Abstract
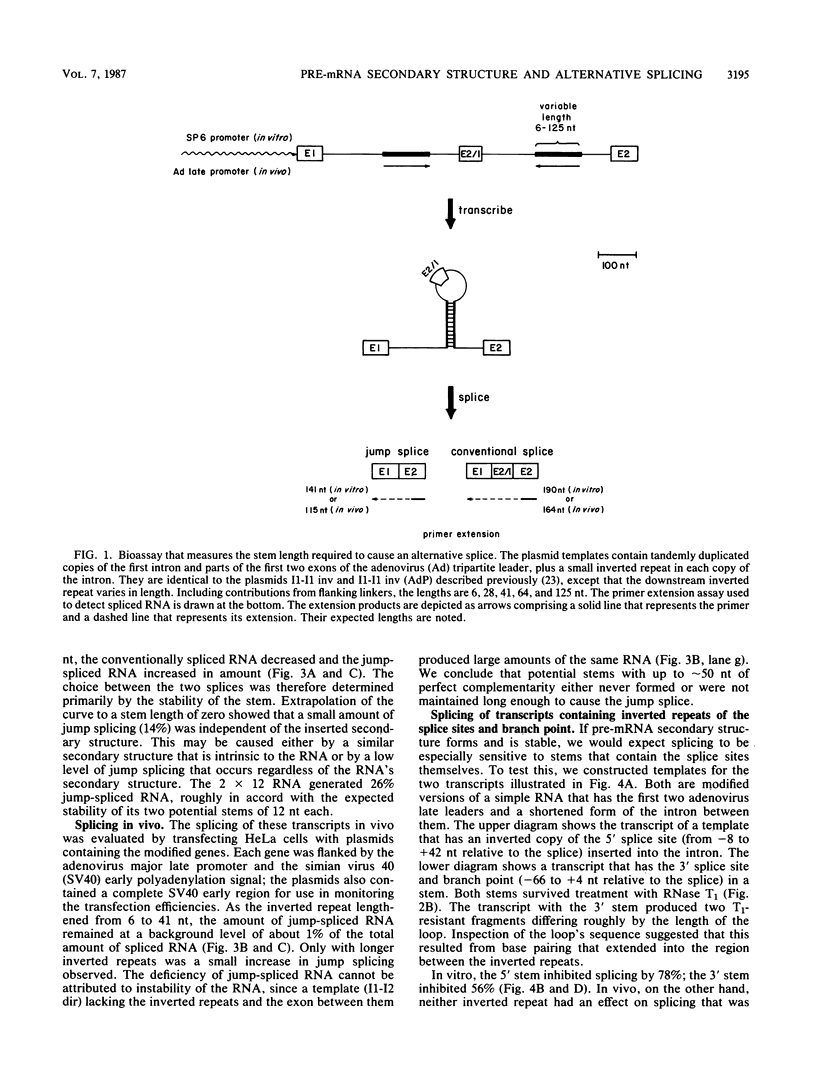
We set up an alternative splicing system in vitro in which the relative amounts of two spliced RNAs, one containing and the other lacking a particular exon, were directly proportional to the length of an inverted repeat inserted into the flanking introns. We then used the system to measure the effect of intramolecular complementarity on alternative splicing in vivo. We found that an alternative splice was induced in vivo only when the introns contained more than approximately 50 nucleotides of perfect complementarity, that is, only when the secondary structure was much more stable than most if not all possible secondary structures in natural mRNA precursors. We showed further that intron insertions containing long complements to splice sites and a branch point inhibited splicing in vitro but not in vivo. These results raise the possibility that in cells most pre-mRNA secondary structures either are not maintained long enough to influence splicing choices, or never form at all.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass B. L., Weintraub H. A developmentally regulated activity that unwinds RNA duplexes. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Folk W., Birnstiel M. L. The terminal RNA stem-loop structure and 80 bp of spacer DNA are required for the formation of 3' termini of sea urchin H2A mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. Y., Wooley J. Set of novel, conserved proteins fold pre-messenger RNA into ribonucleosomes. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):195–210. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon L. P., Estibeiro J. P., Eperon I. C. The role of nucleotide sequences in splice site selection in eukaryotic pre-messenger RNA. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):280–282. doi: 10.1038/324280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Manley J. L. Factors influencing alternative splice site utilization in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Yanofsky C. Attenuation in amino acid biosynthetic operons. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:113–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Trans splicing of mRNA precursors in vitro. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe S. H. A large inverted repeat sequence overlaps two acceptor splice sites in adenovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8891–8900. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Melton D. A. Antisense RNA injections in fertilized frog eggs reveal an RNA duplex unwinding activity. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):599–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Specific and stable intron-factor interactions are established early during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
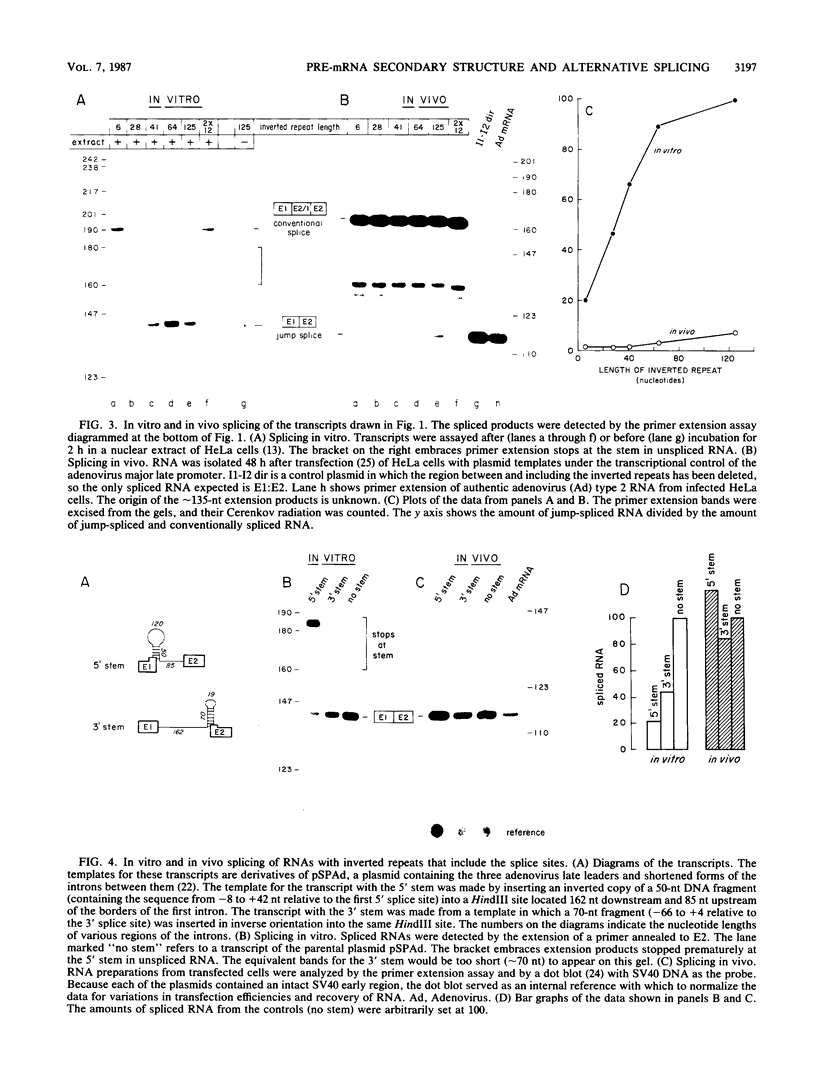
- Solnick D. Alternative splicing caused by RNA secondary structure. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Trans splicing of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]