Abstract
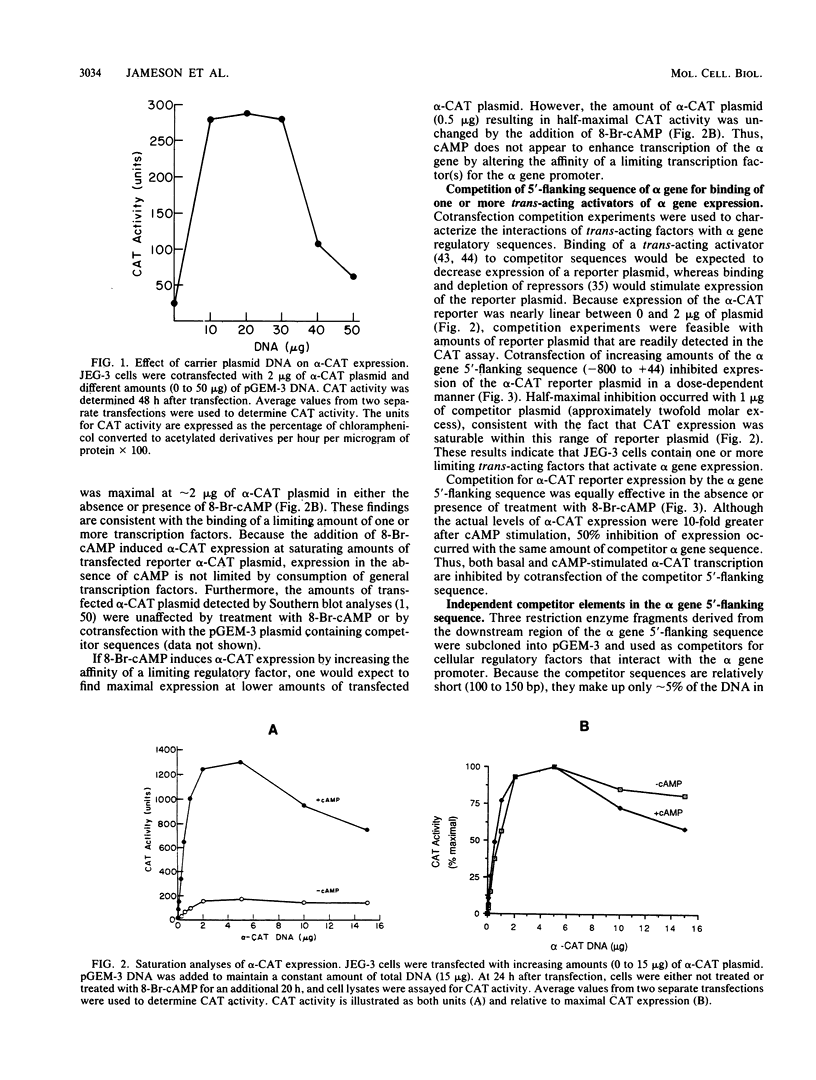
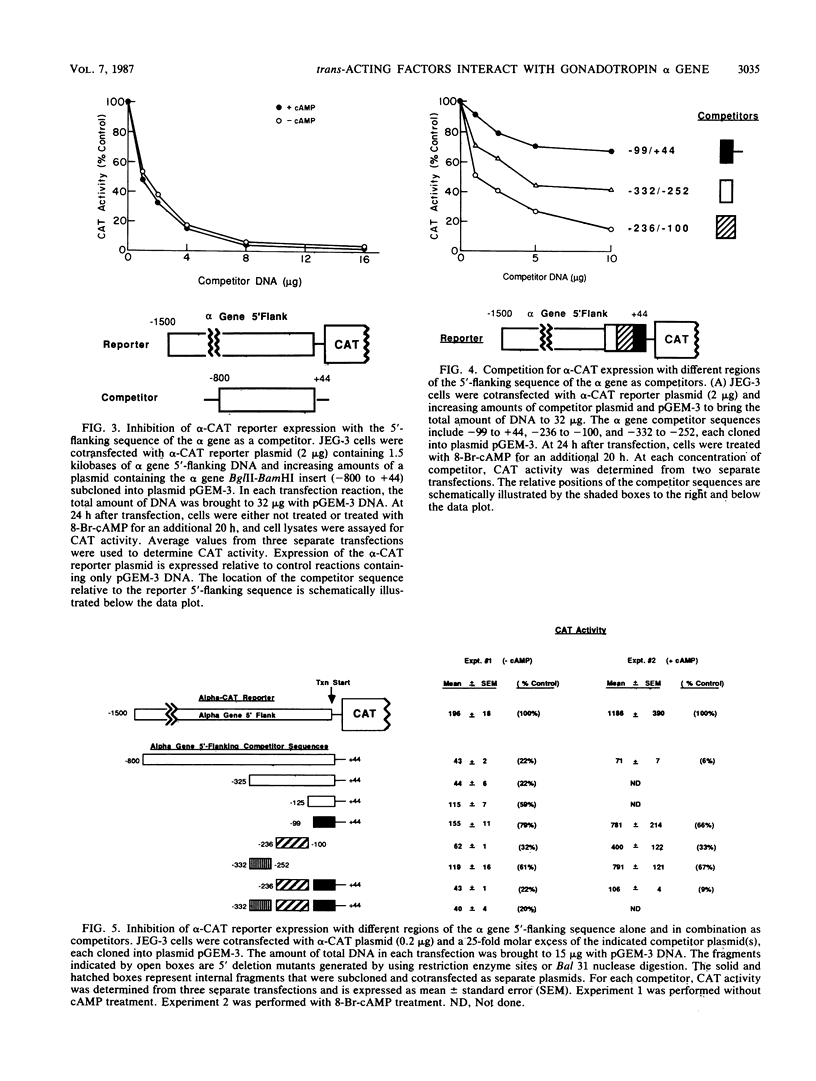
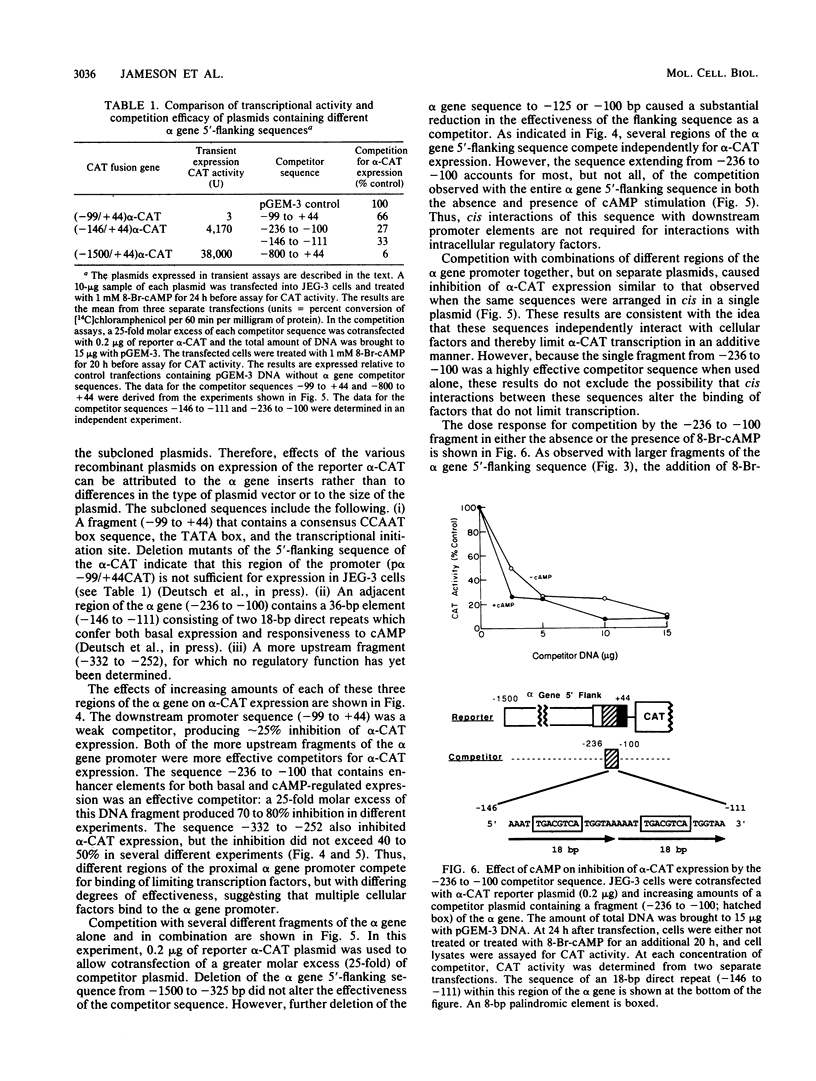
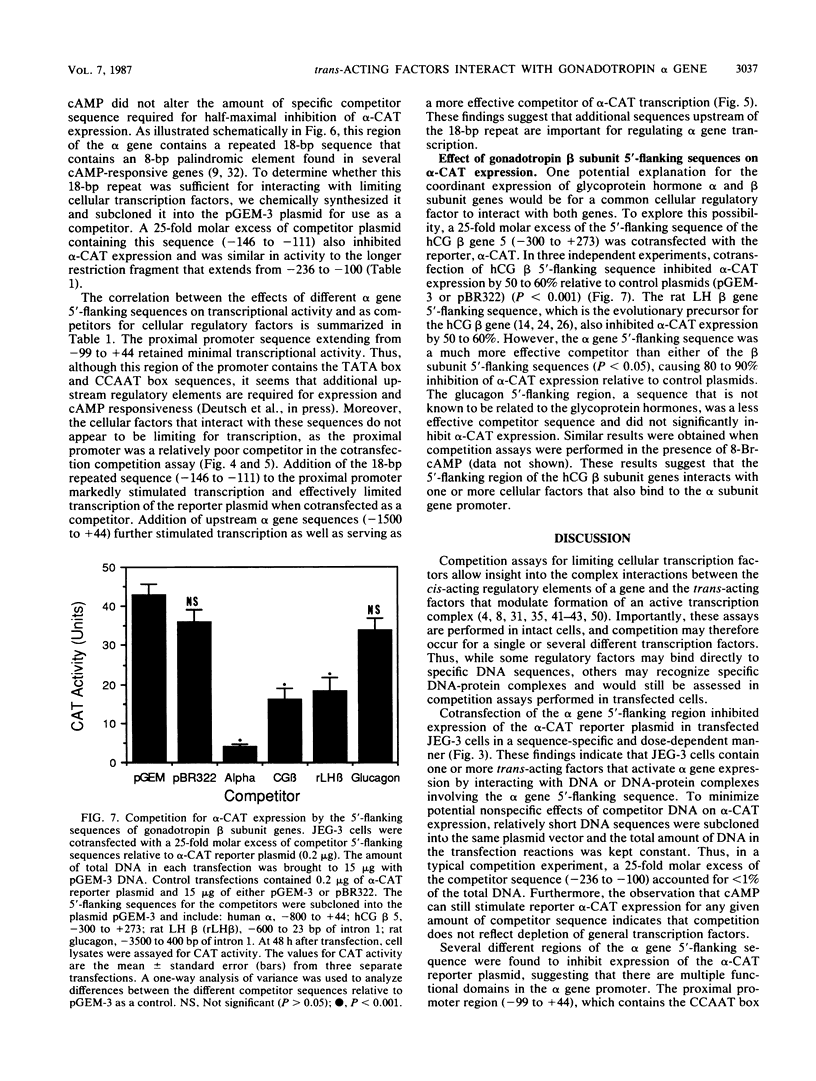
The alpha subunit of the placental hormone chorionic gonadotropin is regulated by cyclic AMP (cAMP) at the transcriptional level. A cAMP-responsive fusion gene (alpha-CAT) containing 1.5 kilobases of the alpha gene 5'-flanking sequence linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene was used as a transcriptional reporter in competition assays in transfected JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cells. Expression of the alpha-CAT fusion gene increased linearly with increasing amounts of transfected plasmid and was maximal at the same amount of alpha-CAT DNA (2 micrograms) with or without cAMP treatment. Various amounts of different competitor DNA sequences were cotransfected with the alpha-CAT reporter plasmid to examine the interactions of intracellular trans-acting factors with the regulatory elements of the alpha gene promoter. An 800-base-pair fragment of alpha gene 5'-flanking sequence inhibited both basal and cAMP-stimulated transcription of the alpha-CAT reporter plasmid in a dose-dependent manner, indicative of interactions with one or more trans-acting factors that activate alpha gene expression. The alpha gene sequences that interact with intracellular regulatory factors were defined by using several discrete regions of the 5'-flanking sequence as competitors for alpha-CAT expression. A proximal promoter sequence (-99 to +44) containing the CCAAT box, TATA box, and transcriptional initiation site was a relatively ineffective competitor of alpha-CAT transcription. In contrast, an upstream sequence between -236 and -100 was an effective competitor for transcriptional activators of alpha-CAT expression. Competition for alpha-CAT expression by this regulatory sequence did not require cis interactions with downstream promoter elements and was equally effective with or without cAMP treatment. An 18-base-pair repeated sequence within this region of the alpha gene (-146 to -111) greatly enhanced both basal gene expression and cAMP responsivity and also competed for limiting cellular transcription factors. These findings suggest that JEG-3 cells contain trans-acting factors that interact with a cAMP response element to activate alpha gene transcription. The chorionic gonadotropin beta gene 5'-flanking sequence also competed for alpha-CAT expression, suggesting that a common trans-acting factor is shared by the regulatory sequences of the alpha and beta genes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C. Transient