Abstract
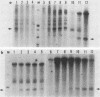
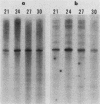
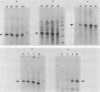
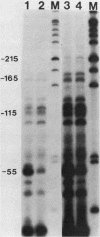
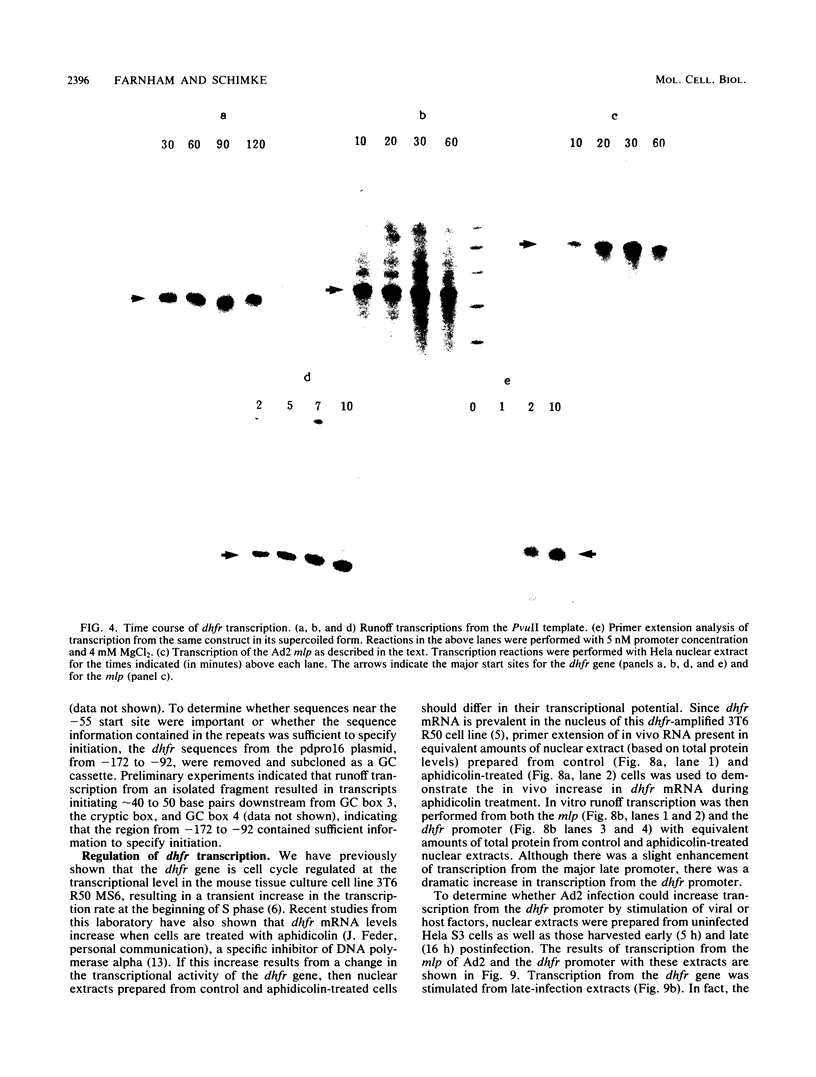
We have developed an in vitro transcription system for the murine dihydrofolate reductase gene. Although transcription in vitro from a linearized template was initiated at the same start sites as in vivo, the correct ratios were more closely approximated when a supercoiled template was used. In addition, whereas the dihydrofolate reductase promoter functions bidirectionally in vivo, the initiation signals directed unidirectional transcription in this in vitro system. The dihydrofolate reductase gene does not have a typical TATA box, but has four GGGCGG hexanucleotides within 300 base pairs 5' of the AUG codon. Deletion analysis suggested that, although sequences surrounding each of the GC boxes could specify initiation approximately 40 to 50 nucleotides downstream, three of the four GC boxes could be removed without changing the accuracy or efficiency of initiation at the major in vivo site. The dihydrofolate reductase promoter initiated transcription very rapidly in vitro, with transcripts visible by 1 min and almost maximal by 2 min at 30 degrees C with no preincubation. Nuclear extracts prepared from cells blocked in the S phase by aphidicolin or from adenovirus-infected cells at 16 h postinfection had enhanced dihydrofolate reductase transcriptional activity. This increased in vitro transcription mimicked the increase in dihydrofolate reductase mRNA seen in S-phase cells and suggested the presence of a cell-cycle-specific factor(s) which stimulated transcription from the dihydrofolate reductase gene.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsoum J., Varshavsky A. Preferential localization of variant nucleosomes near the 5'-end of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7688–7697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. J., Shimada T., Moulton A. D., Cline A., Humphries R. K., Maizel J., Nienhuis A. W. The functional human dihydrofolate reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3933–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Abrams J. M., Schimke R. T. Opposite-strand RNAs from the 5' flanking region of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Murine dihydrofolate reductase transcripts through the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):365–371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Transcriptional regulation of mouse dihydrofolate reductase in the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7675–7680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Baker C. C., Manley J. L., Ziff E. B., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription of adenovirus. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):703–719. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.703-719.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between RNA polymerase II, factors, and template leading to accurate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2509–2516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., Roeder R. G. Separation and partial characterization of three functional steps in transcription initiation by human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8163–8172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Tsuda M., Suzuki Y. Enhanced transcription of fibroin gene in vitro on covalently closed circular templates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10557–10562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami S., Taguchi T., Ohashi M., Oguro M., Nagano H., Mano Y. Aphidicolin prevents mitotic cell division by interfering with the activity of DNA polymerase-alpha. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):458–460. doi: 10.1038/275458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. T., Baserga R., Mercer W. E. Adenovirus type 2 activates cell cycle-dependent genes that are a subset of those activated by serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2936–2942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Simonsen C. C., Smouse D. T., Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Heterogeneity at the 5' termini of mouse dihydrofolate reductase mRNAs. Evidence for multiple promoter regions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2307–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan V., Madden M. J., Salzman N. P. Proximal and distal domains that control in vitro transcription of the adenovirus IVa2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6290–6294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrali-Noy G., Spadari S., Miller-Faurès A., Miller A. O., Kruppa J., Koch G. Synchronization of HeLa cell cultures by inhibition of DNA polymerase alpha with aphidicolin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):377–387. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vivo studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sazer S., Schimke R. T. A re-examination of the 5' termini of mouse dihydrofolate reductase RNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4685–4690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Nunberg J. H., Schimke R. T. Size heterogeneity in the 3' end of dihydrofolate reductase messenger RNAs in mouse cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. T., Larson D., Young L. S., Sprague K. U. A large region controls tRNA gene transcription. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder S. S., Robberson B. L., Leys E. J., Hook A. G., Al-Ubaidi M., Yeung C. Y., Kellems R. E., Berget S. M. Control of cellular gene expression during adenovirus infection: induction and shut-off of dihydrofolate reductase gene expression by adenovirus type 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):819–828. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]