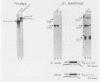Abstract
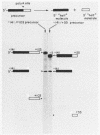
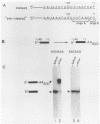
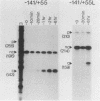
The sequence AAUAAA is found near the polyadenylation site of eucaryotic mRNAs. This sequence is required for accurate and efficient cleavage and polyadenylation of pre-mRNAs in vivo. In this study we show that synthetic simian virus 40 late pre-mRNAs are cleaved and polyadenylated in vitro in a HeLa cell nuclear extract, and that cleavage in vitro is abolished by each of four different single-base changes in AAUAAA. In this same extract, precleaved RNAs (RNAs with 3' termini at the polyadenylation site) are efficiently polyadenylated. This in vitro polyadenylation reaction also requires the AAUAAA sequence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L. Most kappa immunoglobulin mRNA in human lymphocytes is homologous to a small family of germ-line V genes. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):77–80. doi: 10.1038/307077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L., Wickens M. A sequence downstream of A-A-U-A-A-A is required for formation of simian virus 40 late mRNA 3' termini in frog oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3949–3953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Biochemical complementation with RNA in the Xenopus oocyte: a small RNA is required for the generation of 3' histone mRNA termini. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):823–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Lamb J., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Proudfoot N. J. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a polyadenylation signal mutation. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):398–400. doi: 10.1038/306398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Accurate and specific polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in a soluble whole-cell lysate. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Yu H., Ryner L. RNA sequence containing hexanucleotide AAUAAA directs efficient mRNA polyadenylation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):373–379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendecki J., Lee S. Y., Brawerman G. Characteristics of the polyadenylic acid segment associated with messenger ribonucleic acid in mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):792–798. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Inhibition of RNA cleavage but not polyadenylation by a point mutation in mRNA 3' consensus sequence AAUAAA. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):600–605. doi: 10.1038/305600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Site-specific polyadenylation in a cell-free reaction. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Alwine J. C. Sequences on the 3' side of hexanucleotide AAUAAA affect efficiency of cleavage at the polyadenylation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Connelly S., Manley J. L., Alwine J. C. Identification of a sequence element on the 3' side of AAUAAA which is necessary for simian virus 40 late mRNA 3'-end processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2713–2719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Gurdon J. B. Post-transcriptional processing of simian virus 40 late transcripts in injected frog oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 5;163(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Lyons R. H., Post L., Rottman F. M. Requirement for the 3' flanking region of the bovine growth hormone gene for accurate polyadenylylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3944–3948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription and RNA processing by the DNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):491–499. doi: 10.1038/287491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]