Abstract
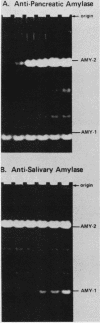
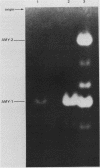
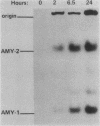
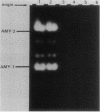
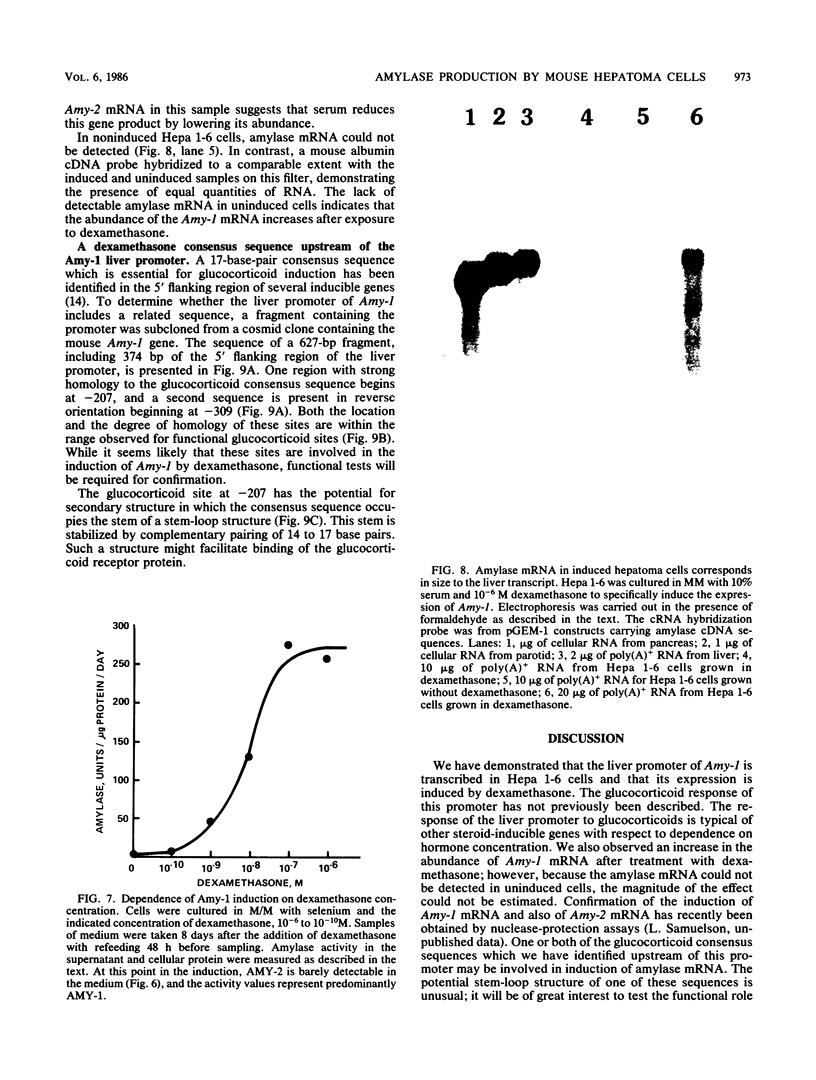
The tissue-specific expression of two types of mouse amylase genes does not overlap in vivo; the Amy-1 locus is transcribed in the parotid gland and the liver, while expression of Amy-2 is limited to the pancreas. We identified a mouse hepatoma cell line, Hepa 1-6, in which both amylase genes can be simultaneously expressed. Amy-1 is constitutively active in these cells and is inducible by dexamethasone at the level of mRNA. We demonstrated that the liver-specific promoter of Amy-1 is utilized by the dexamethasone-treated hepatoma cells, and that glucocorticoid consensus sequences are present upstream of this promoter. Amy-2 is not detectable constitutively, but can be activated if the cells are cultured in serum-free medium containing dexamethasone. Expression of Amy-2 in a nonpancreatic cell type has not previously been observed. We speculate that induction of Amy-1 and activation of Amy-2 may involve different regulatory mechanisms. Hepa 1-6 cells provide an experimental system for molecular analysis of these events.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloor J. H., Meisler M. H. Additional evidence for the close linkage of amy-1 and amy-2 in the mouse. J Hered. 1980 Nov-Dec;71(6):449–451. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a109413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloor J. H., Meisler M. H., Nielsen J. T. Genetic determination of amylase synthesis in the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):373–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. C., Papaconstantinou J. Coordinated modulation of albumin synthesis and mRNA levels in cultured hepatoma cells by hydrocortisone and cyclic AMP analogs. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9379–9384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Bernhard H. P., Miller R. A., Ruddle F. H. Expression of liver phenotypes in cultured mouse hepatoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Apr;64(4):809–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Tosi M., Schibler U., Bovey R., Wellauer P. K., Young R. A. Mouse liver and salivary gland alpha-amylase mRNAs differ only in 5' non-translated sequences. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):643–646. doi: 10.1038/289643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager G. L., Richard-Foy H., Kessel M., Wheeler D., Lichtler A. C., Ostrowski M. C. The mouse mammary tumor virus model in studies of glucocorticoid regulation. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:121–142. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. D., Rutter W. J. Rat pancreatic amylase mRNA. Tissue specificity and accumulation during embryonic development. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8736–8740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth J. P., Meisler M., Nielsen J. T. Genetic variation in amount of salivary amylase in the bank vole, Clethrionomys glareola. Genetics. 1979 Jul;92(3):915–930. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth M. E., Ainley W. M., Shumard D. S., Butow R. A., Grossman L. I. Location and structure of the var1 gene on yeast mitochondrial DNA: nucleotide sequence of the 40.0 allele. