: construction and sequence analysis of cDNA recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6763–6775. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzer P. G., Chapman V. M. X chromosome reactivation in oocytes of Mus caroli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3093–3097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester S. C., Korn N. J., DeMars R. Derepression of genes on the human inactive X chromosome: evidence for differences in locus-specific rates of derepression and rates of transfer of active and inactive genes after DNA-mediated transformation. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Mar;8(2):265–284. doi: 10.1007/BF01538681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskay R. M., Evans R. J. Inactive X chromosome DNA does not function in DNA-mediated cell transformation for the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4895–4898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. X-chromosome inactivation and developmental patterns in mammals. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1972 Jan;47(1):1–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1972.tb00969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Epstein C. J., Travis B., Tucker G., Yatziv S., Martin D. W., Jr, Clift S., Cohen S. X-chromosome inactivation during differentiation of female teratocarcinoma stem cells in vitro. Nature. 1978 Jan 26;271(5643):329–333. doi: 10.1038/271329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathai C. K., Ohno S., Beutler E. Sex-linkage of the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene in Equidae. Nature. 1966 Apr 2;210(5031):115–116. doi: 10.1038/210115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon C., Ohkubo H., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Unusual methylation pattern of the alpha 2 (l) collagen gene. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Shapiro L. J. Reactivation of an inactive human X chromosome: evidence for X inactivation by DNA methylation. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):393–396. doi: 10.1126/science.6164095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Harper M. I. Sequential X chromosome inactivation coupled with cellular differentiation in early mouse embryos. Nature. 1979 Sep 27;281(5729):311–313. doi: 10.1038/281311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D. X inactivation, differentiation, and DNA methylation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(1):9–25. doi: 10.1159/000130315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell G. J., Walker P. M., Elton R. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Doublet frequency analysis of fractionated vertebrate nuclear DNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWARTZ M. N., TRAUTNER T. A., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XI. Further studies on nearest neighbor base sequences in deoxyribonucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Kitchin R. Selective silencing of eukaryotic DNA. Science. 1975 Aug 8;189(4201):426–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M. Genomic analysis of the H-2 complex region associated with mouse t haplotypes. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):961–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Sciaky-Gallili N., Razin A., Cedar H. Pattern of methylation of two genes coding for housekeeping functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2422–2426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi N., Sugawara O., Sasaki M. Regional and temporal changes in the pattern of X-chromosome replication during the early post-implantation development of the female mouse. Chromosoma. 1982;85(2):275–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00294971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., D'Urso M., Martini G., Persico M., Tufano V., Battistuzzi G., Luzzatto L. Specific methylation pattern at the 3' end of the human housekeeping gene for glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):1987–1995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tykocinski M. L., Max E. E. CG dinucleotide clusters in MHC genes and in 5' demethylated genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4385–4396. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venolia L., Gartler S. M. Comparison of transformation efficiency of human active and inactive X-chromosomal DNA. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):82–83. doi: 10.1038/302082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venolia L., Gartler S. M., Wassman E. R., Yen P., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. Transformation with DNA from 5-azacytidine-reactivated X chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2352–2354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Dintzis S., Toniolo D., Persico G., Lunnen K. D., Axelman J., Migeon B. R. Complete concordance between glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and hypomethylation of 3' CpG clusters: implications for X chromosome dosage compensation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9333–9348. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Jolly D. J., Lunnen K. D., Friedmann T., Migeon B. R. Methylation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase locus on the human X chromosome: implications for X-chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2806–2810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Clusters of CpG dinucleotides implicated by nuclease hypersensitivity as control elements of housekeeping genes. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):467–469. doi: 10.1038/314467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Studies of X chromosome DNA methylation in normal human cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):667–671. doi: 10.1038/295667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Patel P., Chinault A. C., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. Differential methylation of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase genes on active and inactive human X chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1759–1763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]