Abstract
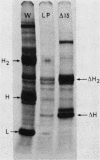
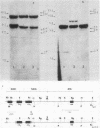
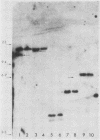
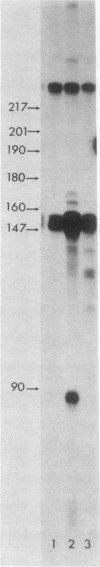
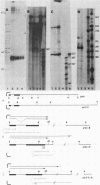
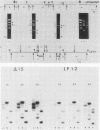
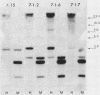
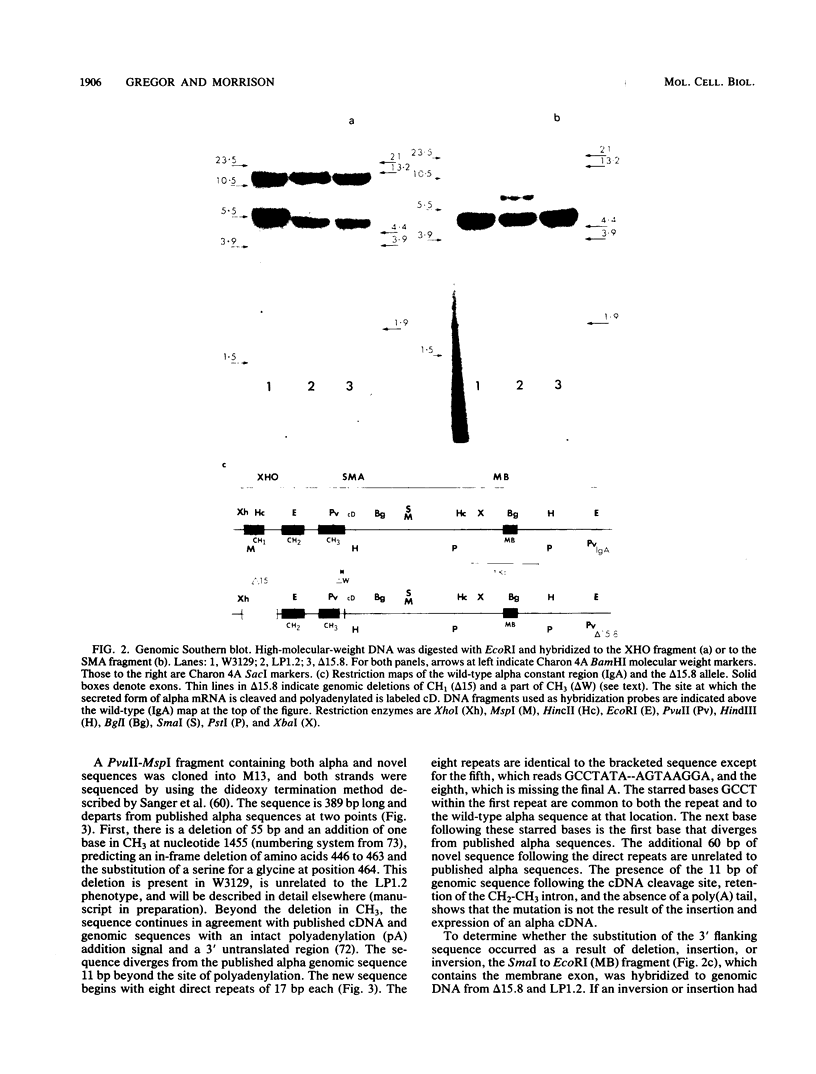
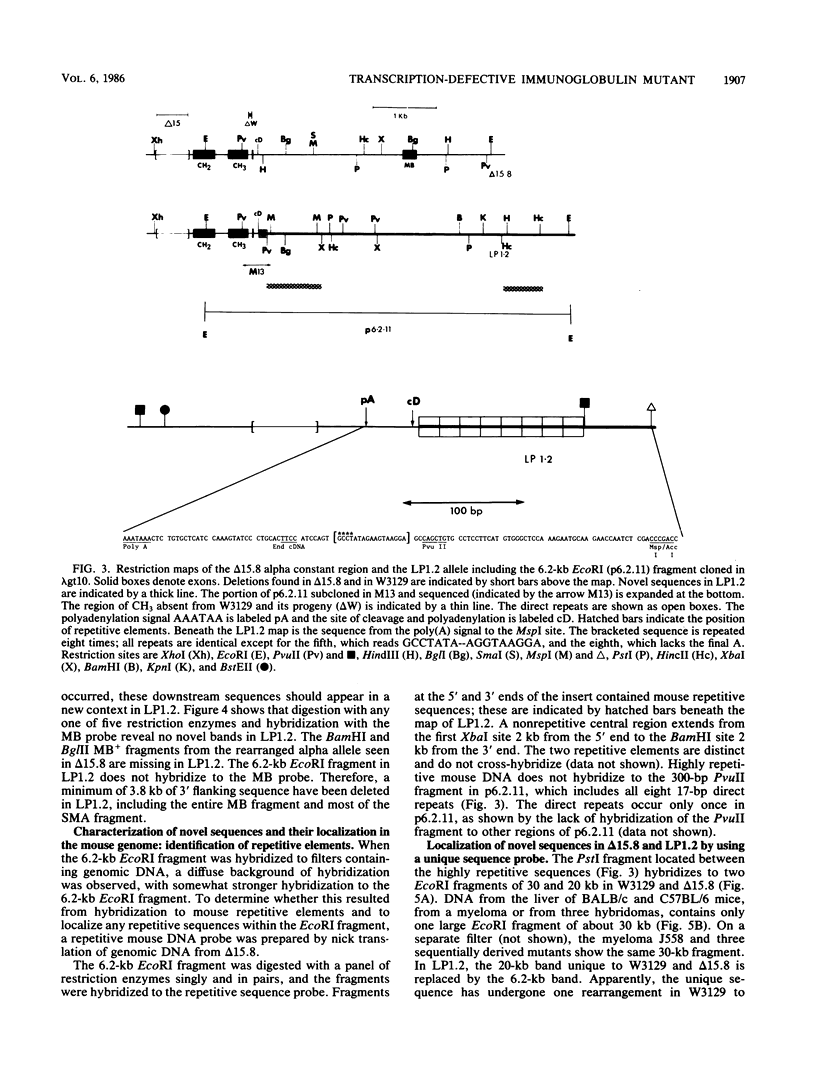
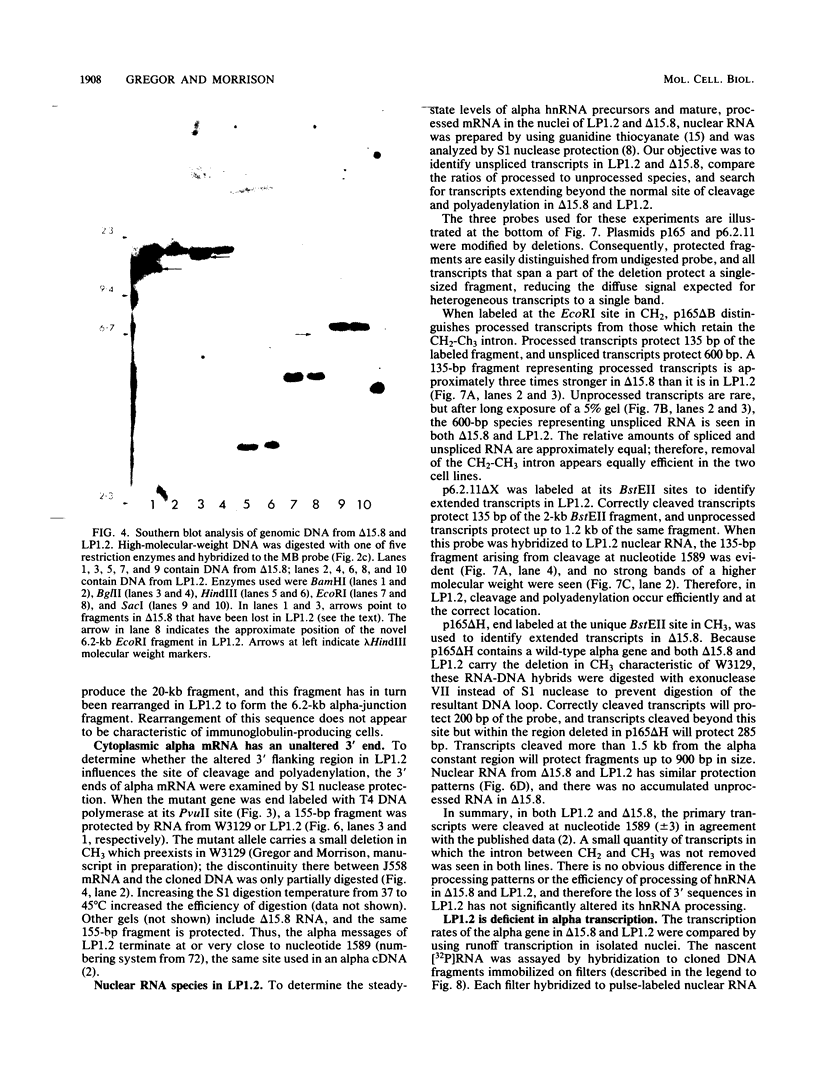
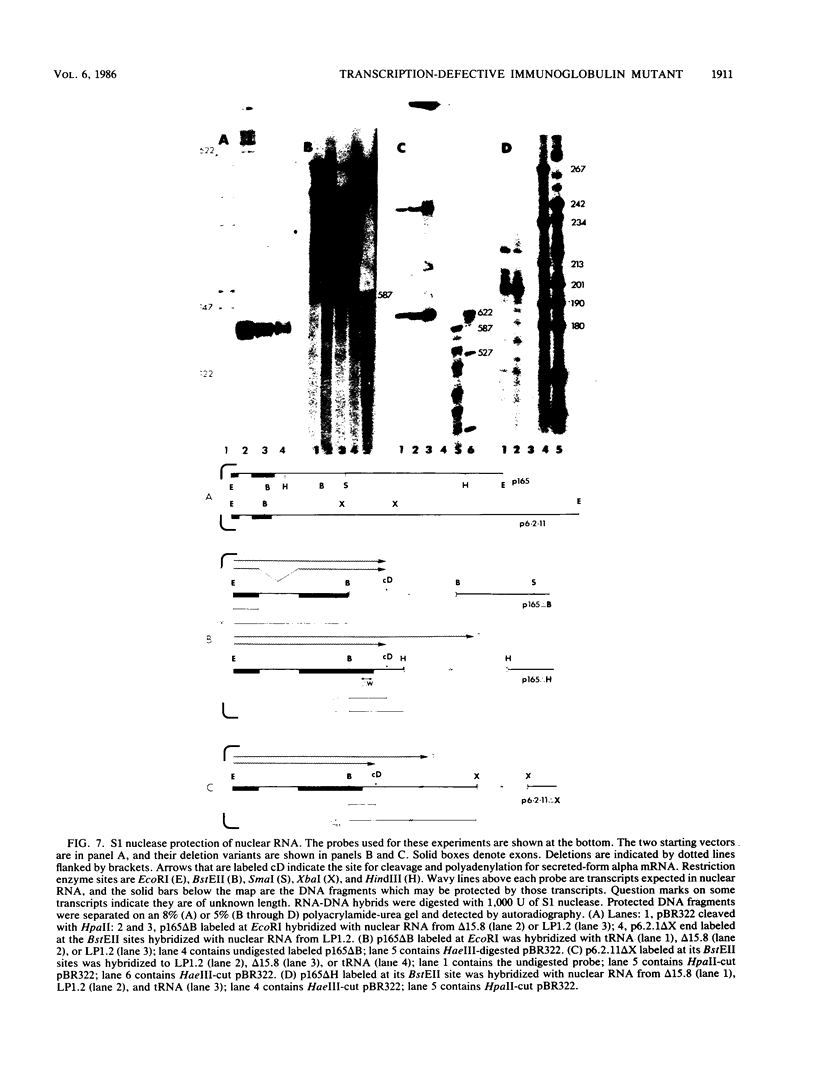
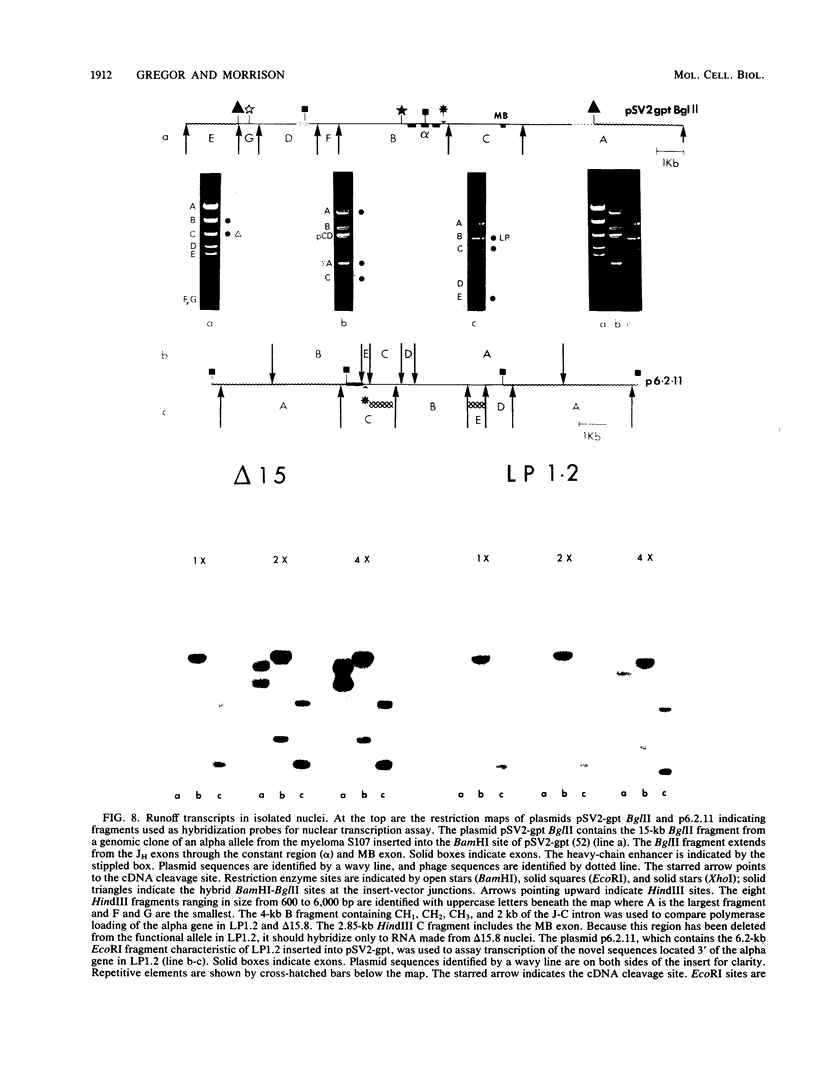
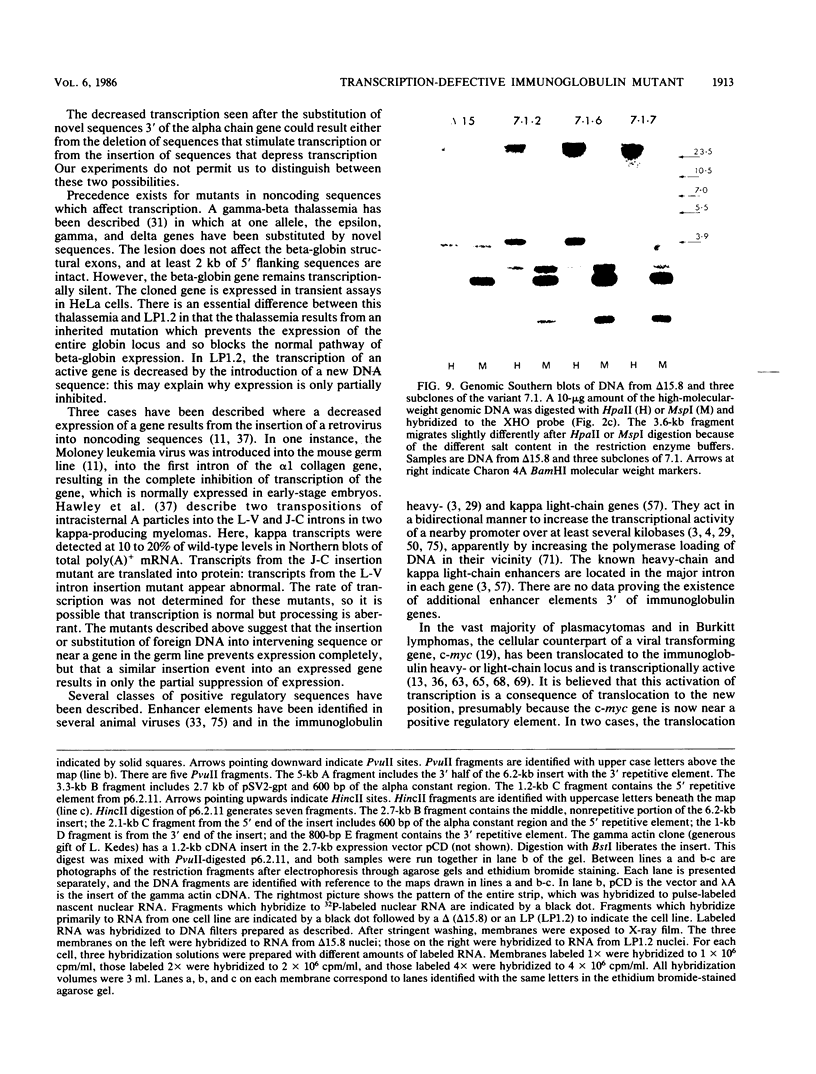
We isolated and characterized LP1.2, a mouse myeloma mutant with a deletion of at least 4 kilobases (kb) immediately 3' of the alpha gene and introduction of at least 5 kb of novel (nonimmunoglobulin) sequence in its place. A 6.2-kb genomic EcoRI fragment from the mutated allele was cloned, and a subfragment was sequenced. The deletion begins 11 base pairs (bp) beyond the normal site of cleavage and polyadenylation for the secreted form of alpha mRNA. A short direct repeat, eight copies of the 17-mer GCCT ATAGAAGTAAGGA, is located at the junction of the alpha and novel sequences. The first 4 bp of the 17-mer are identical to the last 4 bp of the alpha sequence. Novel sequences downstream of the direct repeats in LP1.2 include a low-copy-number sequence flanked by two distinct, highly repetitive elements. The low-copy-number portion of the novel sequence appears on a single 30-kb EcoRI fragment in several myelomas and in liver DNA; one copy of this fragment has rearranged in cell line W3129, and this allele has rearranged a second time in LP1.2. LP1.2 contains low levels of apparently normal alpha protein and mRNA. The S1 nuclease protection of nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs shows that cleavage and polyadenylation are efficient and accurate and that they occur without the accumulation of aberrant transcripts. Alpha transcription in isolated nuclei is decreased sevenfold in LP1.2 relative to its parent, which accounts for the low steady-state levels of cytoplasmic alpha mRNA and protein in LP1.2. Decreased alpha transcription could result either from the deletion of a positive regulator in the 3' flanking region or from the introduction of novel sequences which exert a negative effect.