Abstract
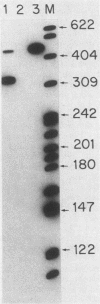
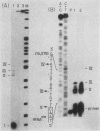
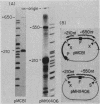
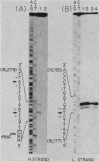
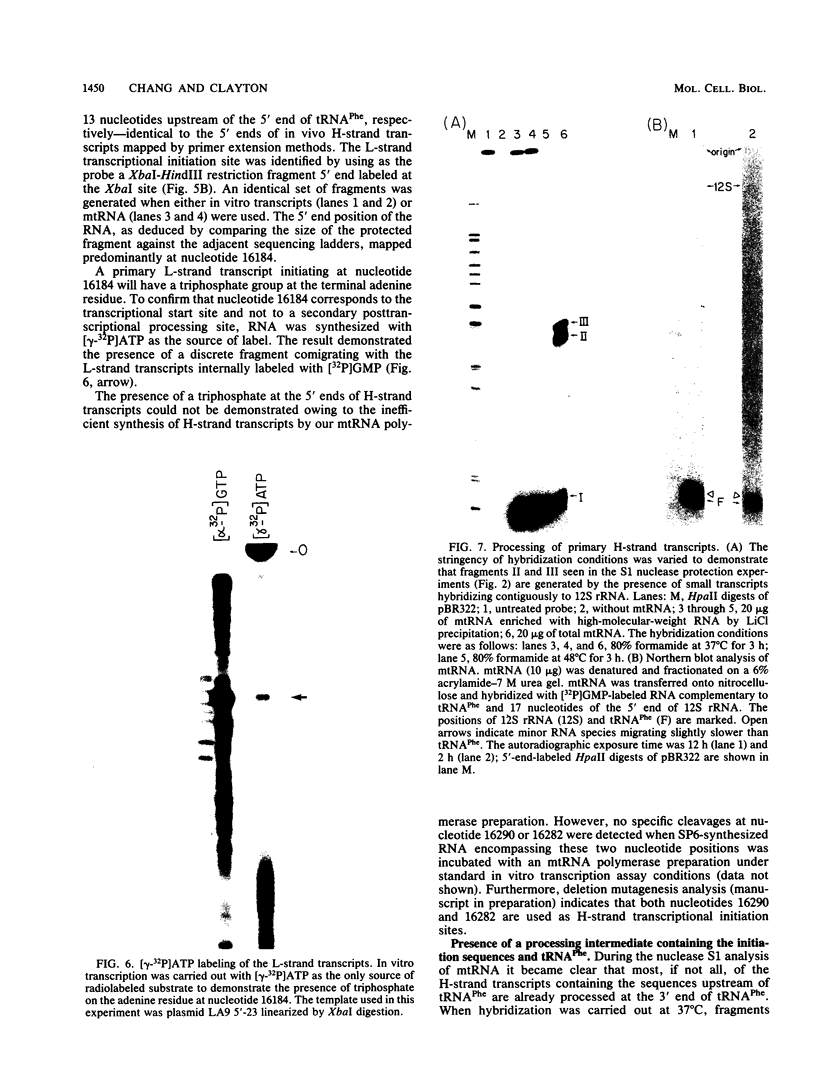
The major transcriptional control sequences of vertebrate mitochondrial DNA lie within the displacement loop region. Transcription events initiating in the displacement loop sequence of the mouse genome were identified by 5' end mapping of primary transcripts by S1 nuclease protection and primer extension techniques. Light-strand transcription initiates at a single site, 165 nucleotides upstream of the major heavy-strand origin of replication. Transcription of the heavy strand occurs at two distinct sites, 5 and 13 nucleotides upstream of the gene for phenylalanyl-tRNA, the first heavy-strand-encoded gene. This spatial relationship of the two transcriptional start sites with each other and with the origin of heavy-strand replication and the gene for tRNAPhe is quite similar to that for human mitochondrial DNA. The predominant form of primary heavy-strand transcript in mouse is a short, ca. 75-nucleotide, RNA containing the sequences of tRNAPhe and a few additional nucleotides at the 5' end of tRNAPhe, suggesting that the processing of tRNA involves independent cleavages at the 5' and 3' ends of tRNA sequences.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Eperon I. C., Sanger F., Young I. G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):683–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Van Etten R. A., Wright C. T., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas T. K., Edwards J. C., Rabinowitz M., Getz G. S. Characterization of a yeast mitochondrial promoter by deletion mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1954–1958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Precise identification of individual promoters for transcription of each strand of human mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Priming of human mitochondrial DNA replication occurs at the light-strand promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):351–355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Hauswirth W. W., Clayton D. A. Replication priming and transcription initiate from precisely the same site in mouse mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1559–1567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T., Rabinowitz M. Identification of multiple transcriptional initiation sites on the yeast mitochondrial genome by in vitro capping with guanylyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14025–14033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Replication of animal mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):693–705. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Transcription of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:573–594. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Clayton D. A. A transcription factor required for promoter recognition by human mitochondrial RNA polymerase. Accurate initiation at the heavy- and light-strand promoters dissected and reconstituted in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11330–11338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines G., Attardi G. Highly efficient RNA-synthesizing system that uses isolated human mitochondria: new initiation events and in vivo-like processing patterns. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1605–1617. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Clayton D. A. Displacement-loop replication initiation sequence in animal mitochondrial DNA exists as a family of discrete lengths. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of mitochondrial DNA replication in mouse L-cells: RNA priming during the initiation of heavy-strand synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):353–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levens D., Ticho B., Ackerman E., Rabinowitz M. Transcriptional initiation and 5' termini of yeast mitochondrial RNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5226–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoya J., Christianson T., Levens D., Rabinowitz M., Attardi G. Identification of initiation sites for heavy-strand and light-strand transcription in human mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7195–7199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagley P., Clayton D. A. Transcriptional mapping of the ribosomal RNA region of mouse L-cell mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2947–2965. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe B. A., Ma D. P., Wilson R. K., Wong J. F. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Xenopus laevis mitochondrial genome. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9759–9774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Wilkinson J. A., Roan J., Reeder R. H. Nested control regions promote Xenopus ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Van Etten R. A., Clayton D. A. Isolation of mammalian mitochondrial DNA and RNA and cloning of the mitochondrial genome. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:426–434. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. In vitro transcription of human mitochondrial DNA. Identification of specific light strand transcripts from the displacement loop region. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1268–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoza B. K., Bogenhagen D. F. Identification and in vitro capping of a primary transcript of human mitochondrial DNA. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3909–3915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]