Abstract
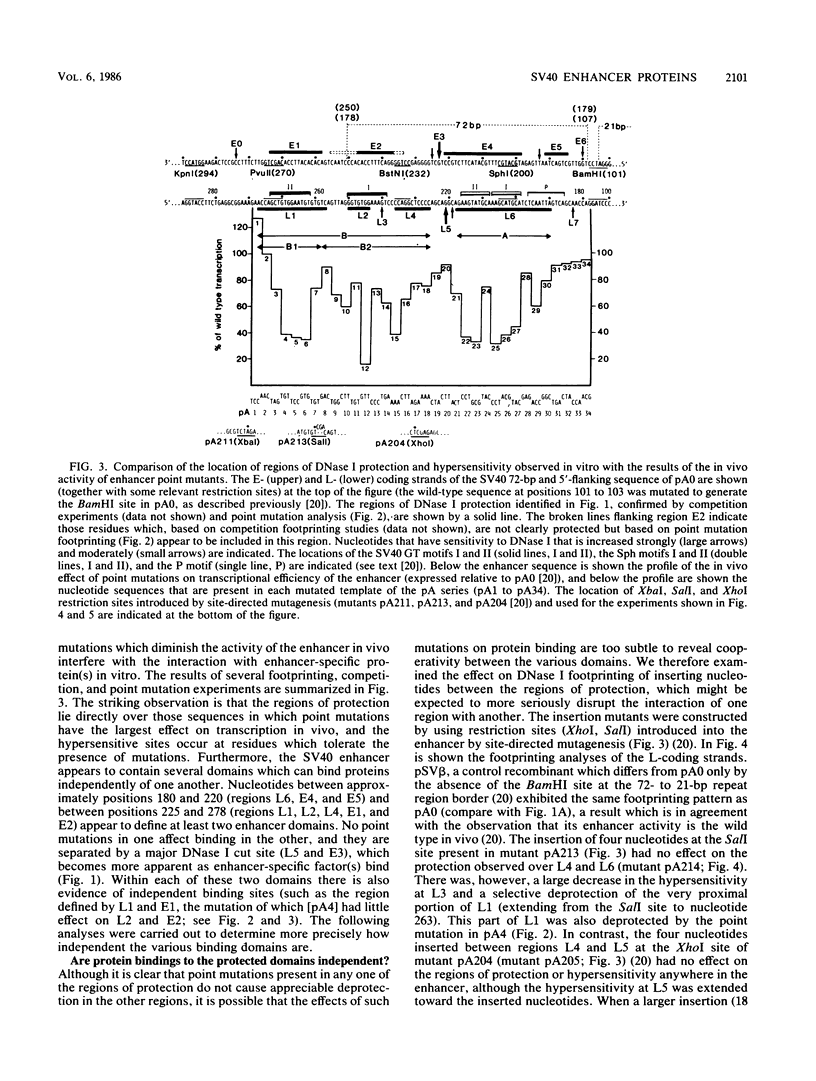
HeLa cell nuclear extracts and wild-type or mutated simian virus 40 enhancer DNA were used in DNase I footprinting experiments to study the interaction of putative trans-acting factors with the multiple enhancer motifs. We show that these nuclear extracts contain proteins that bind to these motifs. Because point mutations which are detrimental to the activity of a particular enhancer motif in vivo specifically prevent protection of that motif against DNase I digestion in vivo, we suggest that the bound proteins correspond to trans-acting factors involved in enhancement of transcription. Using mutants in which the two domains A and B of the simian virus 40 enhancer are either separated by insertion of DNA fragments or inverted with respect to their natural orientation, we also demonstrate that the trans-acting factors bind independently to the two domains.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azorin F., Rich A. Isolation of Z-DNA binding proteins from SV40 minichromosomes: evidence for binding to the viral control region. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):365–374. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera-Saldana H., Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Wildeman A., Davidson I., Chambon P. All six GC-motifs of the SV40 early upstream element contribute to promoter activity in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3839–3849. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04156.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costlow N. A., Simon J. A., Lis J. T. A hypersensitive site in hsp70 chromatin requires adjacent not internal DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):147–149. doi: 10.1038/313147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra J., Reudelhuber T. L., Oudet P., Benoist C., Chae C. B., Jeltsch J. M., Mathis D. J., Chambon P. Induction of altered chromatin structures by simian virus 40 enhancer and promoter elements. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):708–714. doi: 10.1038/307708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Dougherty J. P., Wasylyk B., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from heterologous promoters by the simian virus 40 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):308–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergeant A., Bohmann D., Zentgraf H., Weiher H., Keller W. A transcription enhancer acts in vitro over distances of hundreds of base-pairs on both circular and linear templates but not on chromatin-reconstituted DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):577–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Sassone-Corsi P., Grundström T., Zenke M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from the SV40 early promoter by the enhancer involves a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3129–3133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]