Abstract
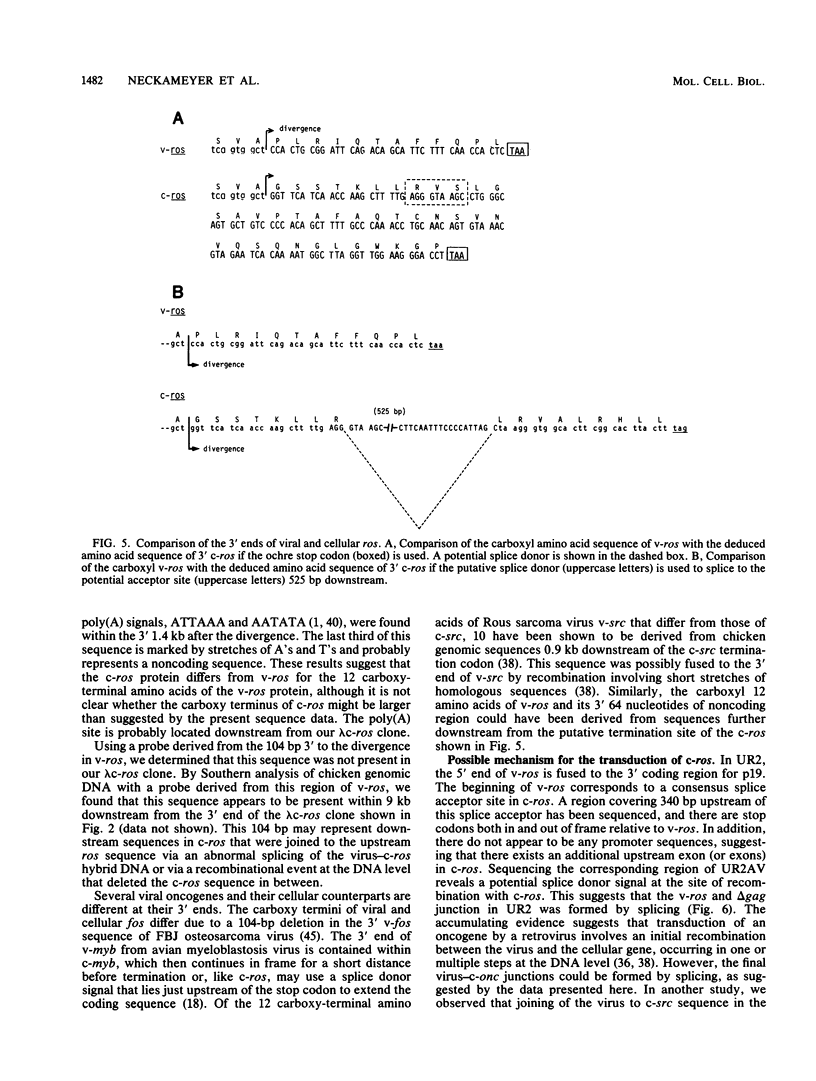
A recombinant DNA clone containing cellular sequences homologous to the transforming sequence, v-ros, of avian sarcoma virus UR2 was isolated from a chicken genomic DNA library. Heteroduplex mapping and nucleotide sequencing reveal that the v-ros sequences are distributed in nine exons ranging from 65 to 204 nucleotides on cellular ros (c-ros) DNA over a range of 11 kilobases. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences of c-ros and v-ros shows two differences: v-ros contains a three-amino-acid insertion within the hydrophobic domain presumed to be involved in membrane association, and (ii) the carboxyl 12 amino acids of v-ros are completely different from those of the deduced c-ros sequence. The deduced amino acid sequence of c-ros bears striking structural features similar to those of insulin and epidermal growth factor receptors, including the presumed hydrophobic membrane binding domain, amino acids flanking the domain, and the distance between the domain and the catalytic region of the kinase activity. The expression of c-ros appears to be under a very stringent control. When tissues at various stages of chicken development were analyzed, only kidney was found to contain a significant level of c-ros RNA. The level of c-ros RNA in kidney tissue is most abundant in 7- to 14-day-old chickens. Finally, nucleotide sequences of c-ros DNA and UR2-associated helper viral genome at regions corresponding to the gag ros recombination site suggest that the junction has been formed by RNA splicing.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed C. M., Chanda R. S., Stow N. D., Zain B. S. The nucleotide sequence of mRNA for the Mr 19 000 glycoprotein from early gene block III of adenovirus 2. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balduzzi P. C., Notter M. F., Morgan H. R., Shibuya M. Some biological properties of two new avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):268–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.268-275.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton P. C., Brugge J. S. Neural tissues express high levels of the cellular src gene product pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1157–1162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Tumor-promoting phorbol diesters cause the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors in normal human fibroblasts at threonine-654. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1974–1978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Strommer J., Engel J. D. Isolation of the chicken beta-globin gene and a linked embryonic beta-like globin gene from a chicken DNA recombinant library. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90328-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Devare S. G., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A., Antoniades H. N. Simian sarcoma virus onc gene, v-sis, is derived from the gene (or genes) encoding a platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.6304883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H., Balduzzi P. C. Avian sarcoma virus UR2 encodes a transforming protein which is associated with a unique protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):228–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.228-236.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. A., Hanafusa H. A fps gene without gag gene sequences transforms cells in culture and induces tumors in chickens. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):744–751. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.744-751.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. A., Shibuya M., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transformation potential of the cellular fps gene. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Membrane association of the transforming protein of avian sarcoma virus UR2 and mutants temperature sensitive for cellular transformation and protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.790-797.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Protein phosphorylation at tyrosine is induced by the v-erbB gene product in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe A., Gobet M., Sherr C. J., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the feline retroviral oncogene v-fms shows unexpected homology with oncogenes encoding tyrosine-specific protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):85–89. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Ling N., Cooper J. A. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of the EGF receptor at a threonine residue close to the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):480–483. doi: 10.1038/311480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Marinetti G. V., Balduzzi P. C. Transforming protein of avian sarcoma virus UR2 is associated with phosphatidylinositol kinase activity: possible role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckameyer W. S., Wang L. H. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus UR2 and comparison of its transforming sequence with those of other avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):914–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.914-921.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckameyer W. S., Wang L. H. Nucleotide sequence of avian sarcoma virus UR2 and comparison of its transforming gene with other members of the tyrosine protein kinase oncogene family. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):879–884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.879-884.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachl C., Biegalke B., Linial M. RNA and protein encoded by MH2 virus: evidence for subgenomic expression of v-myc. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.133-139.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Vande Woude G. F. Expression of c-mos proto-oncogene transcripts in mouse tissues. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):516–518. doi: 10.1038/315516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Foulkes J. G., Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. Sequences of the A-MuLV protein needed for fibroblast and lymphoid cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Hanafusa H., Balduzzi P. C. Cellular sequences related to three new onc genes of avian sarcoma virus (fps, yes, and ros) and their expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.143-152.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge L. K., Levy B. T., Maness P. F. pp60c-src is developmentally regulated in the neural retina. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano S., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activity in virus-transformed and nontransformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2399–2404. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Transduction of a cellular oncogene: the genesis of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2519–2523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Feldman R. A., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the viral and cellular src gene of chickens. 1. Complete nucleotide sequence of an EcoRI fragment of recovered avian sarcoma virus which codes for gp37 and pp60src. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.1-11.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Noda M., Takano T. Structure of the baboon endogenous virus genome: nucleotide sequences of the long terminal repeat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6615–6626. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. Multiple polyadenylation sites in a mouse alpha-amylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2313–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Firestone G. L., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoids and chromosomal position modulate murine mammary tumor virus transcription by affecting efficiency of promoter utilization. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):551–561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. From c-fos to v-fos. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):317–317. doi: 10.1038/308317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Feldman R., Shibuya M., Hanafusa H., Notter M. F., Balduzzi P. C. Genetic structure, transforming sequence, and gene product of avian sarcoma virus UR1. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.258-267.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Hanafusa H., Notter M. F., Balduzzi P. C. Genetic structure and transforming sequence of avian sarcoma virus UR2. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):833–841. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.833-841.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Scrace G. T., Whittle N., Stroobant P., Johnsson A., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):35–39. doi: 10.1038/304035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nishida T., Miyajima N., Kawai S., Ooi T., Toyoshima K. The erbB gene of avian erythroblastosis virus is a member of the src gene family. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]