Abstract
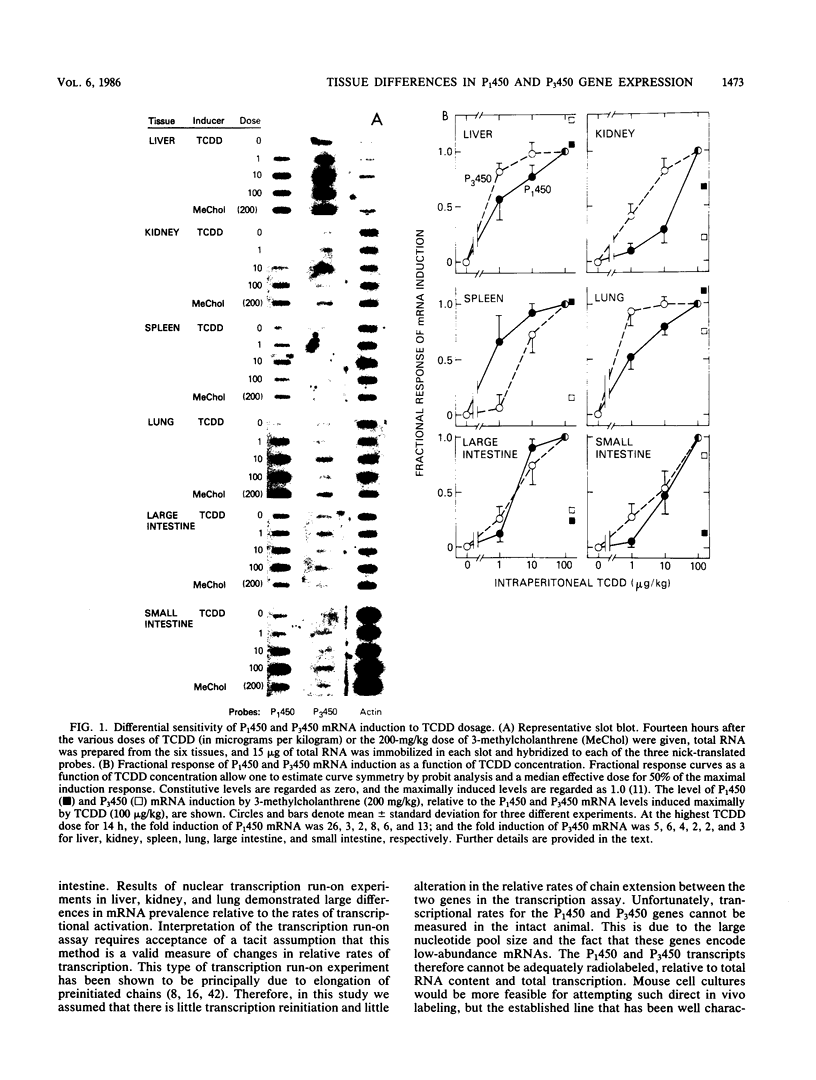
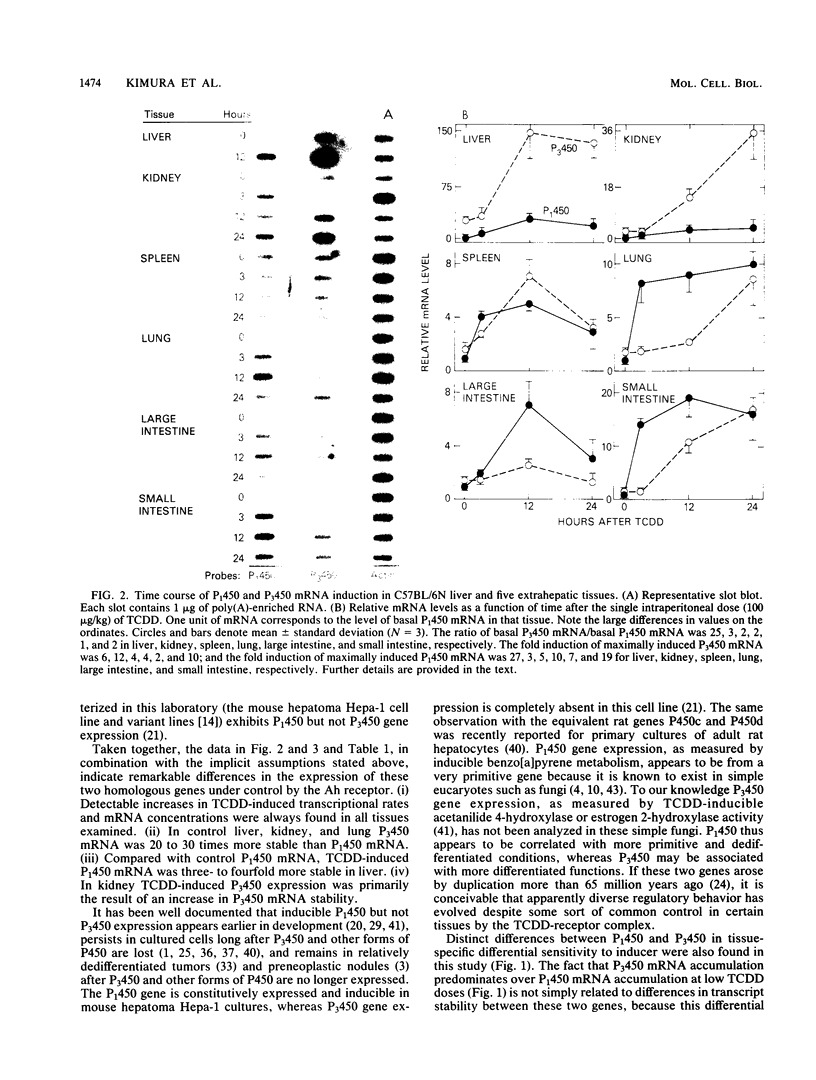
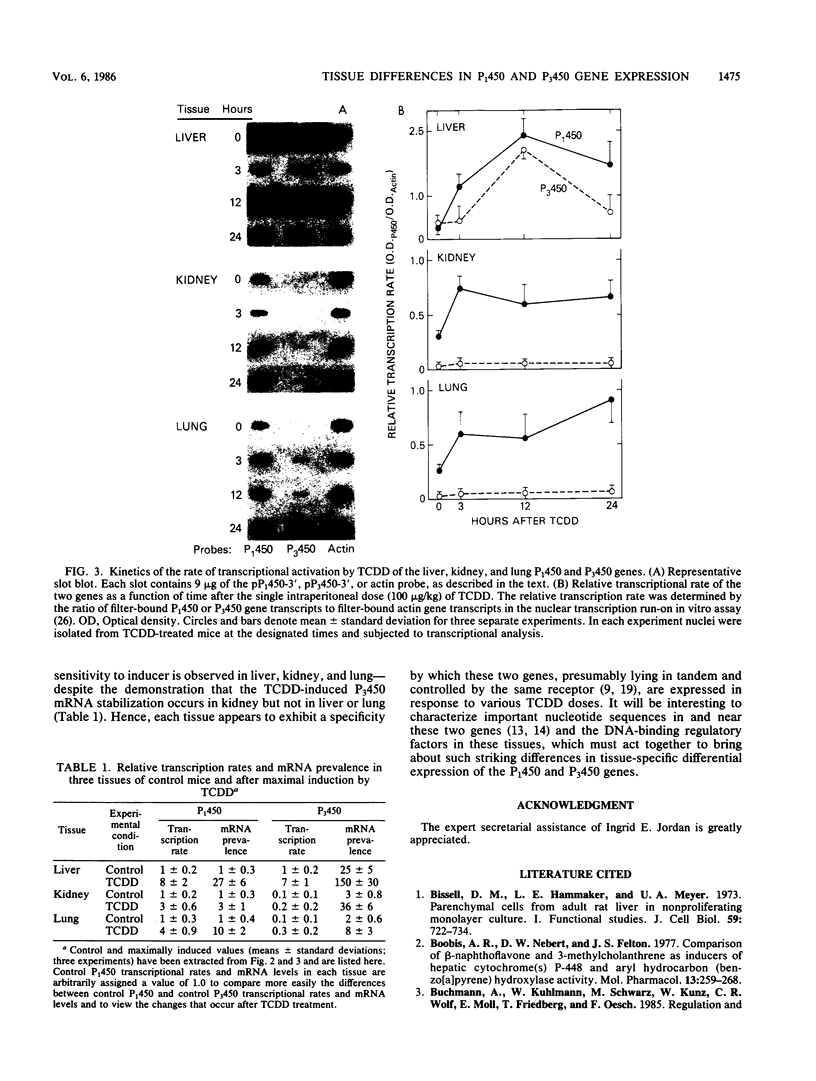
Expression of the P(1)450 and P(3)450 genes was examined in liver and five extrahepatic tissues of mice after they were treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) or 3-methylcholanthrene. All six tissues were shown to have increased P(1)450 and P(3)450 mRNA concentrations after treatment with these inducers. P(3)450 mRNA induction was more sensitive than P(1)450 mRNA induction to small doses of TCDD in liver, kidney, and lung. When transcription run-on assays were compared with mRNA prevalence, control P(3)450 mRNA in liver, kidney, and lung was shown to be 20 to 30 times more stable than control P(1)450 mRNA. After TCDD treatment the increases in mRNA concentrations did not necessarily parallel the increases in transcriptional rate. Thus, the inducer appeared to enhance mRNA stability in some instances. This was evident for liver P(1)450 mRNA, in which an 8-fold rise in transcription was associated with a 27-fold increase in mRNA content, and for kidney P(3)450 mRNA, in which a 2-fold rise in transcription was accompanied by a 12-fold increase in mRNA content. In the kidney and lung of control and TCDD-treated mice, transcriptional rates of the P(3)450 gene were at least 10-fold less than those of the P(1)450 gene. These data indicate that even though both genes are controlled by the same receptor, striking tissue-specific differences in transcription and mRNA stabilization affect the final mRNA concentrations.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissell D. M., Hammaker L. E., Meyer U. A. Parenchymal cells from adult rat liver in nonproliferating monolayer culture. I. Functional studies. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):722–734. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boobis A. R., Nebert D. W., Felton J. S. Comparison of beta-naphthoflavone and 3-methylcholanthrene as inducers of hepatic cytochrome(s) P-448 and aryl hydrocarbon (benzo[a]pyrene) hydroxylase activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;13(2):259–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Gibson D. T. Fungal oxidation of benzo[a]pyrene and (+/-)-trans-7,8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzo[a]pyrene. Evidence for the formation of a benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5159–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Induction of microsomal enzymes by foreign chemicals and carcinogenesis by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: G. H. A. Clowes Memorial Lecture. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):4875–4917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris J. P., MacDonald L. H., Patrie M. A., Martin M. A. Aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in the fungus Cunninghamella bainieri: evidence for the presence of cytochrome P-450. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Aug;175(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelboin H. V. Benzo[alpha]pyrene metabolism, activation and carcinogenesis: role and regulation of mixed-function oxidases and related enzymes. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1107–1166. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Kimura S., Nebert D. W. Comparison of the flanking regions and introns of the mouse 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5040–5049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Autoregulation plus upstream positive and negative control regions associated with transcriptional activation of the mouse P1(450) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7269–7288. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Tukey R. H., Nebert D. W. Structural gene products of the Ah locus. Transcriptional regulation of cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 mRNA levels by 3-methylcholanthrene. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;26(1):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T., Seidman M., Stollar B. D. Characterization of genomic poly(dT-dG).poly(dC-dA) sequences: structure, organization, and conformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2610–2621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen D. A., van der Hoeven T. A., Coon M. J. Purified liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. Separation and characterization of multiple forms. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3567–3570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand C. E., Gonzalez F. J., Kozak C. A., Nebert D. W. Regional linkage analysis of the dioxin-inducible P-450 gene family on mouse chromosome 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 16;130(1):396–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90430-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Altieri M., Chen Y. T., Nakamura M., Tukey R. H., Nebert D. W., Negishi M. Characterization of cytochrome P2-450 (20-S) mRNA. Association with the P1-450 genomic gene and differential response to the inducers 3-methylcholanthrene and isosafrole. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;134(1):13–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal A. K., Nebert D. W., Eisen H. W. Comparison of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase and acetanilide 4-hydroxylase induction by polycyclic aromatic compounds in human and mouse cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Aug 1;34(15):2721–2731. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M. The 1982 Bernard B. brodie Award Lecture. Metabolism of Aromatic hydrocarbons by the cytochrome P-450 system and epoxide hydrolase. Drug Metab Dispos. 1983 Jan-Feb;11(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamataki T., Maeda K., Yamazoe Y., Matsuda N., Ishii K., Kato R. A high-spin form of cytochrome P-450 highly purified from polychlorinated biphenyl-treated rats. Catalytic characterization and immunochemical quantitation in liver microsomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;24(1):146–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. The murine Ah locus. Comparison of the complete cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 cDNA nucleotide and amino acid sequences. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10705–10713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. C., Snodgrass P. J. Primary culture of normal adult rat liver cells which maintain stable urea cycle enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 19;64(2):725–734. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90380-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W. Genetic differences in susceptibility to chemically induced myelotoxicity and leukemia. Environ Health Perspect. 1981 Jun;39:11–22. doi: 10.1289/ehp.813911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Jensen N. M. The Ah locus: genetic regulation of the metabolism of carcinogens, drugs, and other environmental chemicals by cytochrome P-450-mediated monooxygenases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1979;6(4):401–437. doi: 10.3109/10409237909105427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi M., Jensen N. M., Garcia G. S., Nebert D. W. Structural gene products of the murine Ah complex. Differences in ontogenesis and glucosamine incorporation between liver microsomal cytochromes P1-450 and P-448 induced by polycyclic aromatic compounds. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):585–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi M., Nebert D. W. Structural gene products of the Ah locus. Genetic and immunochemical evidence for two forms of mouse liver cytochrome P-450 induced by 3-methylcholanthrene. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11015–11023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman R. L., Johnson E. F., Muller-Eberhard U. Identification of the major cytochrome P-450 form transplacentally induced in neonatal rabbits by 3,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8640–8647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen O., Nebert D. W. Metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: etiologic role in carcinogenesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1982 Jun;34(2):189–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik L. M., Levin W., Ryan D. E., Thomas P. E. Immunochemical relatedness of rat hepatic microsomal cytochromes P-450c and P-450d. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3950–3957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Bonney R. J. Extended expression of differentiated function in primary cultures of adult liver parenchymal cells maintained on nitrocellulose filters. I. Induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and tyrosine aminotransferase. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jul;114(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90488-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirica A. E., Pitot H. C. Drug metabolism and effects of carcinogens in cultured hepatic cells. Pharmacol Rev. 1979 Sep;31(3):205–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Gotoh O., Kawajiri K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Distinct organization of methylcholanthrene- and phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 genes in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Gotoh O., Kawajiri K., Harada T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of a methylcholanthrene-inducible cytochrome P-450 (P-450d) gene in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5026–5032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward A. R., Wrighton S. A., Pasco D. S., Fagan J. B., Li D., Guzelian P. S. Synthesis and degradation of 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible cytochromes P-450 and their mRNAs in primary monolayer cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Sep;241(2):494–508. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90575-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Developmental and tissue-specific differential regulation of the mouse dioxin-inducible P1-450 and P3-450 genes. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Jelinek W., Darnell J. E., Jr The definition of a large viral transcription unit late in Ad2 infection of HeLa cells: mapping of nascent RNA molecules labeled in isolated nuclei. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):611–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods L. F., Wiseman A. Metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene by the cytochrome P-450/P-488 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Feb;7(1):124–127. doi: 10.1042/bst0070124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]