Abstract
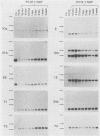
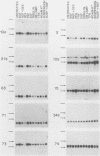
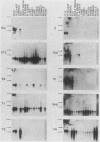
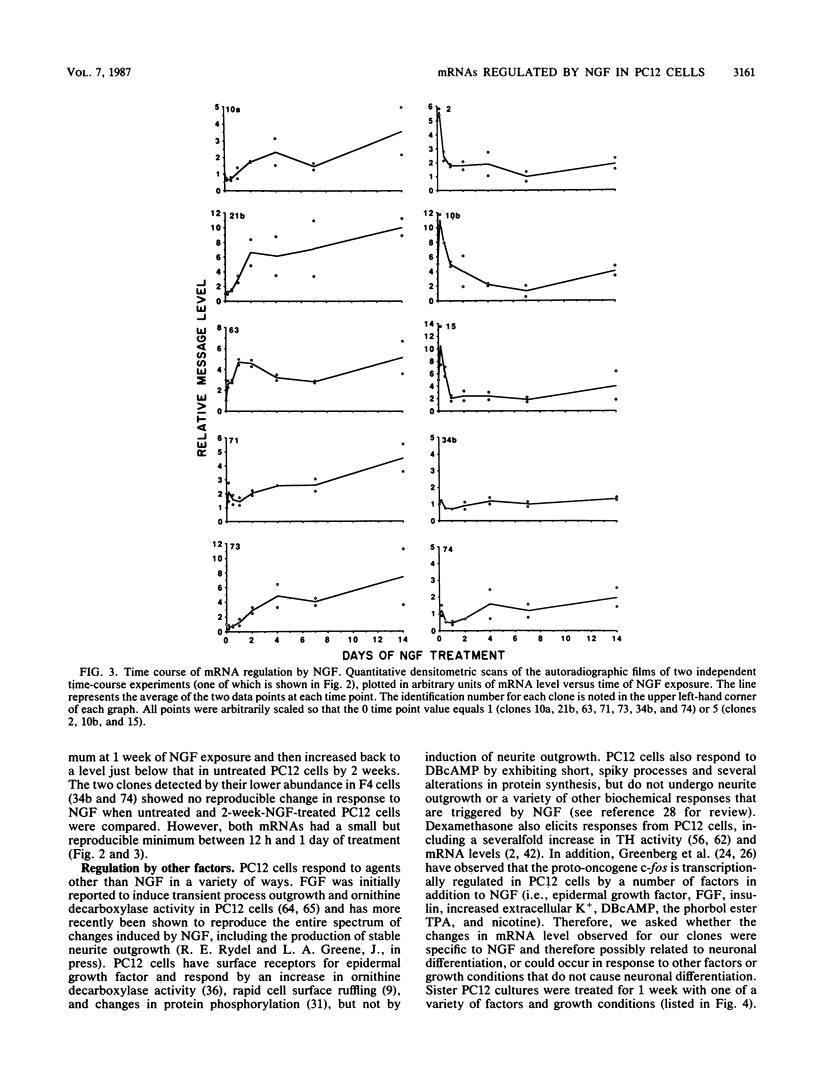
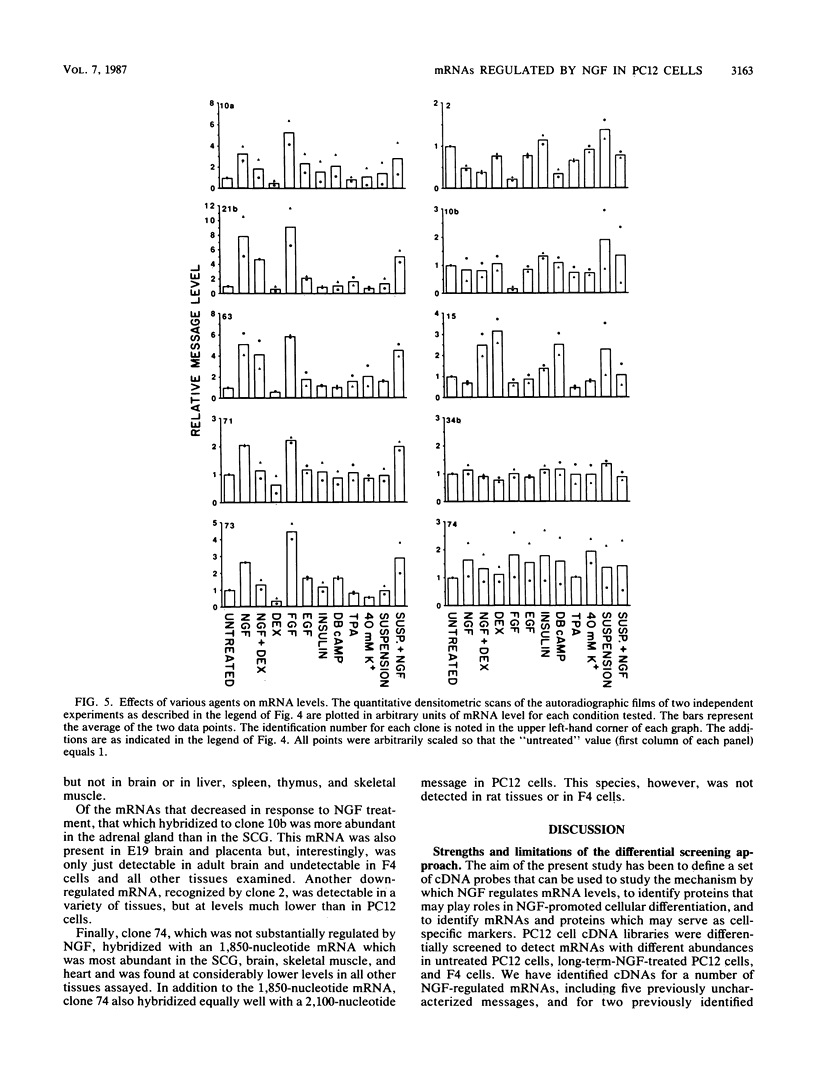
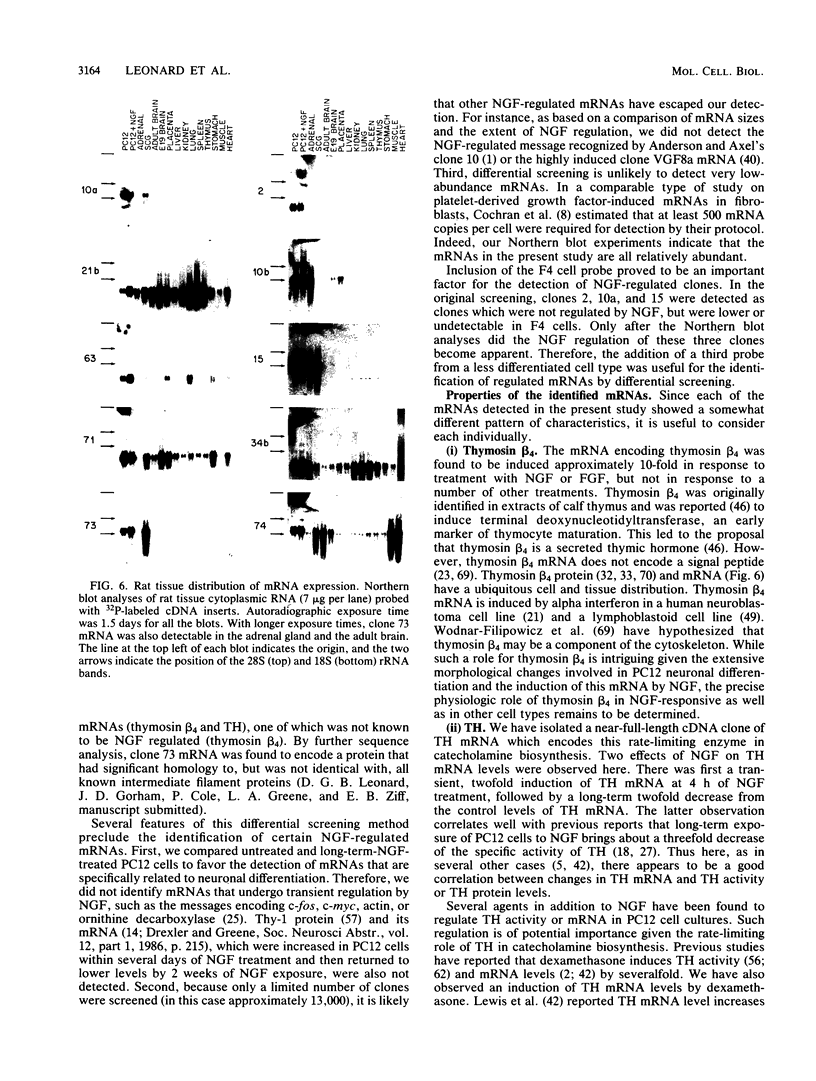
Differential screening of cDNA libraries was used to detect and prepare probes for mRNAs that are regulated in PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells by long-term (2-week) treatment with nerve growth factor (NGF). In response to NGF, PC12 cells change from a chromaffin cell-like to a sympathetic-neuron-like phenotype. Thus, one aim of this study was to identify NGF-regulated mRNAs that may be associated with the attainment of neuronal properties. Eight NGF-regulated mRNAs are described. Five of these increase 3- to 10-fold and three decrease 2- to 10-fold after long-term NGF exposure. Each mRNA was characterized with respect to the time course of the NGF response, regulation by agents other than NGF, and rat tissue distribution. Partial sequences of the cDNAs were used to search for homologies to known sequences. Homology analysis revealed that one mRNA (increased 10-fold) encodes the peptide thymosin beta 4 and a second mRNA (decreased 2-fold) encodes tyrosine hydroxylase. Another of the increased mRNAs was very abundant in sympathetic ganglia, barely detectable in brain and adrenals, and undetectable in all other tissues surveyed. One of the decreased mRNAs, by contrast, was very abundant in the adrenals and nearly absent in the sympathetic ganglia. With the exception of fibroblast growth factor, which is the only other agent known to mimic the differentiating effects of NGF on PC12 cells, none of the treatments tested (epidermal growth factor, insulin, dibutyryl cyclic AMP, dexamethasone, phorbol ester, and depolarization) reproduced the regulation observed with NGF. These and additional findings suggest that the NGF-regulated mRNAs may play roles in the establishment of the neuronal phenotype and that the probes described here will be useful to study the mechanism of action of NGF and the development and differentiation of neurons.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Axel R. Molecular probes for the development and plasticity of neural crest derivatives. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetge E. E., Kaplan B. B., Reis D. J., Joh T. H. Translation of tyrosine hydroxylase from poly(A)-mRNA in pheochromocytoma cells is enhanced by dexamethasone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1269–1273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilofsky H. S., Burks C., Fickett J. W., Goad W. B., Lewitter F. I., Rindone W. P., Swindell C. D., Tung C. S. The GenBank genetic sequence databank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):1–4. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerre B., Björklund A. The production of catecholamine-containing cells in vitro by young chick embryos: effects of "nerve growth factor" (NGF) and its antiserum. Neurobiology. 1973;3(3):140–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B., Chikaraishi D. M., Lewis E. J. Trans-synaptic increase in RNA coding for tyrosine hydroxylase in a rat sympathetic ganglion. Brain Res. 1985 Jul 22;339(1):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90635-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein D. E., Greene L. A. Evidence for RNA synthesis-dependent and -independent pathways in stimulation of neurite outgrowth by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6059–6063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Reffel A. C., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. L., Green S. A., Greene L. A. Comparison of rapid changes in surface morphology and coated pit formation of PC12 cells in response to nerve growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):457–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremins J., Wagner J. A., Halegoua S. Nerve growth factor action is mediated by cyclic AMP- and Ca+2/phospholipid-dependent protein kinases. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):887–893. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Morgan J. I. Superinduction of c-fos by nerve growth factor in the presence of peripherally active benzodiazepines. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.4035354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Peters G., Van Beveren C., Teich N. M., Verma I. M. FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus: identification and molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.674-682.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Tischler A. S., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor-induced increase in electrical excitability and acetylcholine sensitivity of a rat pheochromocytoma cell line. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):501–504. doi: 10.1038/268501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson G., Prentice H., Julien J. P., Ferrari G., Leon A., Walsh F. S. Nerve growth factor activates Thy-1 and neurofilament gene transcription in rat PC12 cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3449–3453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Landis S. C., Patterson P. H. Environmental influences in the development of neural crest derivatives: glucocorticoids, growth factors, and chromaffin cell plasticity. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2119–2142. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Patterson P. H., Landis S. C. Small intensely fluorescent cells in culture: role of glucocorticoids and growth factors in their development and interconversions with other neural crest derivatives. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2143–2160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. B., Dawid I. B. Use of a cloned library for the study of abundant poly(A)+RNA during Xenopus laevis development. Dev Biol. 1980 May;76(2):449–464. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D. H., Thoenen H. Selective enzyme induction in a nerve growth factor-responsive pheochromocytoma cell line (PC 12). Brain Res. 1978 Oct 6;154(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein S. C., Dana S. L., McConlogue L., Shooter E. M., Coffino P. Nerve growth factor rapidly induces ornithine decarboxylase mRNA in PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5761–5765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Otten U., Hunt S. P., Bond A., Chapman D., Schlumpf M., Lichtensteiger W. Biochemical and anatomical effects of antibodies against nerve growth factor on developing rat sensory ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1580–1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Richardson M., Furuichi Y., Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Horecker B. L. Sequence of a cloned 523-bp cDNA for thymosin beta 4. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jan;236(1):445–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90646-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B., Greene L. A. Stimulation of neuronal acetylcholine receptors induces rapid gene transcription. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):80–83. doi: 10.1126/science.3749894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grima B., Lamouroux A., Blanot F., Biguet N. F., Mallet J. Complete coding sequence of rat tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):617–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Patrick J. Nerve growth factor mediates phosphorylation of specific proteins. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):571–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Leibold W. Biosynthesis rates and content of thymosin beta 4 in cell lines. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jul;240(1):236–241. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Xu G. J., Morgan J., Hempstead J., Horecker B. L. Thymosin beta 4: a ubiquitous peptide in rat and mouse tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Cohen D. I., Nielsen E. A., Davis M. M. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding T cell-specific membrane-associated proteins. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):149–153. doi: 10.1038/308149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff K. R., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor-induced reduction in epidermal growth factor responsiveness and epidermal growth factor receptors in PC12 cells: an aspect of cell differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90960-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamouroux A., Faucon Biguet N., Samolyk D., Privat A., Salomon J. C., Pujol J. F., Mallet J. Identification of cDNA clones coding for rat tyrosine hydroxylase antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3881–3885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A., Eldridge J. D., Paterson B. M. Molecular cloning of a gene sequence regulated by nerve growth factor. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):393–395. doi: 10.1126/science.3839317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Tank A. W., Weiner N., Chikaraishi D. M. Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA by glucocorticoid and cyclic AMP in a rat pheochromocytoma cell line. Isolation of a cDNA clone for tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14632–14637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Lee S. J., Ogren L., Talamantes F., Nathans D. Identification of proliferin mRNA and protein in mouse placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4356–4359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Growth-related changes in specific mRNAs of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Nucleotide sequence of a growth-related mRNA encoding a member of the prolactin-growth hormone family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4255–4259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Hu S. K., Goldstein A. L. Complete amino acid sequence of bovine thymosin beta 4: a thymic hormone that induces terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity in thymocyte populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1162–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J. C., Greene L. A. Rapid stimulation by nerve growth factor of amino acid uptake by clonal PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3362–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon-induced gene expression in wild-type and interferon-resistant human lymphoblastoid (Daudi) cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.362-366.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Rutkowski J. L., Tennekoon G. I., Buchanan K., Johnston M. V. Choline acetyltransferase activity in striatum of neonatal rats increased by nerve growth factor. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):284–287. doi: 10.1126/science.2861660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Schenker A., Shooter E. M. Characterization and isolation of proteolytically modified nerve growth factor. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 14;15(25):5543–5552. doi: 10.1021/bi00670a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. S., Sharma A., de Vellis J., Bradshaw R. A. Basic fibroblast growth factor supports the survival of cerebral cortical neurons in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7537–7541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Presta M., Rifkin D. B. Purification of a factor from human placenta that stimulates capillary endothelial cell protease production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2091–2095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten U., Towbin M. Permissive action of glucocorticoids in induction of tyrosine hydroxylase by nerve growth factor in a pheochromocytoma cell line. Brain Res. 1980 Jul 7;193(1):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90972-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter-Landsberg C., Greene L. A., Shelanski M. L. Cell surface Thy-1-cross-reactive glycoprotein in cultured PC12 cells: modulation by nerve growth factor and association with the cytoskeleton. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):468–476. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00468.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowekamp W., Firtel R. A. Isolation of developmentally regulated genes from Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., LaCorbiere M., Klier F. G., Steinbach J. H. The modulation of neurotransmitter synthesis by steroid hormones and insulin. Brain Res. 1980 May 19;190(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togari A., Baker D., Dickens G., Guroff G. The neurite-promoting effect of fibroblast growth factor on PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 12;114(3):1189–1193. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90688-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togari A., Dickens G., Kuzuya H., Guroff G. The effect of fibroblast growth factor on PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):307–316. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00307.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Krisch B., Otten U., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor-induced fiber outgrowth from isolated rat adrenal chromaffin cells: impairment by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3498–3502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walicke P., Cowan W. M., Ueno N., Baird A., Guillemin R. Fibroblast growth factor promotes survival of dissociated hippocampal neurons and enhances neurite extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3012–3016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Lloyd M. M. Changes in the abundance of polyadenylated RNA during slime mould development measured using cloned molecular hybridization probes. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):19–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Gubler U., Furuichi Y., Richardson M., Nowoswiat E. F., Poonian M. S., Horecker B. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for rat spleen thymosin beta 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2295–2297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. J., Hannappel E., Morgan J., Hempstead J., Horecker B. L. Synthesis of thymosin beta 4 by peritoneal macrophages and adherent spleen cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4006–4009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]