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):617–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logsdon C. D., Moessner J., Williams J. A., Goldfine I. D. Glucocorticoids increase amylase mRNA levels, secretory organelles, and secretion in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1200–1208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. D. Glucocorticoid regulation of metallothionein-I mRNA synthesis in cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2621–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Preston S. L., McMorris F. A. Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is induced by glucocorticoids in hepatocytes and hepatoma cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Feb;114(2):203–208. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041140209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittet A. C., Schibler U. Mouse alpha-amylase loci, Amy-1a and Amy-2a, are closely linked. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 5;182(3):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L., Pictet R., Githens S., Rutter W. J. Glucocorticoids modulate the in vitro development of the embryonic rat pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):398–409. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki R., Mura M., Takeuchi T., Furihata C., Matsushima T. Premature induction of amylase in pancreas and parotid gland of growing rats by dexamethasone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 28;428(3):619–626. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Pittet A. C. Two promoters of different strengths control the transcription of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a in the parotid gland and the liver. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Pittet A. C., Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Tosi M., Gellman S., Wellauer P. K. The mouse alpha-amylase multigene family. Sequence organization of members expressed in the pancreas, salivary gland and liver. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):247–266. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Sordat B., Schibler U. The two promoters of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a are differentially activated during parotid gland differentiation. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):907–912. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strahler J. R., Meisler M. Two distinct pancreatic amylase genes are active in YBR mice. Genetics. 1982 May;101(1):91–102. doi: 10.1093/genetics/101.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Ogawa M., Sugimura T. Effects of various hormones and adrenalectomy on the levels of amylase in rat pancreas and parotid gland. Experientia. 1977 Nov 15;33(11):1531–1532. doi: 10.1007/BF01918854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannice J. L., Taylor J. M., Ringold G. M. Glucocorticoid-mediated induction of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein: evidence for hormone-regulated RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4241–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebauer K., Gumucio D. L., Jones J. M., Caldwell R. M., Hartle H. T., Meisler M. H. A 78-kilobase region of mouse chromosome 3 contains salivary and pancreatic amylase genes and a pseudogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5446–5449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. A single mouse alpha-amylase gene specifies two different tissue-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]