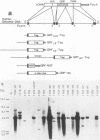
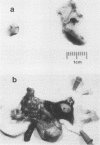
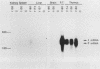
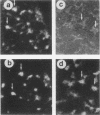
Abstract
The hypothalamic peptide growth hormone-releasing factor (GRF) regulates the secretion and production of growth hormone from the anterior pituitary (M. C. Gelato and G. R. Merriam, Annu. Rev. Physiol. 48:569-591). To study GRF gene regulation, transgenic mice were generated that harbor the human GRF promoter fused to the coding sequences from the simian virus 40 early region. These mice had normal hypothalamic functions but unexpectedly suffered from severe thymic hyperplasia. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that large T antigen was expressed in the thymic epithelial cells. These cells have endocrine properties and are known to produce thymic hormones [corrected]. The thymic hyperplasia was the apparent consequence of inappropriate production of T-cell maturation factors by epithelial cells and could involve increased self renewal of apparently normal T stem cells in the thymus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asa S. L., Scheithauer B. W., Bilbao J. M., Horvath E., Ryan N., Kovacs K., Randall R. V., Laws E. R., Jr, Singer W., Linfoot J. A. A case for hypothalamic acromegaly: a clinicopathological study of six patients with hypothalamic gangliocytomas producing growth hormone-releasing factor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 May;58(5):796–803. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-5-796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E., Harbour-McMenamin D., Smith E. M. Peptide hormones shared by the neuroendocrine and immunologic systems. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2 Suppl):858s–861s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Messing A., van Dyke T., Levine A. J., Palmiter R. D. Transgenic mice harboring SV40 T-antigen genes develop characteristic brain tumors. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90367-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürki K., Ullrich A. Transplantation of the human insulin gene into fertilized mouse eggs. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):127–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. A 3' enhancer is required for temporal and tissue-specific transcriptional activation of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):731–734. doi: 10.1038/323731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Shimizu K., Bowring M. A., Wells S. Expression of receptors for tetanus toxin and monoclonal antibody A2B5 by pancreatic islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelato M. C., Merriam G. R. Growth hormone releasing hormone. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:569–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Tamowski S., Deppert W. Antigenic binding sites of monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1168–1172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1168-1172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F. The human thymic microenvironment. Adv Immunol. 1984;36:87–142. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60900-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Nickol J. M., Lieber M. R., Felsenfeld G. Regulated gene expression in transfected primary chicken erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4312–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R., Lesley J., Schulte R., Trotter J. Progenitor cells in the thymus: most thymus-homing progenitor cells in the adult mouse thymus bear Pgp-1 glycoprotein but not interleukin-2 receptor on their cell surface. Cell Immunol. 1986 Sep;101(2):320–327. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Antigenic relationship of SV40 early proteins to purified large T polypeptide. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laster A. J., Itoh T., Palker T. J., Haynes B. F. The human thymic microenvironment: thymic epithelium contains specific keratins associated with early and late stages of epidermal keratinocyte maturation. Differentiation. 1986;31(1):67–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M., Dieterlen-Lièvre F., Oliver P. D. Ontogeny of primary lymphoid organs and lymphoid stem cells. Am J Anat. 1984 Jul;170(3):261–299. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001700305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine G. D., Rosai J. Thymic hyperplasia and neoplasia: a review of current concepts. Hum Pathol. 1978 Sep;9(5):495–515. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Cerelli G. M., Lebo R. V., Bruce B. D., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Gene encoding human growth hormone-releasing factor precursor: structure, sequence, and chromosomal assignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):63–67. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Vale W., Rivier J., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Expression-cloning and sequence of a cDNA encoding human growth hormone-releasing factor. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):86–88. doi: 10.1038/306086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchenthaler I., Vigh S., Schally A. V., Petrusz P. Immunocytochemical localization of growth hormone-releasing factor in the rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1082–1085. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. F., Reano A., Kaiserlian D., Thivolet J. Epithelial cell heterogeneity in the guinea pig thymus: immunohistochemical characterization of four thymic epithelial subsets defined by monoclonal anti-keratin antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Apr;16(4):457–464. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Messing A., Brinster R. L. SV40 enhancer and large-T antigen are instrumental in development of choroid plexus tumours in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):457–460. doi: 10.1038/316457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino W., Dardenne M. Thymic hormone-containing cells VI. Immunohistologic evidence for the simultaneous presence of thymulin, thymopoietin and thymosin alpha 1 in normal and pathological human thymuses. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Nov;14(11):987–991. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D., Marangos P. J., Brightman M. Neurone-specific enolase is a molecular marker for peripheral and central neuroendocrine cells. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):834–836. doi: 10.1038/276834a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Selby M., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of mouse nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):538–540. doi: 10.1038/302538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Blair D. G., Showalter S. D., Scangos G. A. Analysis of a transgenic mouse containing simian virus 40 and v-myc sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):642–648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Southern P. J. Analysis of gene expression using simian virus 40 vectors. Anal Biochem. 1983 Nov;135(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90723-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Simmons D. M., Arriza J., Hammer R., Brinster R., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Novel developmental specificity in the nervous system of transgenic animals expressing growth hormone fusion genes. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):363–366. doi: 10.1038/317363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. R., Scheithauer B. W., Kovacs K. Neuron-specific enolase in neuroendocrine tumors of the thymus, bronchus, and skin. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jun;79(6):703–707. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/79.6.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. R., Scheithauer B. W. Thymic carcinoid. A histologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of 12 cases. Cancer. 1984 Feb 1;53(3):475–484. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840201)53:3<475::aid-cncr2820530318>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M. M., McClure J. E., Goldstein A. L. Immunoreactive thymosin alpha 1 is associated with murine T-cell lymphomas. Leuk Res. 1984;8(6):1003–1010. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(84)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Terwindt E., Berns A., Jaenisch R. The integration sites of endogenous and exogenous Moloney murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]