gene expression control: effects of transfected DNA stability and trans-activation by viral early proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1034–1042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boney C., Fink D., Schlichter D., Carr K., Wicks W. D. Direct evidence that the protein kinase catalytic subunit mediates the effects of cAMP on tyrosine aminotransferase synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4911–4918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Loeken M. R., Khoury G. Interaction between two transcriptional control sequences required for tumor-antigen-mediated simian virus 40 late gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7299–7303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein G. D., Vaitukaitis J. L., Carbone P. P., Ross G. T. Ectopic production of human chorionic gonadotrophin by neoplasms. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Jan;78(1):39–45. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnside J., Nagelberg S. B., Lippman S. S., Weintraub B. D. Differential regulation of hCG alpha and beta subunit mRNAs in JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cells by 8-bromo-cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12705–12709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Sinn E., Reed R. R., Leder P. Trans-acting elements modulate expression of the human c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7918–7922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell R. B., Boime I. Differential expression of the human gonadotropin alpha gene in ectopic and eutopic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3157–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Goodman H. M. The gene encoding the common alpha subunit of the four human glycoprotein hormones. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(1):3–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Talmadge K. Structure, expression, and evolution of the genes for the human glycoprotein hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:43–78. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Bich-Thuy L. T., Stafford J., Queen C. Synergism between immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):383–385. doi: 10.1038/322383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharib S. D., Bowers S. M., Need L. R., Chin W. W. Regulation of rat luteinizing hormone subunit messenger ribonucleic acids by gonadal steroid hormones. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):582–589. doi: 10.1172/JCI112340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Gros P., Habener J. F. Glucagon gene sequence. Four of six exons encode separate functional domains of rat pre-proglucagon. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14082–14087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussa R. O. Biosynthesis of human chorionic gonadotropin. Endocr Rev. 1980 Summer;1(3):268–294. doi: 10.1210/edrv-1-3-268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Jaffe R. C., Gleason S. L., Habener J. F. Transcriptional regulation of chorionic gonadotropin alpha- and beta-subunit gene expression by 8-bromo-adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2560–2567. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Lindell C. M., Habener J. F. Evolution of different transcriptional start sites in the human luteinizing hormone and chorionic gonadotropin beta-subunit genes. DNA. 1986 Jun;5(3):227–234. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Lindell C. M., Habener J. F. Gonadotropin and thyrotropin alpha- and beta-subunit gene expression in normal and neoplastic tissues characterized using specific messenger ribonucleic acid hybridization probes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Feb;64(2):319–327. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson L., Chin W. W., Hollenberg A. N., Chang A. S., Habener J. F. The gene encoding the beta-subunit of rat luteinizing hormone. Analysis of gene structure and evolution of nucleotide sequence. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15474–15480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyter A., Scangos G. A., Ruddle F. H. Mechanisms of DNA uptake by mammalian cells: fate of exogenously added DNA monitored by the use of fluorescent dyes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):422–426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Reich E. Gene expression and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4606–4610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Franco R., Lira S. A., Albert V. R., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Discrete cis-active genomic sequences dictate the pituitary cell type-specific expression of rat prolactin and growth hormone genes. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):557–562. doi: 10.1038/322557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J. Regulation of rat insulin 1 gene expression: evidence for negative regulation in nonpancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Wong-Staal F. Demonstration of virus-specific transcriptional activator(s) in cells infected with HTLV-III by an in vitro cell-free system. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavasiliou S. S., Zmeili S., Khoury S., Landefeld T. D., Chin W. W., Marshall J. C. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone differentially regulates expression of the genes for luteinizing hormone alpha and beta subunits in male rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4026–4029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Drucker D. J., Habener J. F. Glucagon gene transcription in an islet cell line is regulated via a protein kinase C-activated pathway. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1823–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. G., Parsons T. F. Glycoprotein hormones: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:465–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholer H., Haslinger A., Heguy A., Holtgreve H., Karin M. In vivo competition between a metallothionein regulatory element and the SV40 enhancer. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3006253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Wynshaw-Boris A., Short H. P., Hanson R. W. Characterization of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) promoter-regulatory region. II. Identification of cAMP and glucocorticoid regulatory domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9721–9726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupnik M. A., Chin W. W., Ross D. S., Downing M. F., Habener J. F., Ridgway E. C. Regulation by thyroxine of the mRNA encoding the alpha subunit of mouse thyrotropin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15120–15124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupnik M. A., Greenspan S. L., Ridgway E. C. Transcriptional regulation of thyrotropin subunit genes by thyrotropin-releasing hormone and dopamine in pituitary cell culture. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12675–12679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguin C., Felber B. K., Carter A. D., Hamer D. H. Competition for cellular factors that activate metallothionein gene transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):781–785. doi: 10.1038/312781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M., Murdoch G. H., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Cyclic AMP regulation of eukaryotic gene transcription by two discrete molecular mechanisms. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):267–269. doi: 10.1126/science.2990047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Cheng P. F., Conrad K. Expression of transfected DNA depends on DNA topology. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90865-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



