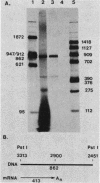
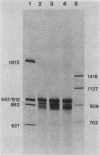
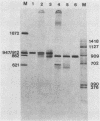
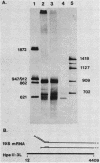
Abstract
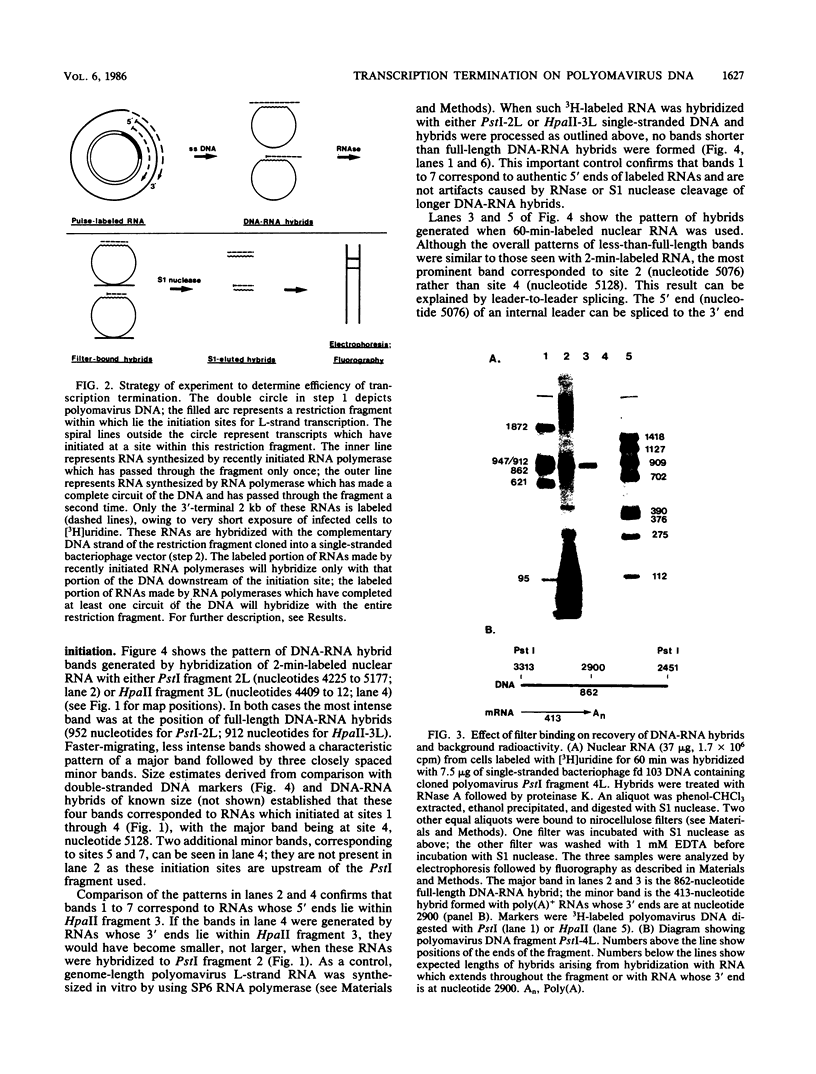
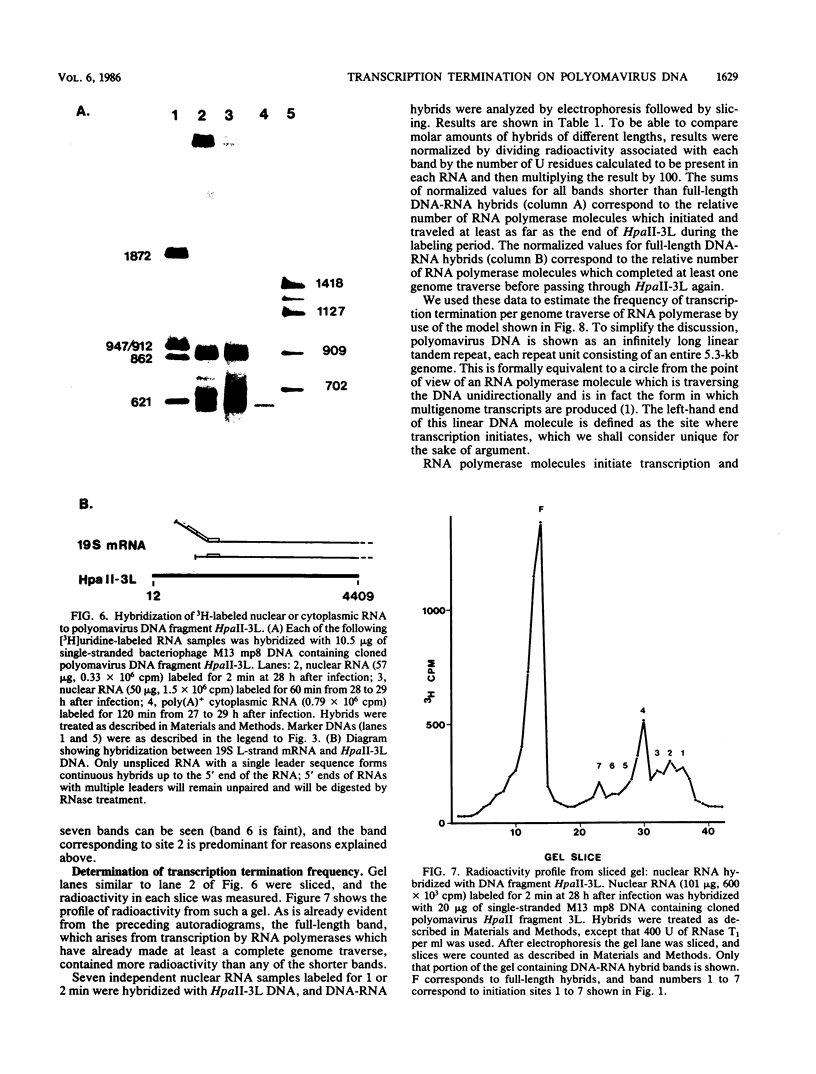
We devised a strategy to measure the efficiency of transcription termination in vivo by RNA polymerase on polyomavirus DNA. Pulse-labeled nuclear RNA was hybridized with a single-stranded polyomavirus DNA fragment which spans the transcription initiation region. Hybrids were treated with RNase, bound to nitrocellulose filters, eluted with S1 nuclease, and analyzed by gel electrophoresis. The ratio of full-length to less-than-full-length DNA-RNA hybrids was used to calculate transcription termination frequency. We found that 50% of the polymerases terminated per traverse of the L DNA strand during the late phase of infection. The method for mapping in vivo pulse-labeled RNAs which we developed is potentially useful for studying unstable cellular or viral RNAs.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H., Buetti E., Scherrer K., Weil R. Transcription of the polyoma virus genome: synthesis and cleavage of giant late polyoma-specific RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2231–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H. Efficiency of processing of viral RNA during the early and late phases of productive infection by polyoma virus. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):628–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.628-635.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H. Kinetics and efficiency of polyadenylation of late polyomavirus nuclear RNA: generation of oligomeric polyadenylated RNAs and their processing into mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):722–729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H., Miéville F. Extent of transcription of the E strand of polyoma virus DNA during the early phase of productive infection. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):885–894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.885-894.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Acheson N. H., Maxwell I. H. Strand-specific transcription of polyoma virus DNA-early in productive infection and in transformed cells. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.20-26.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., McMaster G. K. The analysis of nucleic acids in gels using glyoxal and acridine orange. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):380–391. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Tyndall C., Kamen R. Sequences at the capped 5'-ends of polyoma virus late region mRNAs: an example of extreme terminal heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6305–6322. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P., Esty A., LaPorte P., Friedmann T. Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the polyoma late region: features common to the polyoma early region and SV40. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):771–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Goldberg S., Darnell J. E., Jr hnRNA in HeLa cells: distribution of transcript sizes estimated from nascent molecule profile. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):465–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick R. B., Chelm B. K., Gray P. W., Orozco E. M., Jr Use of aurintricarboxylic acid as an inhibitor of nucleases during nucleic acid isolation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3055–3064. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiser W. C., Eckhart W. Polyoma virus early and late mRNAs in productively infected mouse 3T6 cells. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):175–188. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.175-188.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R., Neugebauer K., Pirkl E., Zentgraf H., Schaller H. Conversion of bacteriophage fd into an efficient single-stranded DNA vector system. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):231–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00267434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Favaloro J., Parker J. Topography of the three late mRNA's of polyoma virus which encode the virion proteins. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):637–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.637-651.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Kamen R. Amplification in the leader sequence of late polyoma virus mRNAs. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):373–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Splicing of adenovirus RNA in a cell-free transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5230–5234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Webster R. E., Zinder N. D. Purification and properties of ribonuclease III from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C. Detection of an unstable RNA in chick fibroblasts after reduction of the UTP pool by glucosamine. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec;24(2):358–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Hausen P. Enzyme from calf thymus degrading the RNA moiety of DNA-RNA Hybrids: effect on DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Science. 1969 Oct 17;166(3903):393–395. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3903.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Characterisation of polyoma late mRNA leader sequences by molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4867–4888. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Kamen R. Structure of polyoma virus late nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):273–301. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall C., La Mantia G., Thacker C. M., Favaloro J., Kamen R. A region of the polyoma virus genome between the replication origin and late protein coding sequences is required in cis for both early gene expression and viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6231–6250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]