Abstract
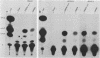
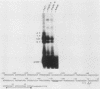
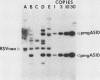
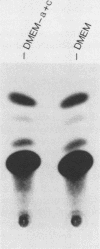
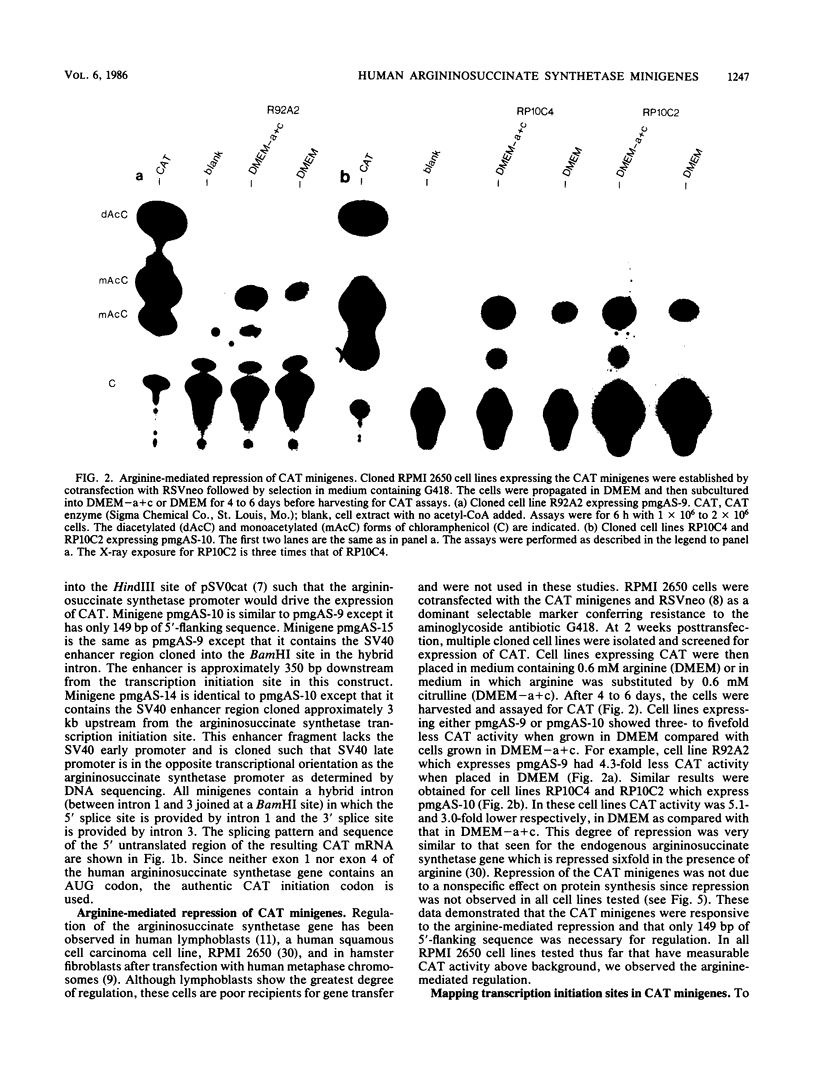
The human argininosuccinate synthetase locus is subject to metabolite-mediated repression by arginine in some cultured cell lines. To gain insight into the mechanism underlying this regulation, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) minigenes under the transcriptional control of the human argininosuccinate synthetase promoter were constructed and tested for regulation. When the minigenes were introduced into RPMI 2650 cells, a human cell line that shows sixfold regulation of the argininosuccinate synthetase gene, CAT expression was repressed three- to fivefold when arginine was present in the culture medium. A minigene containing only 149 base pairs of 5'-flanking sequence was expressed at similar levels and regulated to the same degree as one having approximately 3 kilobases of 5'-flanking sequence. Therefore, the cis-acting sequences required for the arginine-mediated repression are likely to be located within the region of the transcription initiation site. The arginine-mediated repression of the CAT minigenes was not observed in canavanine-resistant variants of RPMI 2650 cells, and therefore they showed the appropriate cell-type specificity. Cultured cells having 200-fold-increased levels of argininosuccinate synthetase can be selected by growth in medium containing the arginine analog canavanine. It was previously demonstrated that the increased expression of argininosuccinate synthetase in canavanine-resistant human lymphoblasts was due to a trans-acting mechanism. To gain further support for a trans-acting mechanism, we tested our CAT minigenes for the trans induction in canavanine-resistant variants of RPMI 2650 cells. Transfection of the CAT minigenes into RPMI 2650 cells and canavanine-resistant variants of this cell line yielded no difference in transient CAT expression. Furthermore, cloned canavanine-resistant variant cells having integrated copies of the CAT minigenes expressed CAT at similar levels as compared to the parental cell lines. Since these cell lines do exhibit arginine-mediated repression of CAT but not trans induction, these data indicate that the argine-mediated repression is a regulatory event that occurs independently of the trans induction.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bock H. G., Su T. S., O'Brien W. E., Beaudet A. L. Sequence for human argininosuccinate synthetase cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6505–6512. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. D., Felber B. K., Walling M. J., Jubier M. F., Schmidt C. J., Hamer D. H. Duplicated heavy metal control sequences of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7392–7396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Beaudet A. L., Bock H. G., O'Brien W. E. Molecular structure of the human argininosuccinate synthetase gene: occurrence of alternative mRNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1978–1984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Collier K. J. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for human pyruvate carboxylase. Structural relationship to other biotin-containing carboxylases and regulation of mRNA content in differentiating preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12831–12837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. D., Erbe R. W., Jacoby L. B. Expression of the human argininosuccinate synthetase gene in hamster transferents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4234–4238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irr J. D., Jacoby L. B. Control of argininosuccinate synthetase by arginine in human lymphoblasts. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 Jan;4(1):111–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01546496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby L. B. Canavanine-resistant variants of human lymphoblasts. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 Mar;4(2):221–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01538986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luskey K. L., Faust J. R., Chin D. J., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Amplification of the gene for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, but not for the 53-kDa protein, in UT-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8462–8469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Purified glucocorticoid receptors bind selectively in vitro to a cloned DNA fragment whose transcription is regulated by glucocorticoids in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6628–6632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Heguy A., Karin M. Structural and functional analysis of the human metallothionein-IA gene: differential induction by metal ions and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Glucocorticoid-stimulated accumulation of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: increased rate of synthesis of viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2879–2883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T. ENZYMES OF ARGININE METABOLISM IN MAMMALIAN CELL CULTURE. I. REPRESSION OF ARGININOSUCCINATE SYNTHETASE AND ARGININOSUCCINASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:136–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. A 12-base-pair DNA motif that is repeated several times in metallothionein gene promoters confers metal regulation to a heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. S., Beaudet A. L., O'Brien W. E. Increased translatable messenger ribonucleic acid for argininosuccinate synthetase in canavanine-resistant human cells. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2956–2960. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. S., Bock H. G., O'Brien W. E., Beaudet A. L. Cloning of cDNA for argininosuccinate synthetase mRNA and study of enzyme overproduction in a human cell line. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11826–11831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguin C., Felber B. K., Carter A. D., Hamer D. H. Competition for cellular factors that activate metallothionein gene transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):781–785. doi: 10.1038/312781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]