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini A. M., Hofer M., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. On the formation of spontaneous deletions: the importance of short sequence homologies in the generation of large deletions. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Nageotte R., Sikorav J. L., Heidmann O., Rougeon F. Mouse immunoglobulin A: nucleotide sequence of the structural gene for the alpha heavy chain derived from cloned cDNAs. Gene. 1981 May;13(4):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Farrell P. J., Rabbitts T. H. Unrearranged immunoglobulin variable region genes have a functional promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1841–1856. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Retrovirus-induced lethal mutation in collagen I gene of mice is associated with an altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90521-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D. The role of stable complexes that repress and activate eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame K., Kim S., Lalley P., Hill R., Davis M., Hood L. Molecular cloning of translocations involving chromosome 15 and the immunoglobulin C alpha gene from chromosome 12 in two murine plasmacytomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6994–6998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Philippsen P., Davis R. W. Analysis of chromosomal integration and deletions of yeast plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1429–1448. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Baumal R., Laskov R., Scharff M. D. Cloning of mouse myeloma cells and detection of rare variants. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Jun;79(3):429–440. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040790313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. M. Cellular transforming genes. Science. 1982 Aug 27;217(4562):801–806. doi: 10.1126/science.6285471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dackowski W., Morrison S. L. Two alpha heavy chain disease proteins with different genomic deletions demonstrate that nonexpressed alpha heavy chain genes contain methylated bases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7091–7095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Kent R. B., Sonenshein G. E. Transcriptional activation of immunoglobulin alpha heavy-chain genes by translocation of the c-myc oncogene. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):443–446. doi: 10.1038/305443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberwine J. H., Roberts J. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of pro-opiomelanocortin gene transcription in the rat pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2166–2170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt L. A., Birshtein B. K. Independent immunoglobulin class-switch events occurring in a single myeloma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):856–868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrlander P. D., Sümegi J., Yang J. Q., Wiener F., Marcu K. B., Klein G. Activation of the c-myc oncogene by the immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene enhancer after multiple switch region-mediated chromosome rearrangements in a murine plasmacytoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3746–3750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck-Pedersen E., Logan J., Shenk T., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription termination within the E1A gene of adenovirus induced by insertion of the mouse beta-major globin terminator element. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):897–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo G., Razvi F., Worcel A. Assembly of transcriptionally active chromatin in Xenopus oocytes requires specific DNA binding factors. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):511–521. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90506-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P. Magic enhancers? DNA. 1984;3(1):1–5. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Cribbs D. L., Schibler U. Termination of transcription in the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-2a occurs at multiple sites downstream of the polyadenylation site. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):737–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M. Inheritance of DNA methylation in microinjected eggs of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2323–2327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. J., Lang R. B., Marcu K. B. Non-immunoglobulin-associated DNA rearrangements in mouse plasmacytomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4175–4179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Shulman M. J., Hozumi N. Transposition of two different intracisternal A particle elements into an immunoglobulin kappa-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2565–2572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayday A. C., Gillies S. D., Saito H., Wood C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of a translocated human c-myc gene by an enhancer in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):334–340. doi: 10.1038/307334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. S., Potter S. S. L1 sequences in HeLa extrachromosomal circular DNA: evidence for circularization by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1989–1993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Sablitzky F., Radbruch A. Deletion of the IgH enhancer does not reduce immunoglobulin heavy chain production of a hybridoma IgD class switch variant. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2473–2476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Perry R. P. Transcriptional regulation of immunoglobulin V genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6855–6867. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuuchi L., Morrison S. L. Isolation and characterization of a variant of mouse plasmacytoma J558 synthesizing a 110,000-dalton immunoglobulin heavy chain and of secondary variants synthesizing either a 55,000-dalton or an 80,000-dalton immunoglobulin heavy chain: possible implications. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1134–1144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. L. Sequentially derived mutants of the constant region of the heavy chain of murine immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naveh-Many T., Cedar H. Active gene sequences are undermethylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4246–4250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Characterization of productive and sterile transcripts from the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus: processing of micron and muS mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1317–1332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Morrison S. L., Herzenberg L. A., Berg P. Immunoglobulin gene expression in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli S. P., Caimi P. G., Cole M. D. A conserved sequence at c-myc oncogene chromosomal translocation breakpoints in plasmacytomas. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):327–330. doi: 10.1038/310327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Alwine J. C. Sequences on the 3' side of hexanucleotide AAUAAA affect efficiency of cleavage at the polyadenylation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Brown D. D. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Cortese R. A fast and simple method for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded bacteriophage M13. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Keath E. J., Piccoli S. P., Cole M. D. Novel myc oncogene RNA from abortive immunoglobulin-gene recombination in mouse plasmacytomas. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Yang J. Q., Eckhardt L. A., Harris L. J., Birshtein B. K., Marcu K. B. Products of a reciprocal chromosome translocation involving the c-myc gene in a murine plasmacytoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):829–833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Razin A., Cedar H. In vitro methylation of the hamster adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene inhibits its expression in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3418–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. In vitro packaging of a lambda Dam vector containing EcoRI DNA fragments of Escherichia coli and phage P1. Gene. 1977 May;1(3-4):255–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Moulding C., Battey J., Murphy W., Vasicek T., Lenoir G. M., Leder P. Activation and somatic mutation of the translocated c-myc gene in burkitt lymphoma cells. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Slightom J. L., Blattner F. R. Mouse IgA heavy chain gene sequence: implications for evolution of immunoglobulin hinge axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7684–7688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Weigert M., Coleclough C., Mather E. L., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Transcription of the unrearranged mouse C kappa locus: sequence of the initiation region and comparison of activity with a rearranged V kappa-C kappa gene. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):593–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90401-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M. H. The inheritance of methylation patterns in vertebrates. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):285–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Developmentally controlled and tissue-specific expression of unrearranged VH gene segments. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaller D. M., Eckhardt L. A. Deletion of a B-cell-specific enhancer affects transfected, but not endogenous, immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5088–5092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]